Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase
Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
What sample is needed for Gamma-glutamyl Transferase?
- The venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
- The serum is stable for one month at 4 °C.
- The serum can be stored for one year at -20 °C.
- Heparinized samples interfere with various methods.
What are the Indications for Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)?
- This test is done for liver dysfunction.
- This is also useful for detecting alcohol-induced liver cell injury and chronic alcoholics.
- This test can detect the slightest degree of cholestasis.
- GGT is very sensitive to biliary obstruction, cholangitis, and cholecystitis.
- GGT is a good pancreatic, prostatic, and liver cell carcinoma marker.
- GGT level indicates remission and recurrence.
What are the precautions for Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)?
- Keep in mind that the value may be low in late pregnancy.
- Drugs that decreased the value are Clofibrate and oral contraceptives.
- Drugs that increase the value are Alcohol, Dilantin, and Phenobarbital.
- GGT is raised in patients who are taking antiepileptic drugs.
How will you define Gamma-Glutamyl-transferase (GGT)?
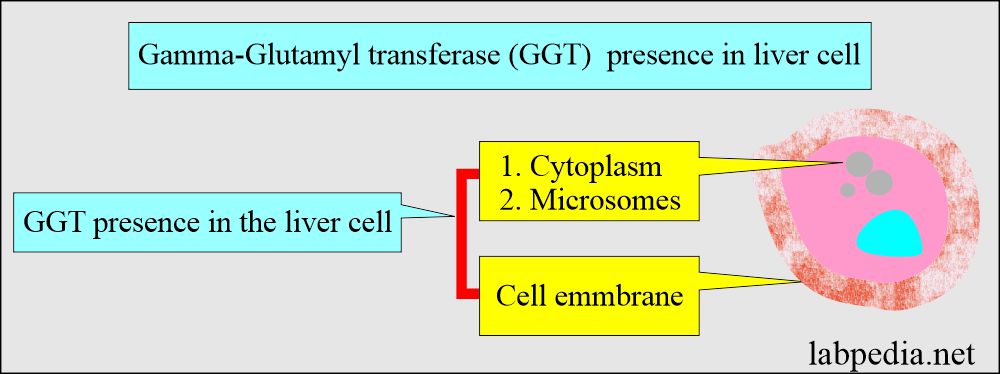
- γ-glutamyl-transferase is a membrane-bound enzyme in the liver and cells lining the bile ductules and bile canaliculi.
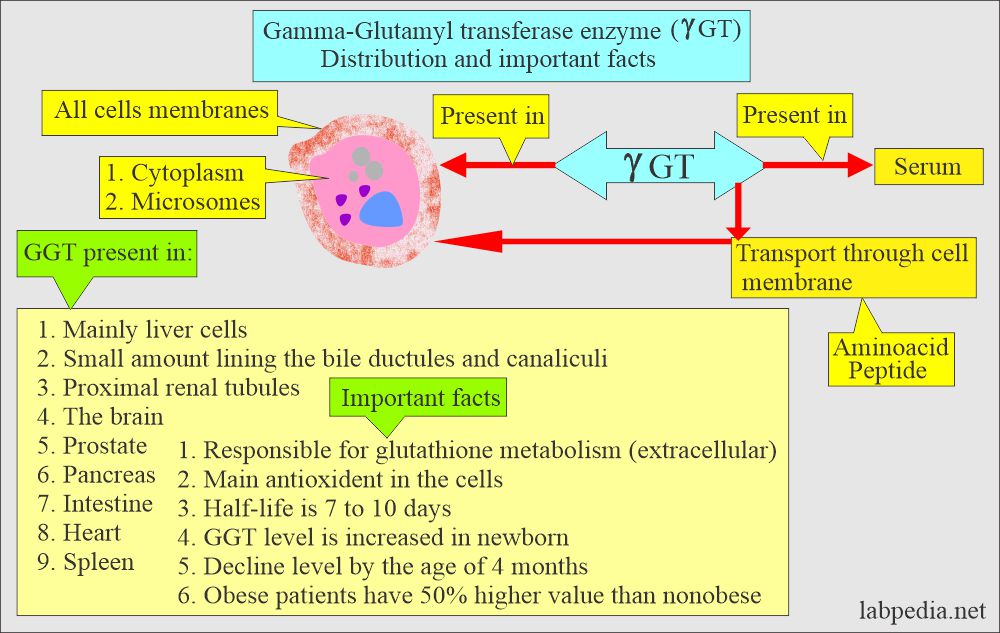
- γ-glutamyl-transferase was formerly called gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase, which is mainly present in hepatocytes.
- To a lesser extent, it is present in the kidneys, biliary tract epithelium, intestine, pancreas, brain, heart, and spleen.
