Hemoglobin:- Part 2 – Hemoglobin (Hb) Electrophoresis
Hemoglobin (Hb) Electrophoresis
What sample is needed for Hemoglobin Electrophoresis?
- Hemolysate is prepared from blood in EDTA, citrate, or heparin.
- Use fresh or refrigerated samples.
How will you prepare the hemolysate?
- Method 1:
- Take clotted blood or RBCs with an equal volume of water.
- Keep overnight in the freezer (or freeze overnight).
- The supernatant will be ready.
- Method 2:
- 1 gram ethylenediaminetetracetic acid (EDTA).
- 0.1 gram of saponin.
- Dissolve in 500 ml of D. water.
- Take normal saline washed Red blood cells.
- Mix an equal volume of reagent and the washed RBCs for 5 minutes.
- Hemolysate will be ready.
- Method 3:
- How do you prepare the hemolysate?
- Centrifuge the EDTA blood and remove the upper liquid portion (supernatant plasma and buffy coat).
- Wash these cells with saline three times, and discard the saline from the last centrifuge.
- Add an equal volume of distle water and 1/2 volume of carbon tetrachloride.
- Now, shake it vigorously.
- Centrifuge for 5 minutes at 1500 G.
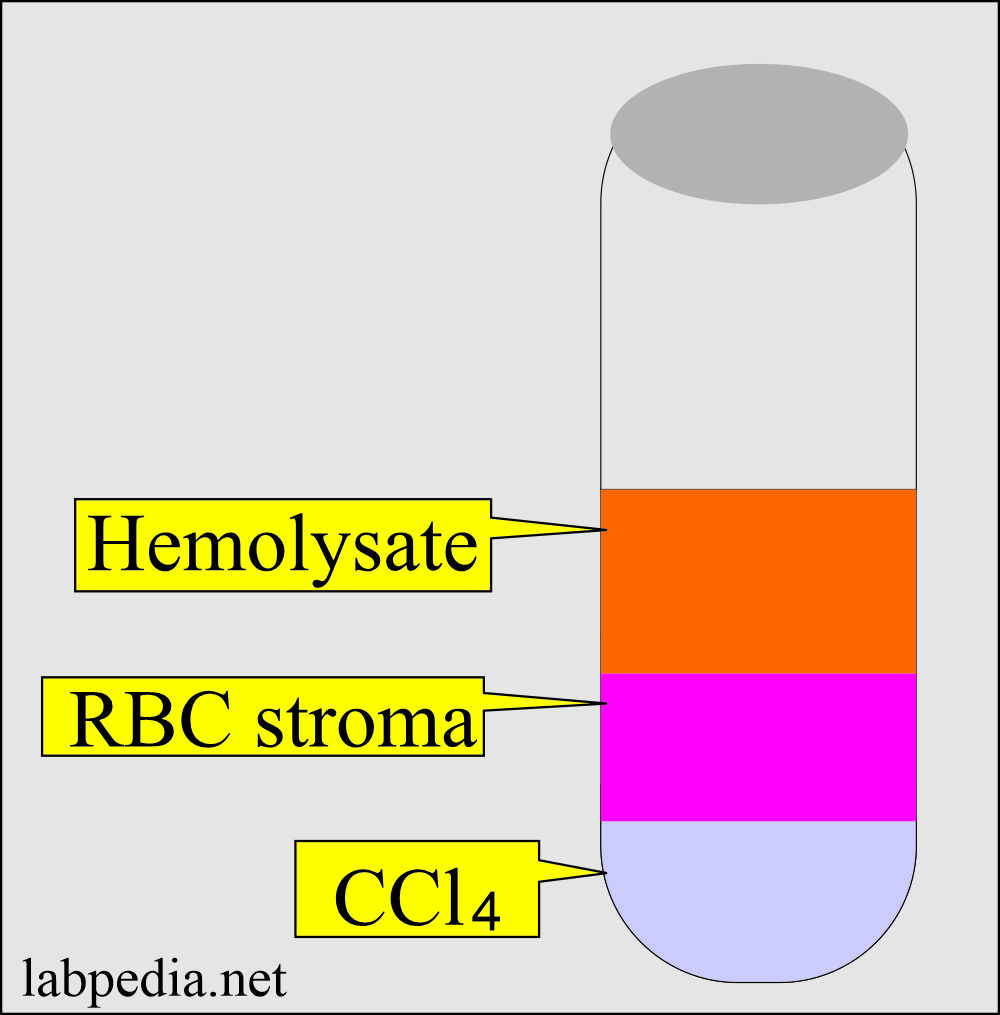
- Three layers will form.
- Upper layer hemolysate.
