Solutions:- Part 6 – Field Stain A and B, Preparation
Field Stain A and B
What ate the contents of Field stain?
- Field stain A
- Field stain B
- Thin and thick blood films are made and fixed in methanol for one minute.
How do you make Field Stain A (Dark violet color)?
Using Commercially Available Powder.
- Field stain A commercially available powder = 5 grams
- Distilled water is heated to 80°C or 60°C for 30 minutes. = 600 mL.
How to make Field stan A from commercial powder?
Field stain A (ready-made powder).
- Mix the powder into the water until it is dissolved.
- Filter the solution.
- Label the date.
What are the reagents of Field Stain A?
- Methylene blue (analytical grade) = 1.6 grams.
- Azur = 1 gram.
- Disodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous = 10 grams.
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous = 12.5 grams.
- Distilled water = 1000 mL.
What is the procedure for Field stain A preparation?
- Take Methylene blue (analytical grade) = 1.6 grams.
- Take Azur = 1 gram.
- Take Disodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous = 10 grams.
- Take Potassium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous = 12.5 grams.
- Distilled water = 1000 mL.
- Mix both salts (3 and 4) in the water.
- Add 500 ml from above into a bottle containing glass beads.
- Add the stain powders (Methylene blue and Azur) and mix well.
- Then, add the remainder of the solution.
- Mix well and filter into another clean bottle.
- Label the bottle Field stain A and also write the date.
How will you prepare Field Stain B (Orange color)?
How will you make Field Stain B from commercially available powder?
- Field stain B commercially available powder = 4.8 grams.
- Distilled water is heated to 80°C or kept at 60°C for 30 min. = 600 mL.
- Mix well the field stain B until it is dissolved.
- Filter and label the date.
What are the reagents of the Field stain B?
- Eosin(yellow water soluble) powder = 2.0 grams.
- Disodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous = 10 grams.
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous = 12.5 grams.
- Distilled water = 1000 mL.
How will you prepare Field Stain B?
- Mix both salts (2 and 3) in the distle water (1000 mL) to make the solution.
- Add 500 ml from above into a bottle containing glass beads.
- Add the stain powders Eosin and mix well.
- Then, add the remainder of the solution.
- Mix well and filter into another clean bottle.
- Label the bottle Field stain B, and also write the date.
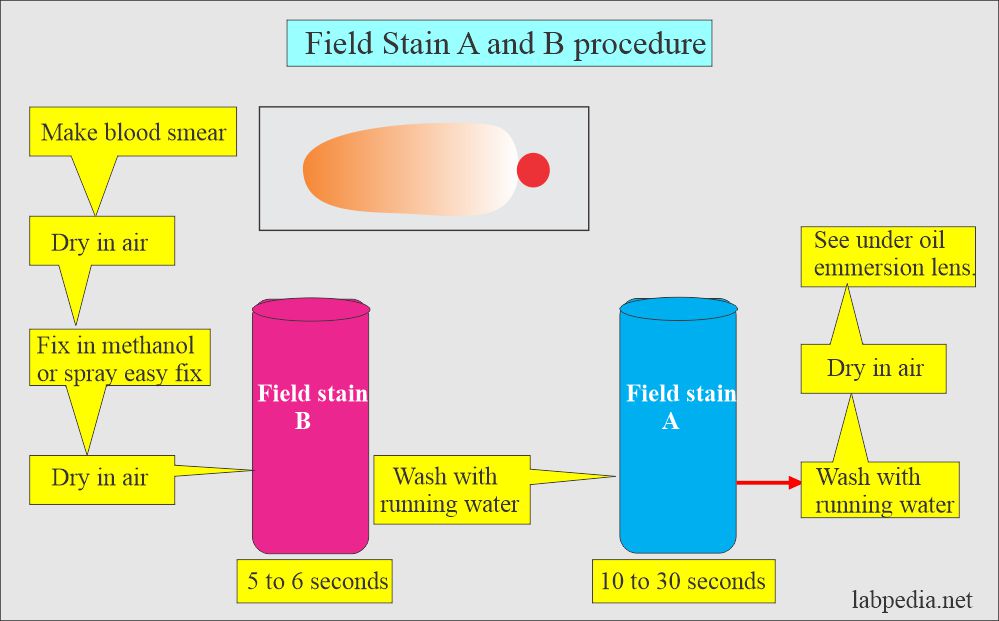
What is the staining Procedure for Field Stains A and B?