- GGT activity is also seen in the capillary endothelium.
- GGT is responsible for the extracellular metabolism of glutathione, and it is the main antioxidant in the cells.
- Serum GGT is raised in the newborn and comes to the adult level by 4 months of age.
- GGT value may be higher in obese patients than in lean people.
What is the biochemical function of Gamma-glutamyl-transferase (GGT)?
- γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase is one of many peptidases cleaving terminal peptide bonds of proteins or peptides.
- The C-terminal amino acid must be glutamic.
- Specificity resides in the (γ) Glutamyl portion of the substrate.
- Three different reactions have been attributed to this enzyme:
- Hydrolysis.
- Internal transpeptidation.
- External transpeptidation.
- Glutathione is the common substrate of this enzyme in the body.
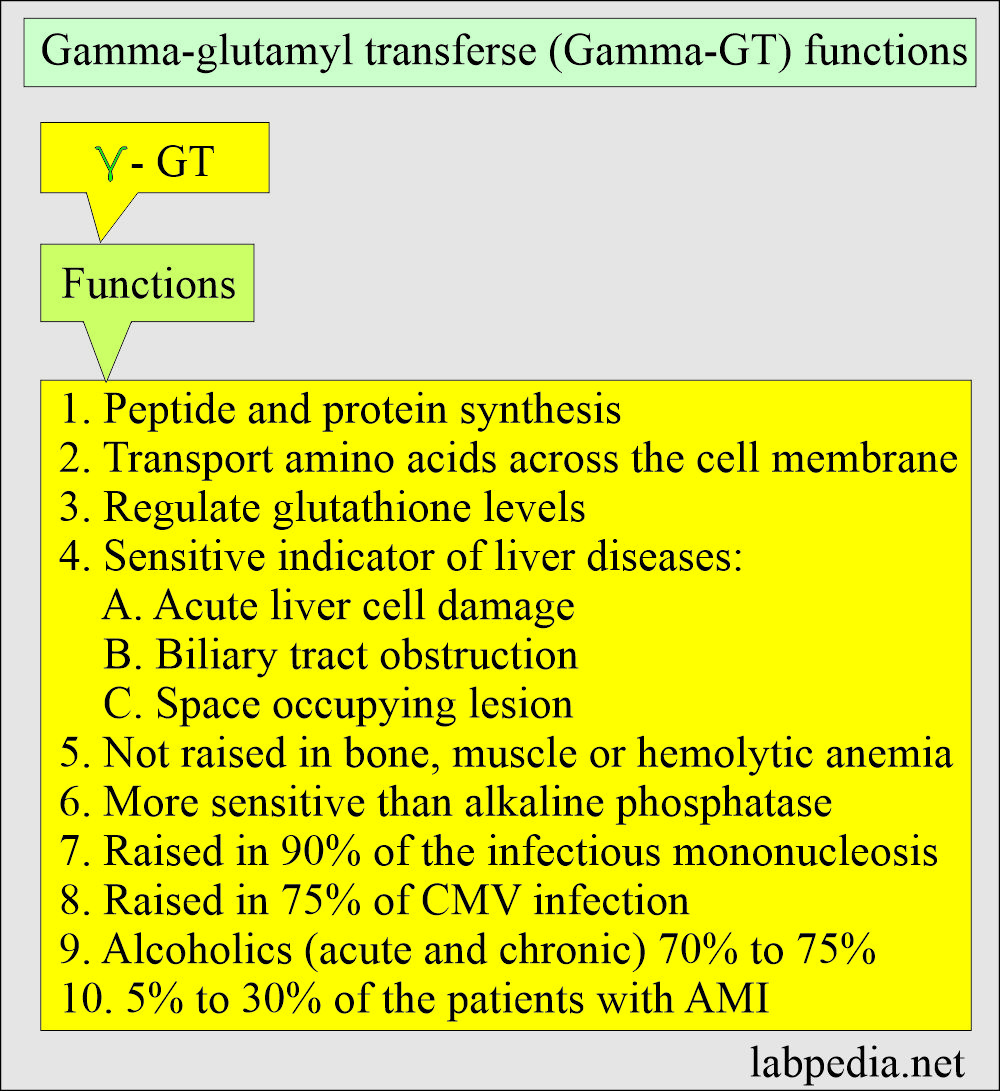
- This enzyme participates in amino acid transport by transferring the γ-Glutamyl portion of glutathione to other amino acids, enabling them to cross cell membranes more easily.
- GGT is present in the following:
- Liver.
- The proximal tubule of the kidney.
- Brain.
- Pancreas.
- Intestine.
- Prostate.
- Capillary endothelial cell.
What is the concentration of the Gamma-glutamyl-transferase (GGT) at different sites?