- Middle layer RBC leftover (stroma).
- The third layer is a Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
-
- Carefully pipette off the upper layer of the hemolysate (supernatant). It will be ruby-colored and clear.
- Adjust the hemoglobin concentration with distle water to 70 to 100 g/L.
- This is ready to run the hemoglobin electrophoresis.
- If you want to store it for another time, add one drop of potassium cyanide (KCN = M/100); otherwise, you can run electrophoresis immediately.
What are the Indications for Hemoglobin Electrophoresis?
- This will detect abnormal hemoglobinopathies and quantify them.
- This Hb electrophoresis will diagnose:
- Thalassemia.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Other abnormal hemoglobins.
What are the precautions for Hemoglobin Electrophoresis?
- Blood transfusion in the last 12 weeks may alter the electrophoretic pattern.
What is the principle of Hemoglobin Electrophoresis?
- The first hemolysate from the EDTA blood is made, and then it is run for electrophoresis, where Hb is separated into different bands.
- We can find the presence of an abnormal Hb pattern.
- Cellulose acetate or starch gel electrophoresis is run on the hemolysate at a pH of 8.6.
- Then, Hb is quantified by elution and spectrophotography.
- Or by a densitometer.
- Hb-F is alkali-resistant, so it needs to be quantified using another method.
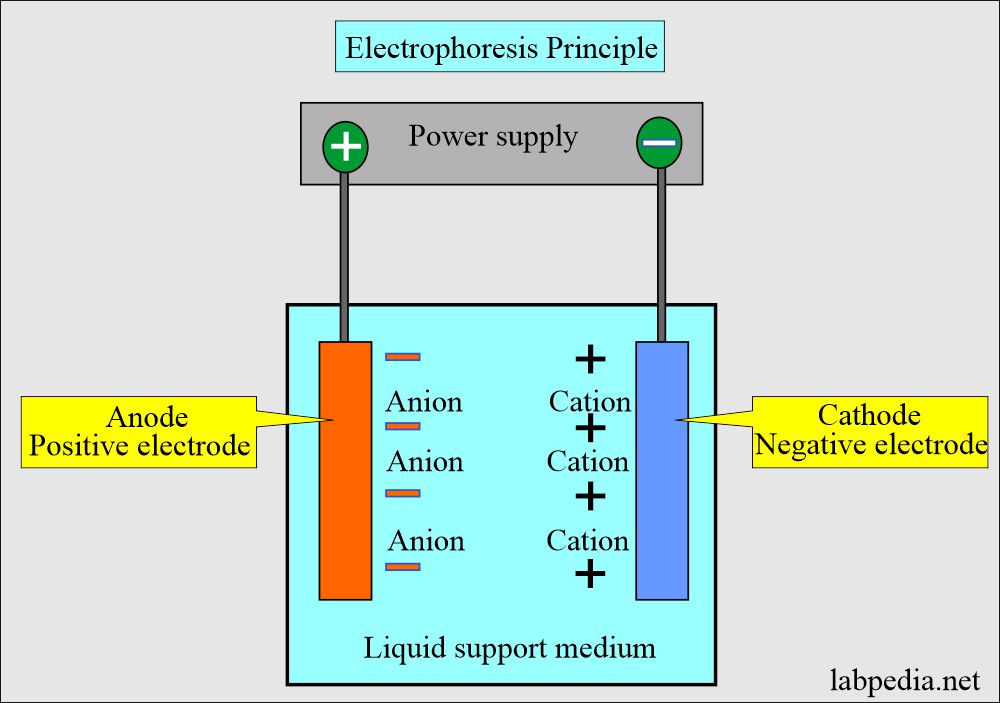
How will you explain the principle of Electrophoresis?
- It is a migration of charged solutes or particles in a liquid medium under the influence of the electric field.
- Positive ions (cations) move toward the cathode.
- Negative ions (anions) move toward the anode.
How will you explain the pathophysiology of Hemoglobin electrophoresis?
