Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAC), Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB)
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)
What are the sites from where you can take samples for Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC)?
- FNA sample may be obtained from:
- All parts of the body:
- Lymph nodes.
- Breast.
- Liver.
- Respiratory tract.
- Oral cavity.
- Thyroid.
- Genital Tract.
- The most common sites are the breast, thyroid, and palpable lymph nodes.
What are the benefits of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC)?
- FNAC is an inexpensive and less traumatic procedure.
- FNA has good results with the help of ultrasound in the Liver and other abdominal masses.
- FNA may be done with the help of a CT scan, mammogram, or ultrasound-guided.
What are the indications of Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAC)?
- FNA material gives a cytological diagnosis of benign or malignant lesions.
- FNA has excellent results in palpable lumps like breast or superficial masses.
- FNA material may be subjected to bacterial examination.
- FNA is recommended in areas suspected of cystic fluid, nodules, lumps, and enlarged lymph nodes.
How will you perform Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)?
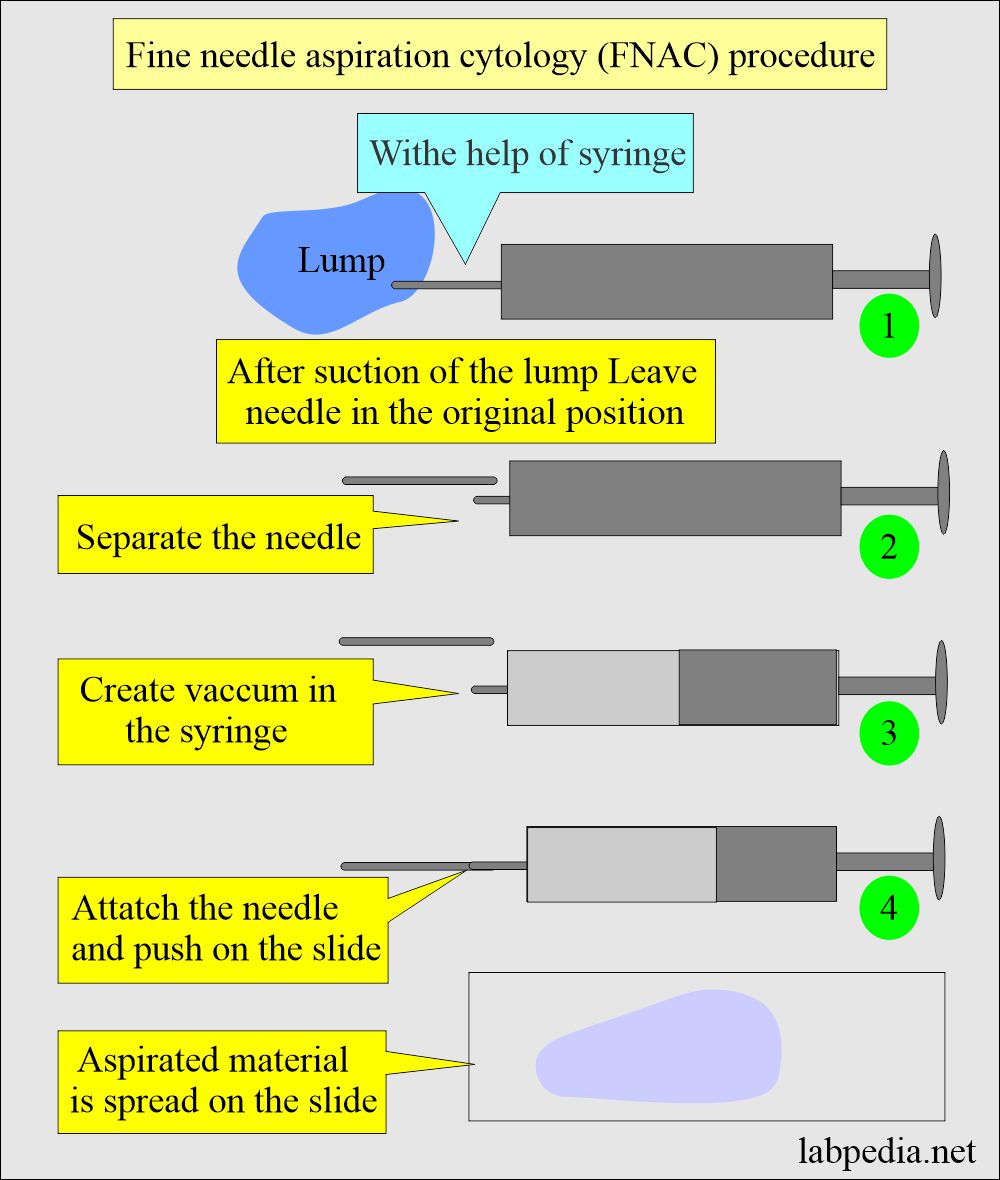
- This procedure is performed with local analgesia or without it, and 25 g needles are used to get a sample from the suspected mass. (Our experience is with 25 G needles, and we get adequate material). But most people use a 22/23 G needle.