- The main concentration is present in the hepatocytes.
- GGTis found in the biliary tree’s epithelial cells, mostly in the interlobular bile ducts and bile ductules. This is the reason that it is susceptible to biliary injury.
- GGT is present in the kidney, pancreas, spleen, heart, intestine, brain, and prostate gland.
- GGT level is higher in men because of the additional amount due to the prostate.
- The kidney has a maximum amount, but the liver is considered the normal source of serum activity.
- It is found throughout the hepatobiliary system and other tissues.
- GGT is present in the microsomes of the cytoplasm and the cell membrane.
- The Minimal amount detected in the endothelium of capillaries.
- GGT takes part in transferring amino acids and peptides across the cell membrane.
What is the importance of the gamma-glutamyl-transferase?
- This test has been useful in detecting a male in nearly-risk drinkers (Not in females).
- This is most applicable as part of an alcoholic screening program.
- It returns to normal after abstinence from alcohol for 3 weeks.
- It can be used as a follow-up marker of alcohol intake.
- It is a more sensitive indicator of liver disease in children than alkaline phosphatase.
- This is a susceptible test for liver cell injury and its correlation with the alkaline phosphatase level.
- GGT is raised in acute myocardial infarction, and the mechanism is unclear.
- If it occurs in the first 7 days, it may be due to liver insult.
- Otherwise, it is usually raised in 1 to 2 weeks.
- However, its raised level is nonspecific because it is raised in cardiac, pulmonary, pancreatic, renal disorders, diabetes, and alcoholism.
- GGT correlates with alkaline phosphatase in obstructive jaundice and metastatic liver infiltration.
- In such a case, GGT is more sensitive and specific.
- GGT is not raised in bone disease, while GGT and alkaline phosphatase will be raised in liver disease.
- The overall clinical significance is limited.
What are the functions of the gamma-glutamyl-transferase (GGT)?
- GGT transports amino acids across the cell membrane.
- GGT is a sensitive indicator of liver disease, especially hepatobiliary obstruction.
- GGT is not raised in bone, muscle, and hemolytic anemia.
- GGT is normal with raised alkaline phosphatase, which indicates skeletal muscle disease.
- GGT raised with alkaline phosphatase indicates hepatobiliary disease.
What is the normal value of Gamma- Glutamyl-Transferase (GGT)?
Source 2
- Male and female age 45 years and older = 8 to 38 units/L (8 to 38 IU/L)
- Female younger than 45 years = 5 to 27 units/L (5 to 27 IU/L)
- Older people = Slightly higher than the adults
- Newborn = 5 times higher than adults.
- Child = Similar to adult level.
Another Source
- Male = 7 to 47 U/L.
- Female = 5 to 25 U/L.
- Newborn = 5 times higher than an adult.
- Another reference
- Adult male = up to 55 U/L.
- Adult female = 38 U/L.
- The newborn is 6 to 7 times higher than the adults.
- It is like an adult after 5 to 7 months.
- Another reference
When will you see the raised Gamma- Glutamyl-Transferase (GGT)?
- Obstructive liver disease and posthepatic obstruction.
- This may reach 5 to 30 times the normal value.
- Infectious hepatitis, where the rise is 2 to 5 times the normal value. It is seen in 90% of the cases.
- Liver diseases like cirrhosis have space-occupying lesions.
- The mild increase in the fatty liver.
- Infectious mononucleosis,
- Renal transplant.
- It may be increased in renal failure.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Pancreatitis.
- The increase may be 5 to 15 times the normal value.
- Myocardial infarction.
- There is an increase in 50% of the AMI cases.
- The increase is mild and may occur after the fourth day of infarction, and the peak reaches in the next 4 days (another reference says 7 to 14 days after the infarction).
- GGT rise in AMI is seen in 5% to 30% of the cases.
- Alcohol ingestion. There is an average increase of >3.5 of the normal value.
- In the case of alcohol abuse, there is a GGT/Alkaline phosphatase ratio >2.5.
- GGT is raised in EBV infection (Infectious mononucleosis), cytomegalic viral infection, and Reye syndrome.
- Drugs like Warfarin, Barbiturates, Valproic acid, Dilantin, and alcohol.
When will you see the decreased value of Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)?
- Hypothyroidism.
Where will you see normal values of Gamma-glutamyl transfers (γ-GT)?
- Bone disorder and bone growth.
- Pregnancy.
- Skeletal muscle disease.
- Renal failure.
- GGT is the choice of enzyme in the case of Alcoholism.
- Very good at monitoring liver disease. Its return to normal in liver disease is an excellent indicator.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of GGT in liver diseases?
Question 2: What is the significance of GGT in alcoholics?