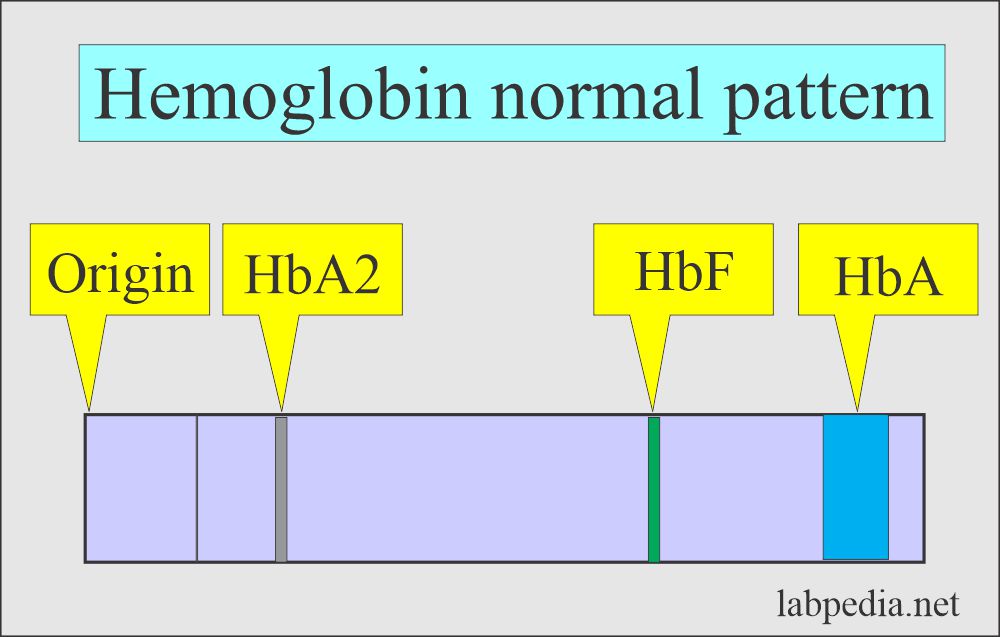
- There are various types of hemoglobins, like A1, A2, S, C, and F.
- The hemoglobin moves at different rates in the electromagnetic field and forms various bands.
- The patient sample is compared to the normal Hb pattern.
- Each band is quantitated as a percentage of total hemoglobin.
- Hb A1 is the major hemoglobin in the normal RBC.
- While Hb A2 is the minor component (2% to 3 %).
- Hb F is the main hemoglobin in the fetal RBC. There is a minimal amount in the normal adult.
- Hb F, more than 3% after 3 years, is considered abnormal.
- Hb F can carry O2 when a small amount is present in the blood, like in the fetus.
- Hb S and C occur in American blacks.
- RBCs with Hb C have decreased lifespan and are easily lysed.
What are the normal values of hemoglobin?
- Hb A1 = > 95 % (95% to 98 %).
- Hb A2 = 1.5% to 3.7 %
- Hb F = < 2 % (0.8 to 2 %).
- Hb S = 0 %.
- Hb C = 0 %.
- Newborn Hb F = 50% to 80%.
- <6 months = <8 %.
- >6 months = 1% to 2 %.
What are the different patterns of Hb electrophoresis in different conditions?
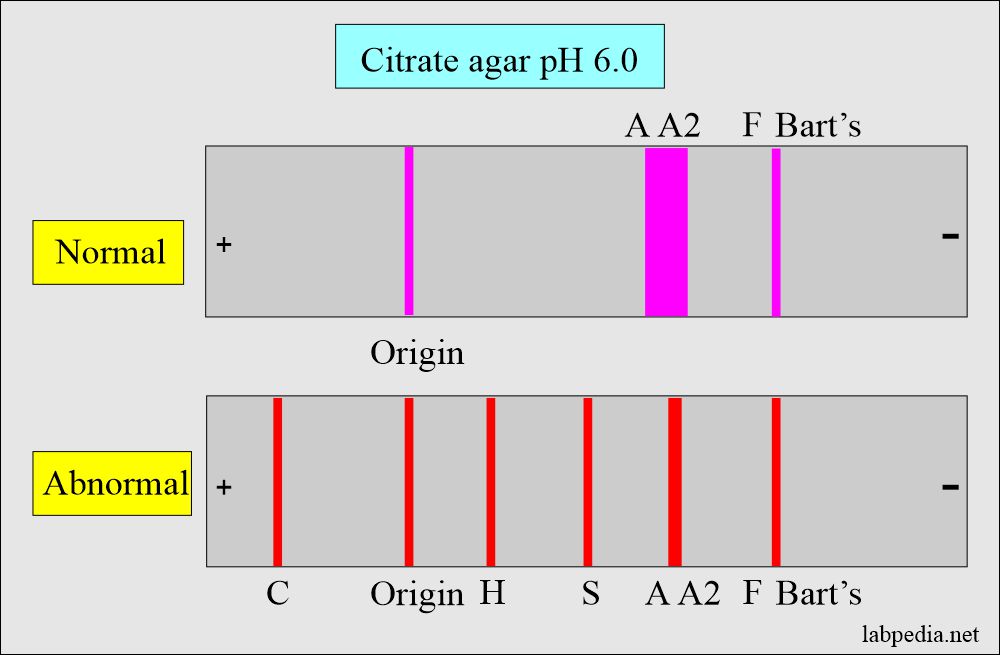
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis produces a good separation of Hb-S from Hb-A and C.
