Examination of Placenta and Umbilical Cord
Placenta and Umbilical Cord
How do you get a sample of the Placenta and Umbilical Cord?
- This is a histopathological study of the fetus, with gross and microscopic examinations.
- This is an autopsy of the Foetus to find any abnormalities.
- Examine the placenta.
What are the Indications for the examination of the placenta?
- In the case of premature birth.
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- In the case of asphyxia.
- In the case of prenatal death.
- In the case of third-trimester bleeding.
- In the case of fetal or maternal infection.
How will you define the placenta?
- The placenta grows throughout the pregnancy. It is delivered through the birth canal immediately after birth.
- It is the organ in which the placenta develops in the uterus during pregnancy.
- The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus and removes waste products from the fetus’s blood.
- The placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus.
- The umbilical cord connects the placenta with the fetus.
How will you discuss the placenta’s structure?
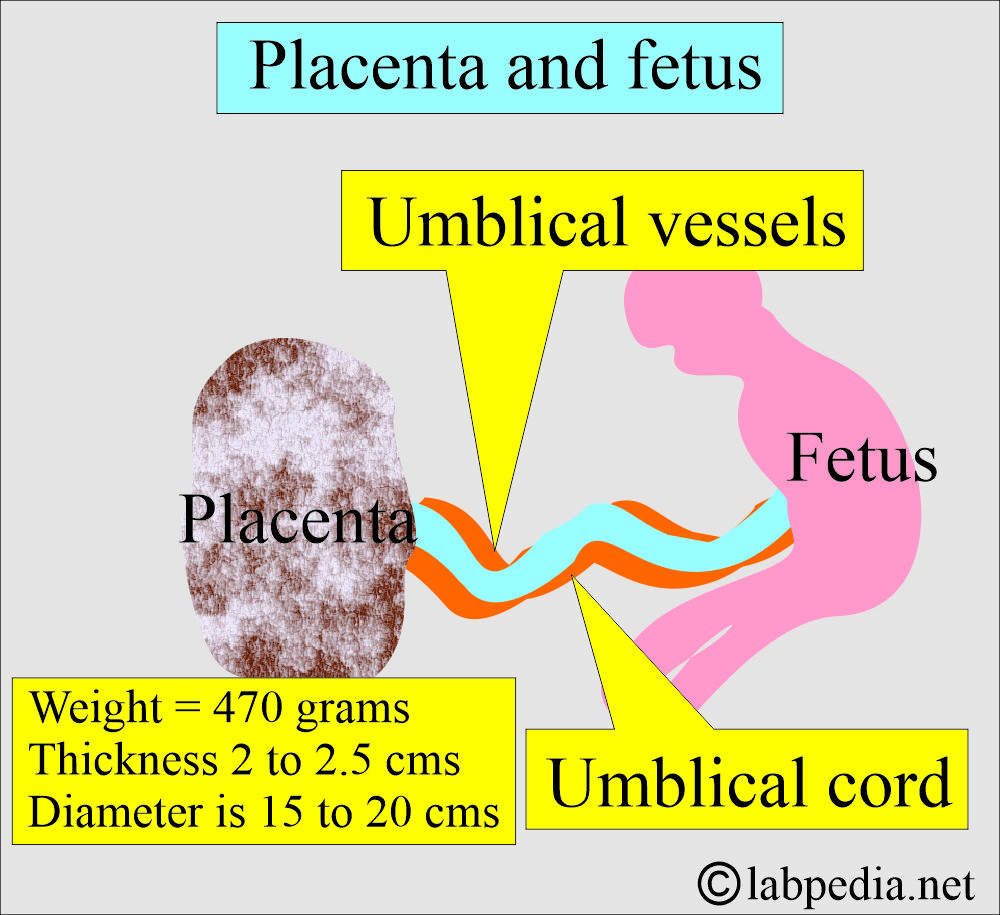
- Normally, the placenta measures about 22 cm and is 2 to 2.5 cm thick.
- Usually, the placenta weighs around 470 g (500-600 G) and is 15-20 cm in diameter.
- The maternal surface is dark brown and divided into lobules.
- It is a collection of fetal blood vessels called villi, surrounded by intervillous spaces in which maternal blood flows.
- The fetal surface is gray and shiny.
How would you describe the umbilical cord?
