Indications for The Most Common Tests
What sample is needed for routine blood tests?
- The best sample is fasting blood.
- Few common tests should be done routinely after a certain period or in some diseases.
What common tests are indicated in the various diseases?
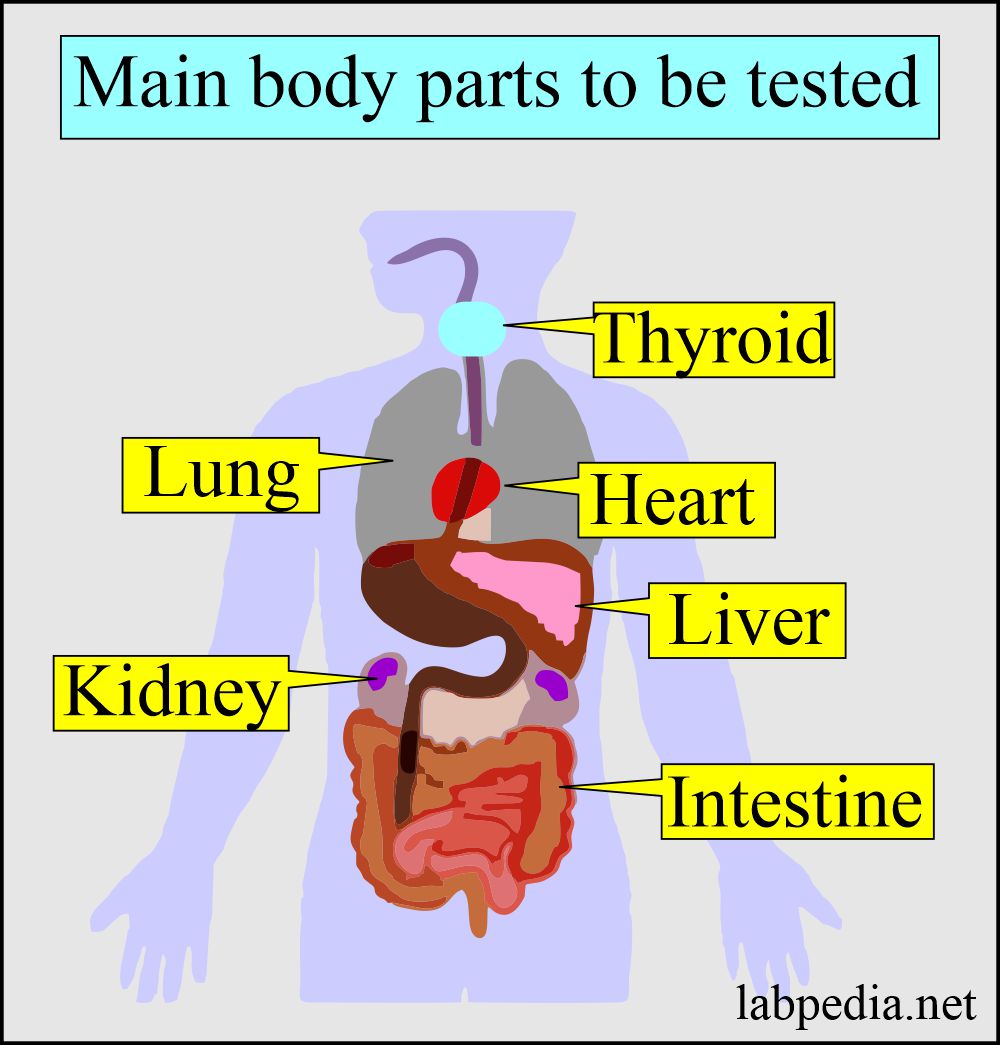
- Most common tests give the functional status of various organs:
- Liver function.
- Kidney function.
- Thyroid function.
- Anemia.
- Prostatic cancer in males.
- PAP smear to detect cervical cancer.
- The possibility of colon cancer.
What are interpretations of Most Common Tests?
| Test | When indicated |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|