Diabetes Mellitus:- Part 4 – Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Oral glucose tolerance test, (OGTT)
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
What Samples are needed for patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
- The patient is advised to come to the laboratory in a fasting state, where, after taking a fasting blood sample, the patient is given 75 grams of glucose.
- It is better to give glucose in 7-Up, which will be well tolerated.
- Collect fasting blood and then collect blood samples at 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes.
- Multiple samples are taken at half-hour intervals along with the urine sample.
- In pregnant women, collect blood at 60, 120, and 180 minutes after glucose administration.
- Sometimes, the sample is taken at 1, 2, 3, and up to 4 hours.
What are the Indications for the diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
- To confirm the diagnosis of gestational diabetes.
- It is used to diagnose Diabetes mellitus.
- It is also used to evaluate hypoglycemia.
- Patient with family H/o diabetes.
- Patients with obesity.
- Patients with H/O recurrent infection.
- Patients with H/O delayed wound healing.
- Ladies with H/O stillbirths or delivering obese babies.
- Patients with H/O random glycosuria or hyperglycemia during pregnancy or after myocardial infarction, surgery, or stress.
What are the Precautions for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
- Advise the patient to consume more than 150 grams of carbohydrates in their diet over the last 3 days before the test.
- Stop these drugs at least 3 days before the test, such as hormones, contraceptives, steroids, salicylates, and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Stop diuretics, hypoglycemic agents, antihypertensive drugs, and anticonvulsants.
- Stress can increase glucose levels.
- If the patient does not tolerate the glucose and vomits, that may give a false result.
- Avoid glucose tolerance tests in the following conditions:
- If there is persistent fasting hyperglycemia >140 mg/dL (>7.8 mmol/L).
- In the event of a normal fasting glucose level.
- Patient with known diabetes mellitus.
- In the case of two hours, glucose >200 mg/dL (>11.1 mmol/L).
What are the recommendations for pregnant ladies?
- It is recommended that screening be done on all pregnant women between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation.
- This should be advised for women aged 25 years or older.
- Also advised before the age of 25 years if the woman is obese or there is a family history of DM.
What is the definition of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)?
- Gestational diabetes mellitus is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance that is seen during pregnancy.
- Usually seen around 24 weeks of gestation.
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is also defined as hyperglycemia that develops for the first time during pregnancy. This condition is observed in approximately 4% of pregnant women.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)?
- A normal pregnancy is associated with increased insulin resistance, especially in the late second and third trimesters.
- GDM, in which hormones produced by the placenta prevent the body from utilizing insulin. This will lead to an increase in blood glucose levels.
- This will occur in pregnant women who cannot maintain a sufficient insulin level.
- The risk factors are:
- Family history of a first-degree relative with diabetes mellitus.
- In obese ladies.
- In the case of late maternal age, it typically occurs after the age of 40.
- If there is glycosuria.
- Bad previous delivery history, such as stillbirth and macrosomia.
- Screening should be performed between 24 to 28 weeks of gestation.
- 3% to 8% of pregnant women have gestational diabetes.
What are the complications of gestational diabetes mellitus?
- The detection of early GDM will reduce the risk of prenatal fatal outcomes, such as:
- Excessive fetal growth.
- Birth trauma.
- Fetal morbidity.
How will you do screening for gestational diabetes mellitus(GDM) during pregnancy?
- It can be assessed by a one-hour blood glucose level if it is greater than 140 mg/dL. Then, advise OGTT for three hours.
- The O’Sullivan test is a one-hour glucose tolerance test administered after the ingestion of 50 grams of oral glucose.
- Screening for GDM advises OGTT with 50 grams of glucose.
- Check the one-hour glucose level, also known as the O’Sullivan test.
- Screening should be done between 24 to 28 weeks of gestation.
- If one one-hour sample is >140 mg/dL, then taking a 3-hour 100-gram glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is necessary.
- Normal pregnancy is associated with increased insulin resistance, especially in the second and third trimesters.
How will you screen for gestational diabetes mellitus during the postpartum period?
- If the results are abnormal during pregnancy, then take the OGTT postpartum.
- If postpartum OGTT is normal, then label diabetes mellitus during pregnancy.
- Check blood glucose on every visit because of the increased risk of diabetes mellitus, which is 30% during the next 5 to 10 years.