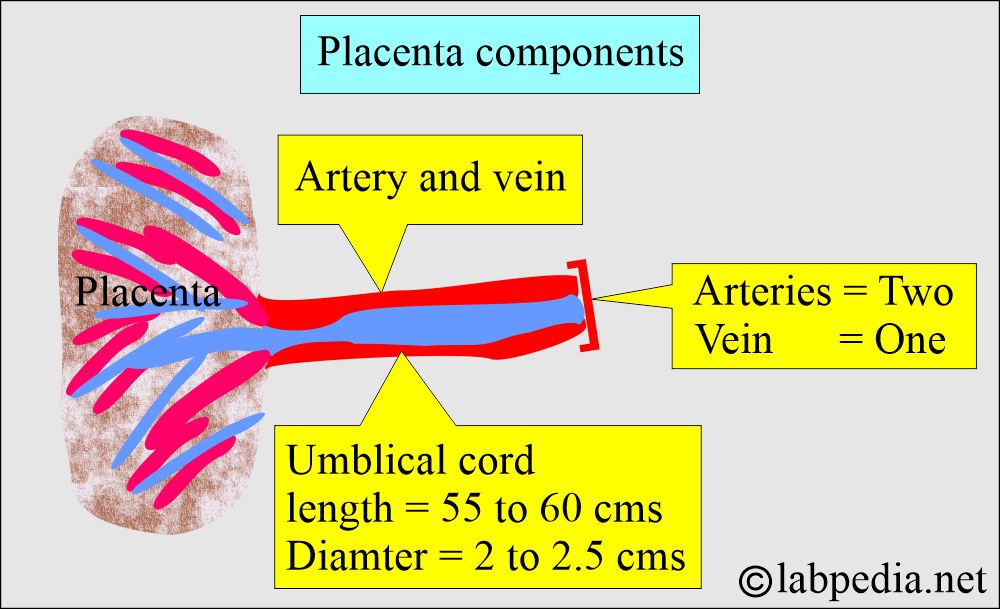
- At birth, the umbilical cord is 55 to 60 cm in length and 2 to 2.5 cm in diameter.
- It has two Arteries and one vein.
How will you examine the umbilical cord?
- It’s the length.
- Point of insertion.
- Check for the presence of any knots.
- If one artery is absent, then renal agenesis is possible.
- Presence of any thrombosis.
- Evaluate the fetal membranes.
- Check for the presence of Wharton’s jelly.
What are the abnormalities of the umbilical cord?
- Supernumerary vessels.
- Persistent right umbilical vein.
- Cord compression.
- Cord prolapse.
- Nuchal cord.
- Cord torsion.
- Hematoma of the cord.
- Wharton’s jelly deficiency.
- Long cord leading to prolapse of the cord.
- The cord may be short or long.
- The short cord is less than 40 cm in length.
- The long cord is more than 100 cm in length.
- Cord knot.
- An abnormal number of vessels.
- Thrombosis of the vessels.
- A different smell indicates infection.
What are the Placenta’s functions?
- It keeps maternal and fetal circulation separate.
- It nourishes the fetus.
- It eliminates fetal waste.
- It produces hormones vital to maintaining pregnancy, including placental hormones.
- Maternal immunoglobulins (IgG) cross the placenta by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
- Because IgG has a long half-life, the newborn is protected for 6 months.
- The placenta is an effective barrier to large proteins and hydrophobic compounds bound to plasma proteins.
What are the Placental hormones?
- Placental lactogen.
- Chorionic gonadotropin.
- Steroid hormones are:
- Progesterone.
- Estradiol.
- Estriol.
- Estrone.
How will you determine whether placental function is normal or predict impending fetal death?
- You can check:
- Uriner estriol.
- Estriol is an estrogenic hormone produced by the placenta, derived from the adrenal cortex and fetal liver.
- Check urine total estrogens.
- Urine glucose falsely increase result.
- Total estrogen levels in urine indicate placental function.
- Serum unconjugated estriol.
- Serum placental lactogen.
- This hormone is produced by the placenta.
- Its metabolic activity is similar to that of prolactin and growth hormone.
How will you examine the placenta?
- Note the size, shape, and color, and check for any smell.
- Check the placenta for completeness.
- Check for accessory lobes.
- Any placental infarcts.
- Any hemorrhage.
- Presence of tumors or nodules.