- Fill up two Coplin jars or wide-mouth bottles:
- Field Stain A (Blue stain).
- Field Stain B (Red stain).
- Make a blood smear on a clean glass slide, and it is dried in the air.
- Fix in methanol for one minute or get Spray ‘Easyfix’.
- Dry in the air.
- Dip fixed smear to Field Stain B (Red Stain) for 5 to 6 seconds.
- Wash in running tap water.
- Dip smear into Field Stain A (Blue Stain) for 10 to 30 seconds (adjust it).
- Wash in running tap water.
- Dry at air and see under oil immersion objective.
- The staining time may be adjusted.
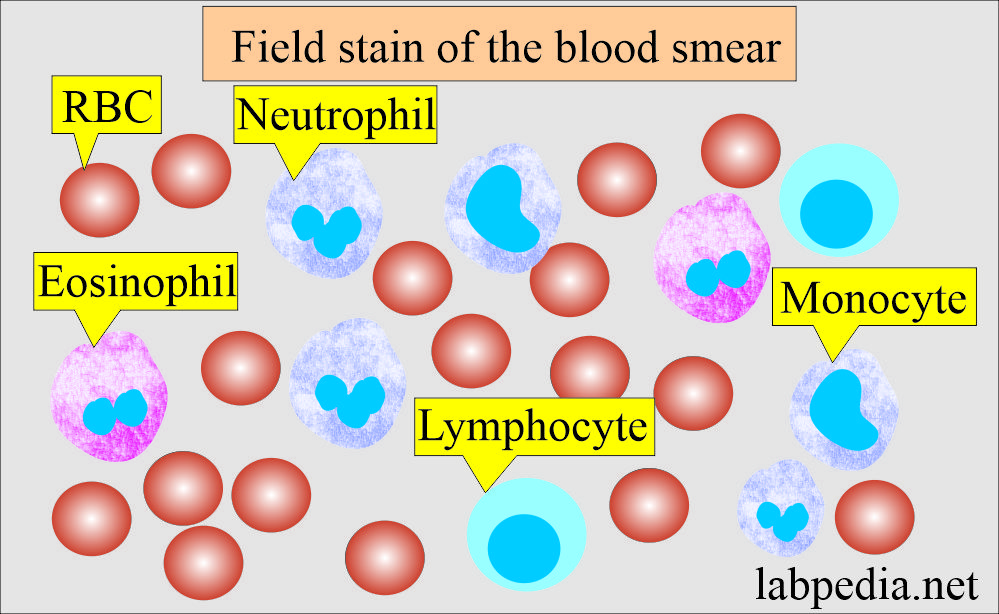
How will you interpret cells in Field stain?
