Fluid Analysis:- Part 2 – Fluid Analysis Parameters
Fluid Analysis
What are the samples for Fluid Analysis?
- The fluid for the analysis are:
- Ascitic fluid.
- Pleural fluid.
- Pericardial fluid.
- Amniotic fluid.
- Cerebrospinal fluid.
- Semen analysis.
- Cervical mucus test.
- Joint fluid (synovial fluid).
- Sweat chloride test.
- Urine analysis.
What are the indications for Fluid Analysis?
- To diagnose the cause of the fluids.
- This could be therapeutic.
- To diagnose the diseases.
What are the precautions for Fluid Analysis?
- The fluid analysis should be done immediately to prevent false results due to cellular or chemical deterioration.
- Follow precautions if there is a delay in the testing of fluid.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Fluids?
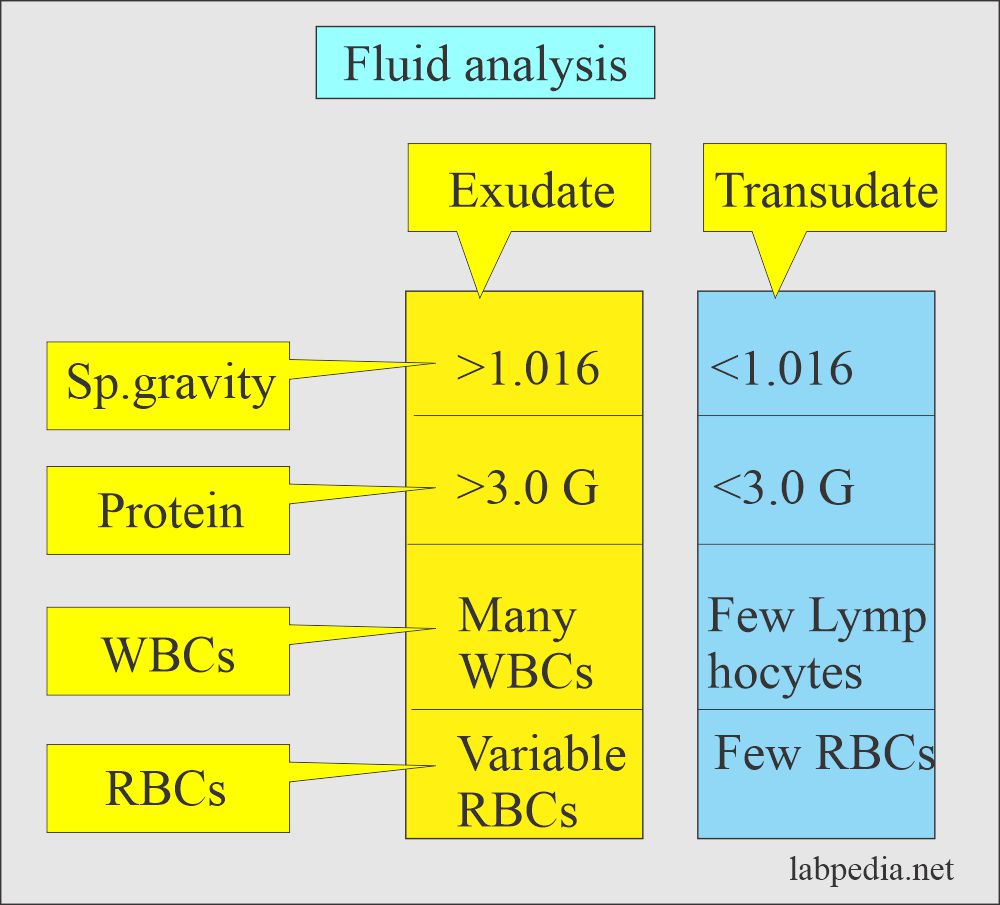
- Effusions from the abdomen, pleura, pericardium, and joints are classified into exudate and transudate.
- Exudates are caused by the inflammatory, infectious, or neoplastic diseases.
- Transudates are caused by venous congestion, hypoproteinemia, and fluid overload.
- Some of the fluids are analyzed to diagnose the disease, like sweat for cystic fibrosis.
