Chapter 31: Common serological test, Antistreptolysin O (ASO), C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Antistreptolysin O (ASO)
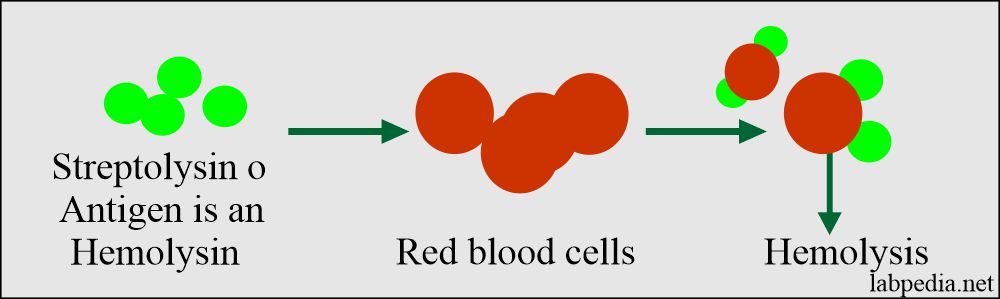
ASO titer is advised for the diagnosis of rheumatoid fever. The Streptolysin O(SO) is antigenic and cause hemolysis of RBCs. So there is antibody formation (Antistreptolysin-Ab) in the blood.
Principle:
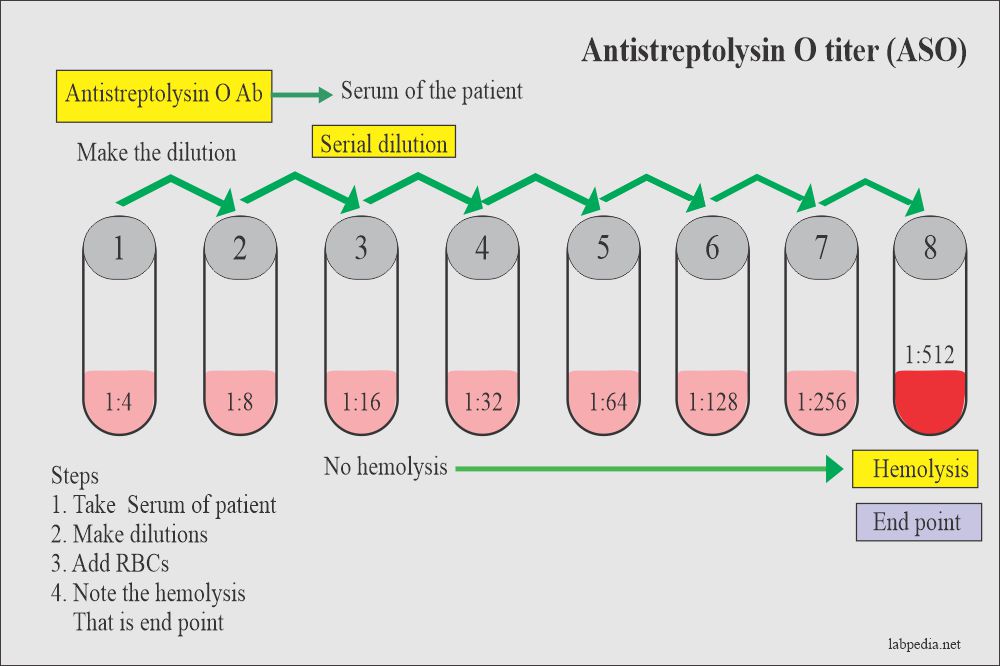
Patient serum with dilution is mixed with a fixed amount of streptolysin O- Ag and Abreaction take place.
Now add Ab-coated RBC. There will be hemolysis in the tube, where streptolysin O is free.
The result is reciprocal of the highest dilution where hemolysis starts. These are described as Todd units. Other units are international units (IU).
Positive ASO indicates:
- Rheumatic fever.