| Type of cells | Color appearance |
| Red blood cells |
Pink |
| Neutrophils granules | Lilac color |
| Eosinophils | Orange granules |
| Malarial parasites | Deep red chromatin and pale blue cytoplasm |
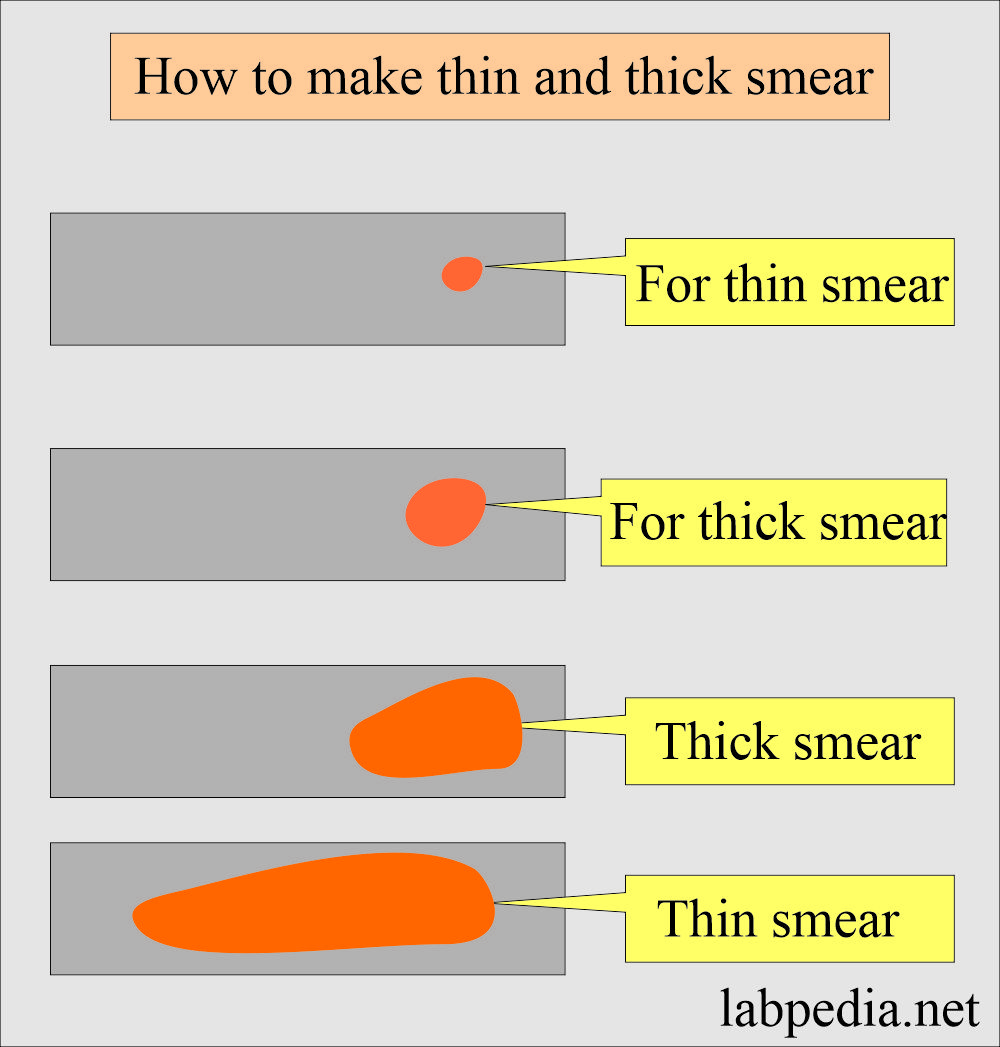
How do you prepare thick and thin smears?
- Thick and thin blood smears can be made into two separate slides.
- Put two separate drops of the blood. For a thin smear, put a small drop and a large drop for a thick smear.
- Spread the drops by the cover glass.
Note: The timings can be adjusted by staining a few slides.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the purpose of thick and thin smears?
Question 2: Will you fix the thick smears?

Sjaelewa kbsa
Thanks
Thanks.
Thanks, welcome.
Sir pleased say
Which agur use in stain
Azur B is used.
Whice agur use in stain
Azure B is used.
Thanks
Why we use field B stain first?
Field stain A lyses the red cells, so we need to see the red cells complete that’s why we use B stain first.
Very informative, thank you sir.
Thanks.
Why we are using field stain b for first staining
That is correct.
Afternoon sir how can I use for stains during Field stain b
I have described the procedure, and you can follow those instructions. Rest you have to do trial on how many seconds or minutes are needed to get a good result. The time will be different for different solutions.
Hello Dr. Riaz,
Does not filtering the constituted solution affect the staining of the samples?
If solutions are well mixed, I don’t think there will be any issue with staining quality after filtration.
But there is no conc of those field A and B
Field stains final preparations are the working solutions.
what is concentration of field stain specifically in working solution ?
Field stains preparations are the working solution, no need for further dilution. You have to adjust the timings for good stains, which will depend upon the pH of the water.