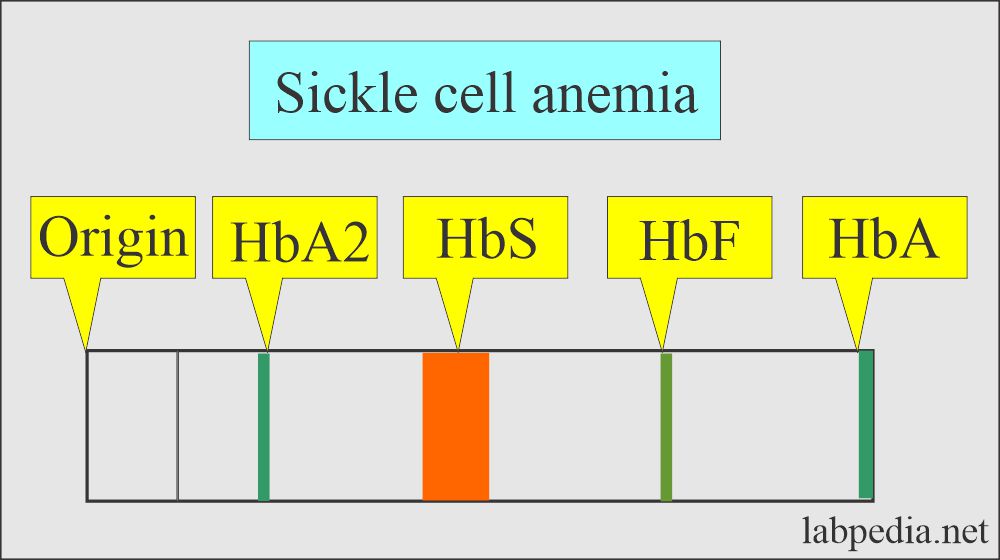
- Sickle cell anemia:
- It is done on the cord blood, and electrophoresis shows Hb F and Hb-FS patterns, where Hb-F consists of 60% to 80% of the total.
- After the age of 3 to 6 months, electrophoresis shows an SS pattern (80% to 90% Hb S), and the remaining is Hb-F.
- Sickle cell trait:
- It has more than 50% of Hb-A than Hb-S. Therefore, more Hb-A than Hb-S.
- S-Beta-Thalassemia:
- It has 50% or more Hb-S with about 25% Hb-A and more Hb-A than Hb-F.
- Hb-A and Hb-F can not be separated reliably in some cases.
- Hb-C and Hb-A2 migrate separately on citrate, whereas these will migrate together on cellulose acetate.
- Citrate agar gives a little better separation of Hb-F from Hb-A in newborn cord blood.
- The alkali denaturation method or suitable electrophoresis can identify and quantify Hb-F.
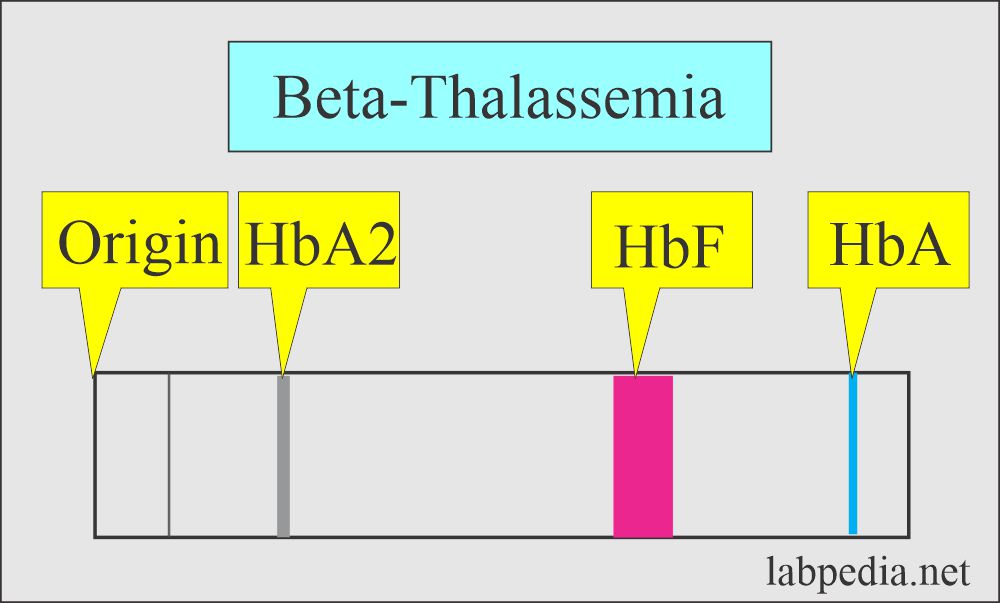
What is the picture of Hb electrophoresis in Thalassemia?