- We made the smear and air dry it before staining.
- In the routine, we use Field stain.
- Also, we do not give negative pressure unless we see poor yield. Most of the time, enough material comes without any aspiration.
- After the procedure, separate the needle.
- Create negative pressure in the syringe and connect the needle.
- Push the material on the slide.
- Spread the material with another slide or with cover glass.
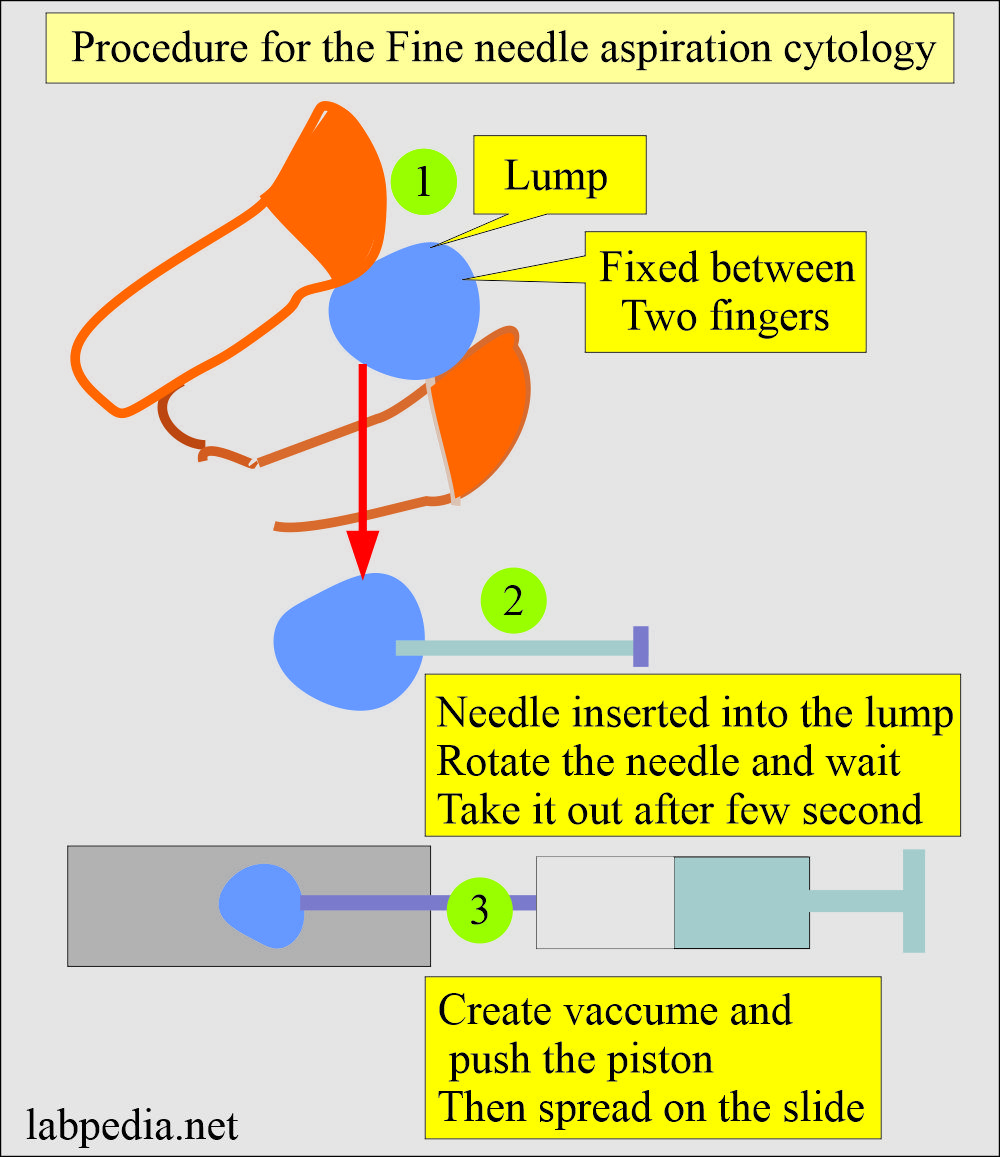
How will you do the Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAC) without the syringe suction?
- You can do the Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAC) without a syringe.
- We are doing Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAC) in most of the cases without a syringe.
- Our experience shows a very good yield.
- I have tried to show the procedure in the diagram.
Important facts of Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAB):
- This is one of the best tools for diagnosing tumors in expert hands.
- FNA is a procedure to obtain diagnostic material for cytologic (Cells) study.
- FNA causes minimal trauma to the patient.
What are the advantages of Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAB)?
- It is economical.
- No anesthesia is required.
- No need for hospitalization.
- It is less painful.
- It is less invasive. No surgery is needed.
- It takes less time compared to tissue biopsy.
- Results are satisfactory in the expert hands.
What are the medical benefits of Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)?
- Diagnostic value: Cytopathologists can make the diagnosis of a lump as benign or malignant.
- Role of ultrasound: Ultrasound is a very helpful tool for mass in the liver or lungs. With the guidance of ultrasonography, it can reach the hidden masses.