- Acute glomerulonephritis.
- Erythema nodosum.
- Useful for differentiation of rheumatic fever/rheumatoid arthritis.
Normal
0-125 Todd units.
Definite value = 400 or more.
Rising titer from 50-250 is significant.
While persistent low level rules out a rheumatic fever.
C – reactive protein (CRP)
This was recognized in 1930.
Definition
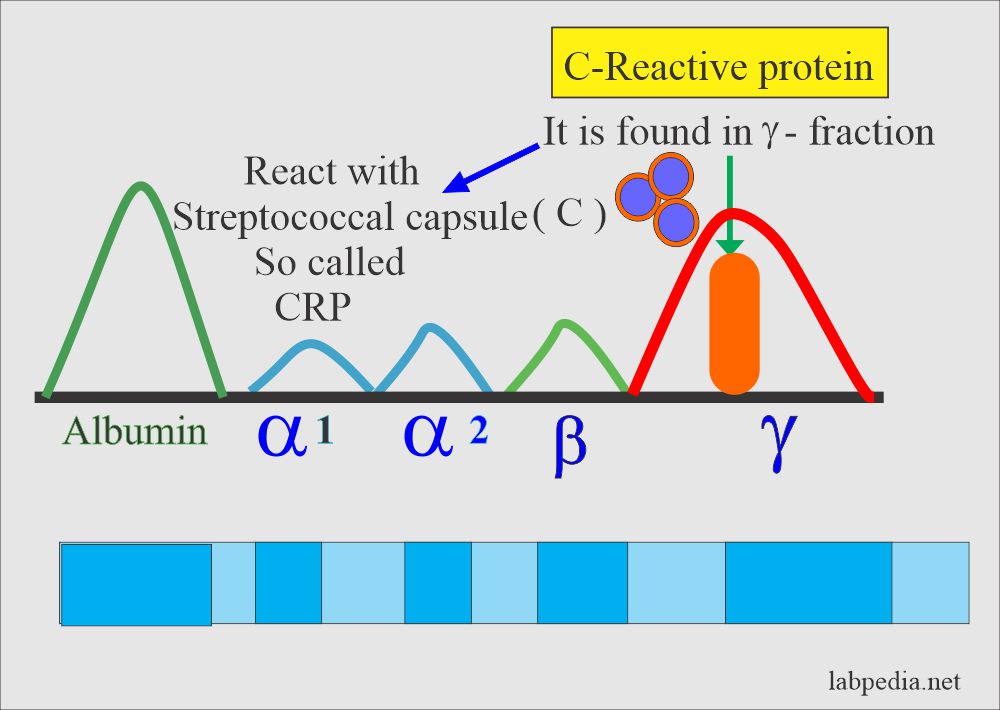
- CRP is γ-globulin (found in the γ-region) is found in various inflammatory diseases. This is also called acute-phase protein.