- If the postpartum OGTT is abnormal, label these patients as having Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or Impaired fasting glucose (IFG), which can occur in ∼approximately 5% to 10% of cases.
- Another possibility is a clear-cut case of diabetes mellitus, which can occur in 10% of cases.
- The rest of the ladies are normal and may develop diabetes mellitus in the next 5 to 10 years.
What are the risk factors for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
- A family history of diabetes in first-degree relatives.
- Obesity.
- Advanced maternal age.
- Glycosuria.
- A selected bad outcome in the last pregnancy, like stillbirth or macrosomia.
What is the modified criteria for the diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)?
- Low-risk patients are:
- Below the age of 25 years.
- Normal weight before the pregnancy.
- The ethnic group with a low incidence of GDM.
- No known first-degree relative with diabetes mellitus.
- No history of poor obstetric outcomes.
- There is no history of abnormal glucose tolerance.
- Average-risk patients are:
- All those patients fall between low and high-risk patients.
- They should be tested between 24 to 28 weeks of gestation.
- High-risk patients are:
- Marked obesity.
- Glycosuria.
- History of GDM.
- Strong family history of diabetes mellitus.
What is the importance of Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)?
- OGTT is not recommended to diagnose the complications of Diabetes mellitus.
- Its use is also discouraged for fasting hypoglycemia.
- The OGTT is not recommended as a screening test in non-pregnant women and children.
- For a pregnant lady, 50 g of glucose is recommended for screening.
- The serum glucose level of >150 mg/dL at 1 hour is considered for further testing.
- Insulin responds rapidly to oral glucose, with peaks at 30 and 60 minutes.
- Glucose levels return to normal within 3 hours.
- Glucose will not appear in the urine in a normal pattern.
What is the procedure for the Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)?
- Record patient weight.
- The pediatric dose for glucose amount is based on their weight, calculated as 1.75 g/Kg, and should not exceed a total of 75 grams.
- Pregnant ladies can be given 100 grams.
- Can perform the test on pregnant ladies with 50 grams of glucose.
- Non-pregnant ladies can be given 75 grams.
- Take the fasting blood for fasting glucose levels.
- Give glucose (Glaxo ‘s-D) 75 to 100 grams in 5 minutes.
- Pregnant ladies can perform the test with 50 grams of glucose.
- Take the blood sample at 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes (some books recommend 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 3 hours) after glucose intake.
- To check for hypoglycemia, advise taking 4 4-hour samples.
- Also, take the urine sample with every blood sample.
How will you record the collection of blood and urine during OGTT?
| When to take a sample | Blood sample to be taken | A urine sample is taken | Some recommend |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
|
|
|
|
What are the Normal values of glucose?
Source 1
- NORMAL WHEN
- Fasting glucose = < 110 mg/dl.
- Random glucose = < 140 mg/dl.
- Child fasting = <130 mg/dl.
- at 120 min = < 140 mg/dl.
- Impaired glucose tolerance in children:
- Fasting = <140 mg/dl.
- 120 min = >140 mg/dl.
Adult non-pregnant OGTT result:
- Fasting = 79 to 105 mg/dl.
- 30 min = 110 to 179 mg/dl
- 60 min = 120 to 170 mg/dl
- 90 min = 100 to 140 mg/dl
- 120 min = 70 to 120 mg/dl
- All urine samples are negative.
- >60 years fasting = 70 to 115 mg/dL
Gestational diabetes normal one hour = <140 mg/dL
Diabetes Mellitus when:
- Fasting glucose = 126 mg/dl or above
- Postprandial glucose = 200 mg/dl or above
- Random glucose more than 200 mg/dl with H/o polyuria, polydipsia, ketonuria, and weight loss.
IMPAIRED GLUCOSE when:
- Impaired fasting Glucose = 110 to <126 mg/dl
- Impaired glucose tolerance = 140 to <200 mg/dl
| Diagnosis | Fasting glucose level | Random glucose level | 2-hour glucose level (in OGTT) | HbA1c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source 2
Normal values of OGTT in Adults:
| Time | Glucose value | Urine glucose |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the values of the OGTT in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)?