When will you send the placenta for histopathology?
- Send the placenta for histopathological examination.
- When there is prematurity.
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- Asphyxia.
- Perinatal death.
- The third trimester is associated with bleeding and suspected fetal or maternal infection.
- If needed, also do the culture.
- In some cases, ultrasonography may be advised.
What are the abnormalities of the placenta?
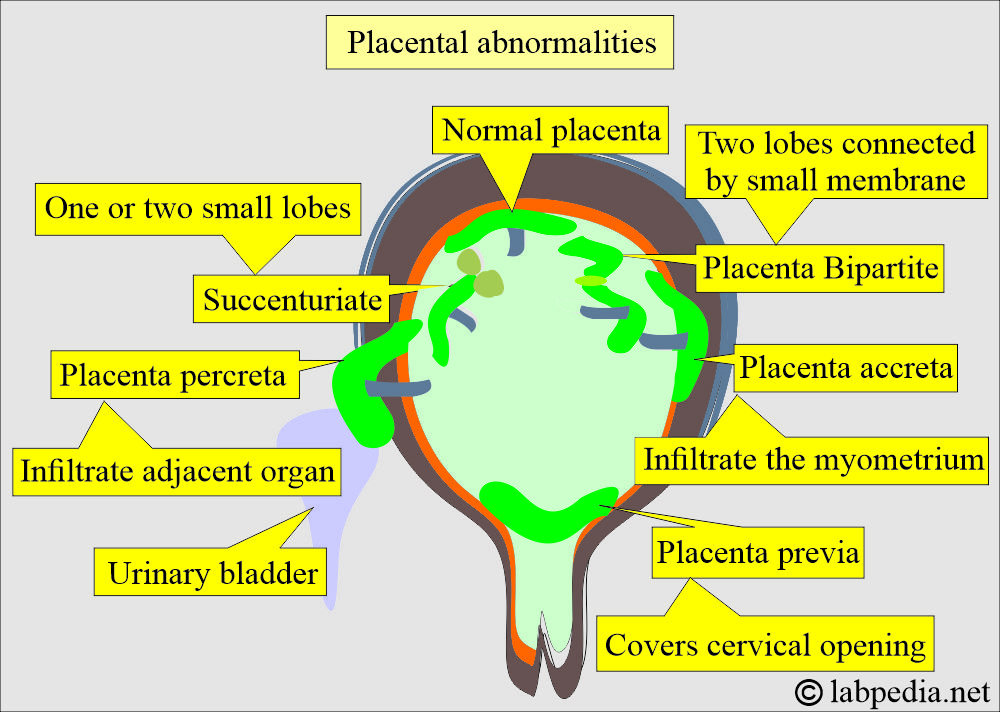
- Multi-lobes or bilobed placenta.
- Bipartite. The membrane connects two lobes, and the umbilical cord is inserted into one of the lobes.
- Accessory lobes.
- Succenturiate. It has second or third lobes, and these are very small in size.
- Placenta accreta. This placenta grows into the uterine wall. After the birth, it remains inside the uterus.
- Placenta percreta. This grows in the uterus and may sometimes involve the urinary bladder.
- The Circumvallate placenta is on the fetal-placental side. This is a placental abnormality and causes the membranes of the placenta to fold back around its edges.
- Placental size:
- Small placenta.
- Large placenta.
- Placental infarcts.
- Chorioamnionitis.
- Chorioangioma.
- Hydatidiform mole. Molar pregnancy.
What are the causes of Inflammation of the placenta?
- Ascending infections are the most common. These are:
- Bacteria associated with premature birth.
- Premature rupture of the membrane.
- Infection beyond the membrane involves the umbilical cord.
- Through blood is a transplacental infection.
- Most commonly, villi are involved.
- There are chances of TORCH in the fetus.
What are the complications of placental abnormalities?
- Any abnormality of the placenta or the umbilical cords may lead to:
- Perinatal morbidity.
- There will be abnormal fetal development.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What are the complications of the abnormal placenta?
Question 2: What is the abnormality of the umbilical cord?


EXCILENT
Thanks, I will try to add more
Assalamualaikum sir how are you. Hopefully you are doing well. I have a request. Kindly sir gave me permission and access to placenta examination checklist
Wailkum salam. You are welcome to use my website.
PLZ MORE INFORMATION SEND THE WED