| Hemoglobin | Normal | Thalassemia Major | Thalassemia Minor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Major Thalassemia = Hb F = 98%, Hb A = 2%
What is the differential diagnosis of different Hemoglobin (Hb) electrophoresis patterns?
| Hemoglobin | Disease |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hemoglobinopathy pattern under different conditions:
| Disease | Hb A1 | Hb A2 | Hb F | Hb S | Hb C | Hb H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Absent | 2% to 3 % | 2 % | 95% to 98% | Absent | Absent |
|
50% to 60 % | 2% to 3 % | 2 % | 35% to 45 % | Absent | Absent |
|
Absent | 0 to 15 % | 85% to 100 % | Absent | Absent | Absent |
|
50 to 85 % | 4 to 8 % | 1 to 5 % | Absent | Absent | Absent |
|
Absent | 2 to 3 % | 2 % | Absent | 90 to 100 % | Absent |
|
65 to 90% | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | 5 to 30 % |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What will be the picture in Sickle cell anemia?
Question 2: What will be the picture of Beta-thalassemia on electrophoresis?


I enjoyed reading the haemoglobin electrophoresis
Thanks.
Does it have a precaution on Severe Anemia Patients? As may carry a small number of Hb in Erythrocytes? Any minimum Hb concentration on sample to be detected by electrophoresis method?
Thanks
Definitely, it would be best if you take more blood samples to get enough amount of Hb for a good electrophoretic result.
What percentage do each of the bands formed represent
All normal and abnormal % of the hemoglobin pattern is given in this topic.
Please help to describe a Washed Red Blood Cell Protocol with normal saline as will be good to know volumes, centrifugation g or rpm and times. This will help us to reproduce in our lab. Or any publication where we can read . Many Thanks for your valueble work
Please see the link for the preparation of the hemolysate.
https://labpedia.net/haemoglobin-part-2-haemoglobin-electrophoresis-hb-electrophoresis/
Hello Dr. Riaz
Very interesting your hemolysate. Question: On Preparation of Hemolysate
can you please let us know : Centrifugation G’s and Time for step number 1 and 2 please. Also KNC concentration or grams per 100 or 1000 mL ?
Thank you a lot for your science contribution. Regards Givi
Step one 1 and 2 when you see clear saline that is the time to stop it. I think 1 to 2 minutes will be enough. This is routine centrifugation. KCN is the molar solution (M/100 mL).
Dear sir,
it is very useful and well-illustrated.
Can I have this protocol as I need it for thalassemia carrier identification?
Thanks, You are welcome.
Thanks For Sharing The Information A2 English Test ,Keep sharing amazing articles like these.
Thanks.
What is the purpose of hemolysate preperation? And why ccl4 is used during its preperation?
For electrophoresis of the blood, you need hemolysate. CCL4 is required to separate the hemolysate into different layers.
What is alternative to CCL4 as it not available easily.
CCl4 is easily available from the chemical stores, who are dealing with student’s lab experiments supply.
It is very informative. Such a great job from Dr. Thank you so much.
Thanks.
So beautifully explained. Thank you so much for sharing!
Thanks.
Excellent write-up. I hope you will consider adding your details for easier referencing in academic works.
Thanks for the comments.
Thank you for your brief explanation.
Question: I have collected a blood from matured chicken by K2 EDTA tube and refrigerated the whole blood under -4 to -8 0C. Then my sample get frozen. Could this sample useful for hemoglobin electrophoresis. Any advice please and the appropriate procedure. Thank you.
I think this sample will work because you have to make hemolysate. I have given the methods to make hemolysate.
Sir, Many thanks.
Please give buffer composition in electrophoresis either using cellulose acetat or starch agar
I am giving composition of one of the buffer. Rest you can find in various books.
Tris-EDTA borate buffer:
1. Tria-(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane = 10.2 grams
2. EDTA = 0.6 grams
3. Boric acid = 3.2 grams
4. Distilled water = Make up to one liter
Please take 500 mL of water and mix all above chemicals. Now after mixing, make up to 1 liter.
label and store at 2 to 8 C.
This buffer can be used for hemoglobin electrophoresis.
If electrophoresis result shows A prominent “S” band and A faint “A” band, what does it means.
Prominent S band is seen in Sickle cell anemia.