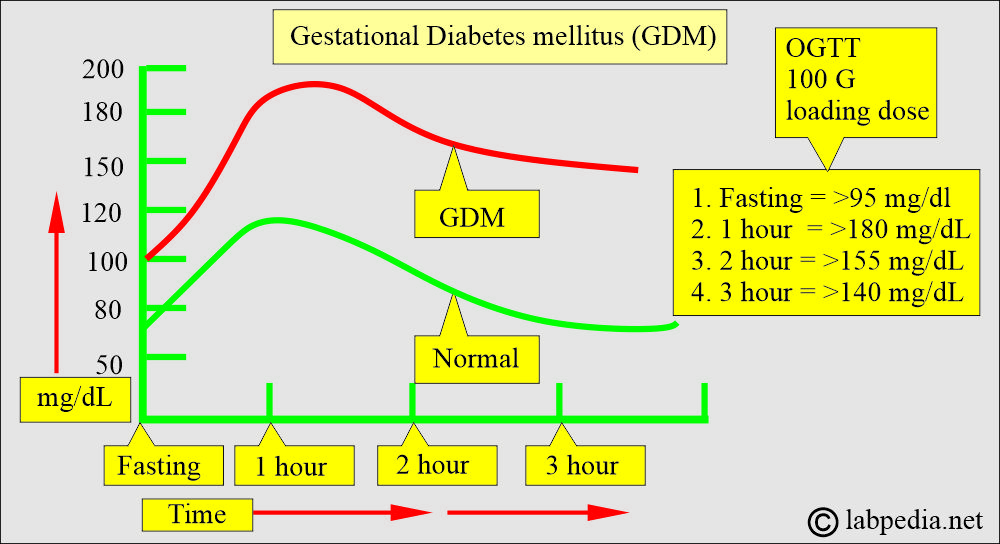
- At least two values of OGTT must exceed the following values for GDM:
- Fasting = >95 mg/dL.
- 1 hour => 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour => 155 mg/dL
- 3 hour => 140 mg/dL
- High glucose level persists throughout the test.
- Another source gives the following values:
| Time | mg/dl in plasma/serum | Urine sugar | mg/dL in whole blood |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At least two values must meet or exceed the following values for GDM based on the oral glucose tolerance test:
| Timings | 75 grams overload mg/dL | 100 grams overload mg/dL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)
How would you summarize the work-up for gestational diabetes mellitus?
Screening workup :
- Perform the work-up of all pregnant ladies during the 24 to 28 weeks of gestation over the age of ≥25 years.
- Also, check the ladies, even if they are <25 years of age, for the risk factor.
- Perform a mini OGTT with 50 grams of glucose without any relation to the food.
- Measure the glucose level for one hour.
- If this glucose level is ≥140 mg/dL, then perform the complete OGTT.
How will you perform a workup for Gestational diabetes mellitus?
- Perform OGTT after 8 to 14 hours of fasting.
- Take fasting glucose orally.
- Give 100 grams of glucose.
- Measure blood glucose hourly for 3 hours.
- At least two values must exceed all values.
- If results are expected in a clinically suspected case, then repeat OGTT in the 3rd trimester.
Criteria for the positive 100-gram (OGTT) in pregnant women (Gestational diabetes):
| Time of the blood taken | Glucose level mg/dL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment of Gestational diabetes mellitus?
- The basic need is to control the diet.
- The second critical need is physical activity.
- Can have a daily glucose level and administer the medication accordingly.
- For management of GDM during pregnancy, keep fasting blood glucose level 60 to 110 mg/dL and postprandial level <150 mg/dL.
- It is needed to measure the 24-hour urine estriol level for fetal viability.
- Also, check the amniotic fluid for fetal pulmonary maturity.
- During labor, maintain a blood glucose level between 80 and 100 mg/dL, as there may be marked insulin sensitivity during the immediate postpartum period.
- Evaluate the patient after 6 weeks of postpartum.
What are the criteria For Adequate Treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus?
- The fasting level should be around 95 mg/dL or less.
- The postprandial, 1-hour level is around 140 mg/dL or less.
- The Postprandial 2-hour level is 120 mg/d or less.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus goes away after pregnancy.
- In ladies with GDM, there is a 2 in 3 chance of developing GDM in other pregnancies.
- For more information, please see other topics on Diabetes mellitus.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What will be the blood glucose level in gestational diabetes mellitus at 2 hours?
Question 2: When will glucose return to normal level in OGTT?