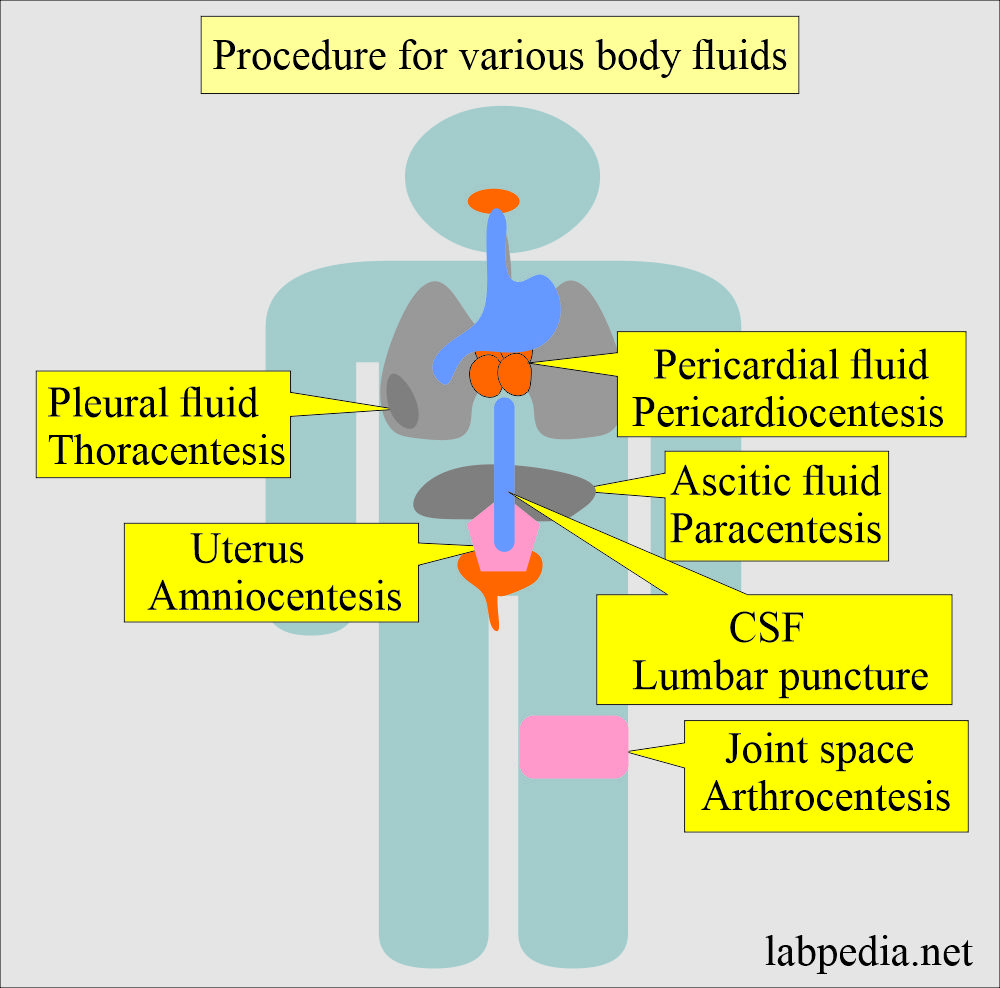
What are the various Procedures to get fluids?
- Lumbar puncture for CSF.
- Amniocentesis to get fluid from the uterus.
- Pericardiocentesis for pericardial fluid.
- Thoracentesis for pleural fluid.
- Paracentesis for the peritoneal fluid.
- Arthrocentesis for the fluid from the joints.
What are the parameters tested for The fluid analysis?
- Gross appearance.
- Specific gravity
- Total protein
- LDH level.
- Total cell count.
- Microscopic examination for the differential count.
- Cytospin For the cytological examination.
- In the case of CSF, the glucose level is estimated.
- In some cases, AFB or Gram stain is done.
- Fluid analysis is to diagnose the etiology of fluid formation, or sometimes it may be therapeutic.
What are the therapeutic advantages of Fluid Analysis?
- Fluid aspirated from the pleural cavity improves ventilation and oxygenation.
- Fluid from the Peritoneum relieves the pressure and ease of breathing and eating.
- Fluid aspirated from the joint relieves the pain and function.
- Fluid aspirated from the pericardial cavity improves diastolic filling and cardiac output.
What is the Difference between various fluids?
| Test | Exudate | Transudate | Chylous |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP = Total protein
MN = Mononuclear cells.
How will you compare Transudate and Exudate?
| Parameter (Characteristic features) | Transudate | Exudate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Please see more details in Fluid Part 3.

Thank
Thank you for the clear explanation and sufficient information.
Thanks.