Hello Dr. Riaz,
How would one diagnose a patient’s sample if malaria parasites are found in it?
If one was to use pluses to diagnose, and following this order: Scanty, +, ++, +++; where +++ is most severe and scanty least severe)
I think when malarial is positive, that is enough for the diagnosis. But need to see a thick smear which sensitivity is 2 parasite/1,000,000 uninfected RBCs.
Smears should be done every 6 to 12 hours for 3 consecutive days.
You can see this reference https://labtestsonline.org/conditions/malaria
well explained,well detailed
Thanks.
SIR WHAT CAN I DO TO GET A CLEAR DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ACROSOME AND NUCLES OF HUMAN SPERMETAZOA WHEN STAINED WITH DIFF QUIK STAIN AS IAM GETTING MORE DARK BLUE COLOUR
I think if you dip in the alcohol (or spirit), The color will get lighter. I hope this technique will help you.
Field stain A lyses the red cells and in this case, we need to see the red cells complete that’s why we use B first.
True. Thanks for the comments.
Thank you so much.
This is very informative.
Thanks.
Thanks sir, for sharing the info on preparation of the stain,,, I was searching for it for so long…. Lucky I found your information…. Thanks and God bless.
Thanks a lot. I am glad that my website labpedia.net helped you.
Sir, is this ( field stain) the same as diff quick stain…. . I need it to study sperm morphology… Could you guide me pls..
Thanks
Sir, is this ( field stain) the same as diff quick stain…. . I need it to study sperm morphology…
Thanks
Both stains are variants of the Rowmanswky stain. You can easily stain the sperms.
1. Sir , can i change this “Disodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous
& Potassium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous” ingredient onto other buffer , because is not ready yet in my country ,
2. and what is the function of two ingredient ?
3. an then, may i adding the acetic acid in field stain B for sharpening analysis purpose
thank ou Dr Riaz
You can take Field stains A and B from the HD supplies, Merck/BDH Chemicals, or other reliable companies.. Then bring 500 mL distle water, heat it to boiling, then add the stain and mix it thoroughly. When it is cool, filter and keep it in the storage bottles.
Thank you sir, your information is so educative
Thanks.
please can your send this document to me , i can used forteaching purpose
Thanks in Advance
how can preserve field stain A and B after preparation , in which bottle ? for how long
You can keep the Field stain in the colored (brown) bottle. After some time, filter the stain. These stains are stable indefinitely.
Sometimes platelets are stained very light to unstained , what could be reason
Please adjust the staining time. If platelets are overstained, then you can decolorize them with methyl alcohol.
What is the time limit for newly prepared filed stain working solution
For newly formed Field stain, you must stain different slides with different timings. Only then can you decide what the best time for staining is.
Dr .Riaz ,may you please tell me clearly on the storage preparation of field stain A and B,how is the working solution prepared?
Thanks
Please read carefully, I have described the reagents needed to prepare the solution. You can store in colored bottles and frequently filter the solution before use.
producer batian video mai
Ok i will send you the link. I will upload on youtube.
Very informative,please what’s the dilution ratio of the field stain
There is no need for the dilution of field stain.
Dr. Riaz,
Good Day. It’s nice reading from you.
Please I have read different methods to prepare Field Stain A & B for Malaria Parasite Diagnosis. One Method is the one you described using – 10 g Na2HPO4, 12.5 g KH2PO4, 1.6 g of Methylene Blue and 1 g of Azure for 1L of Field’s Stain A; 10 g Na2HPO4, 12.5 g KH2PO4, 2 g of Eosin for 1L of Field’s Stain B.
Another Method I have read uses only – 2.6 g Na2HPO4, 2.6 g KH2PO4, 1.6 g of Methylene Blue and 1 g of Azure for 1L of Field’s Stain A & 2.6 g Na2HPO4, 2.6 g KH2PO4 and 2.0 g of Eosin for 1L of Field’s Stain B.
So Which one is the the best method. Is it using 10 g Na2HPO4, 12.5 g KH2PO4 or 2.6 g Na2HPO4, 2.6 g KH2PO4?