- Treatment: By diagnosing the lesion, one can decide the line of action for the lesion.
- Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) can be used to aspirate the cystic lesions, abscess, or villous sampling.
How will you report Fine needle aspiration Cytology (FNAB)?
- The results can be reported as follows:
- Atypical.
- Suspicious of malignancy.
- Positive for malignancy.
- There are the following possibilities.:
- Infectious condition. There will be characteristic cellular components like poly, lymphocytes, and histiocytes.
- Benign conditions. There are characteristic benign cellular changes like uniform nuclei and normal N/C ratio.
- Malignant conditions. The cellular changes are typical of malignancy, like bizarre cellular appearance, changed N/C ratio, etc.
How will you report Thyroid FNAC?
- FNA of thyroid differentiates between thyroid cysts or tumors.
- It can be done with the help of an ultrasound.
- There is a Bethesda reporting system that classified the result into 6 categories.
- Nondiagnostic or unsatisfactory.
- Benign lesion.
- Atypical or undetermined significance or follicular lesion of undetermined significance.
- Follicular lesion or suspicious for follicular neoplasm.
- Suspicious of malignancy.
- Malignant.
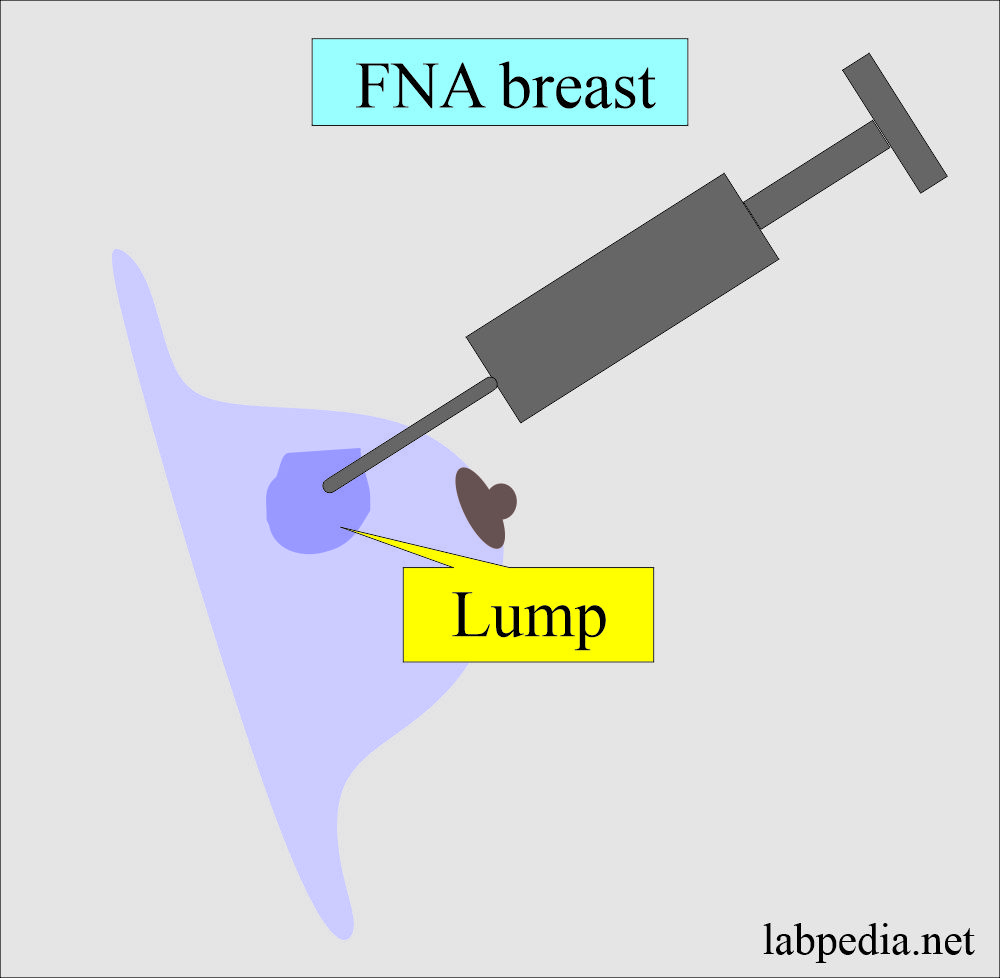
How will you report Breast FNAC?
- It is the aspiration of the breast mass for cytologic examination of the aspirated material.
FNA breast result:
- It is about 1% false-positive results.
- There are 5% to 10% false-negative results.
- It gives good results in experienced hands.
- It will give good results to the experienced pathologist.
- If there is a fluid, that will indicate a cystic lesion.
- FNA will differentiate between benign or malignant smears.
- The FNA is reported as follows:
- Insufficient yield.
- There is a benign lesion.
- Atypical, probably a benign lesion.
- Suspicious, probably in situ, or invasive carcinoma.
- Malignant lesion.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the best use of FNAC?
Question 2: What are the cytological features of malignancy?