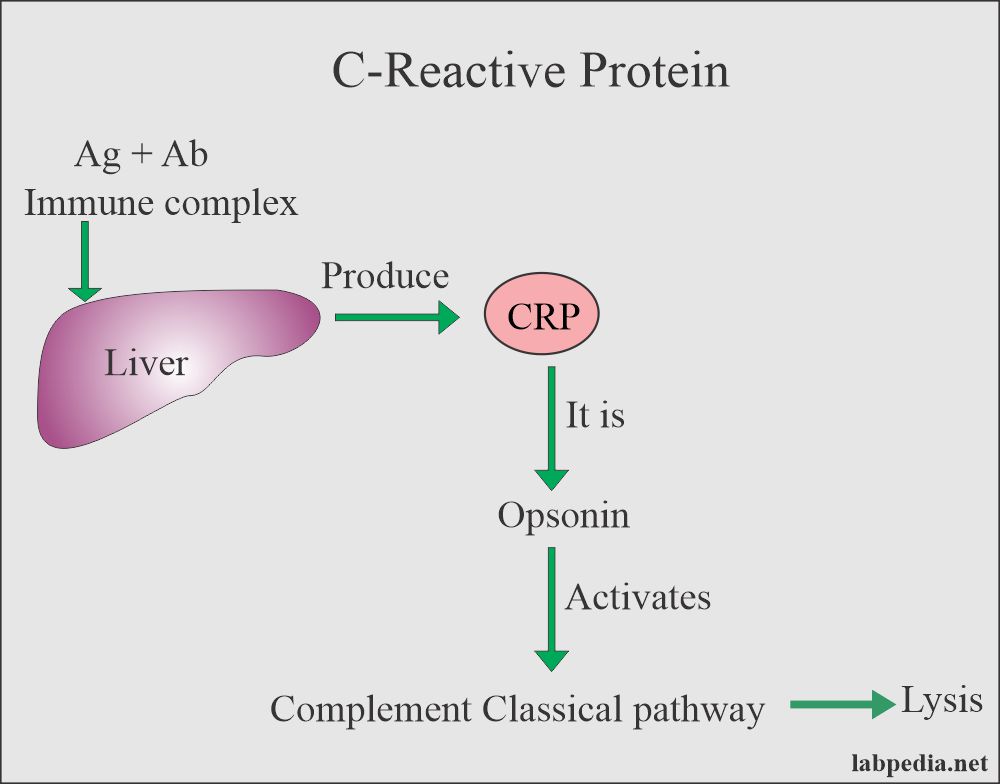
- CRP is produced in the liver.
- CRP name is derived from the reaction with streptococcal capsular (C) polysaccharide.
Principle:
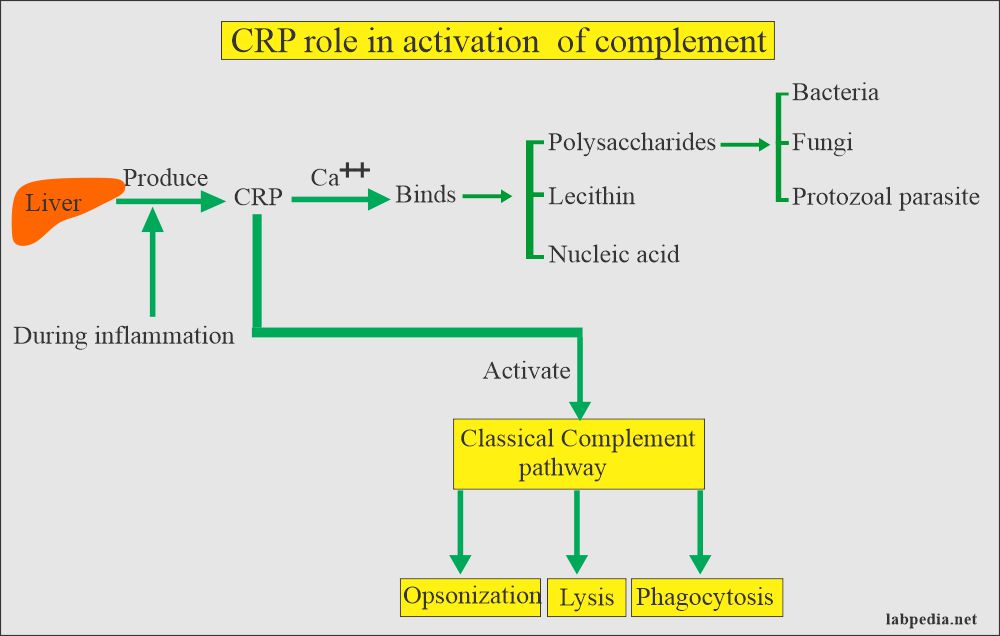
- CRP is opsonin and it activates the complement system and ultimately leads to lysis.
- Serum of the patient (CRP) + Somatic C polysaccharide of pneumococci mixed and gives rise to a precipitate.
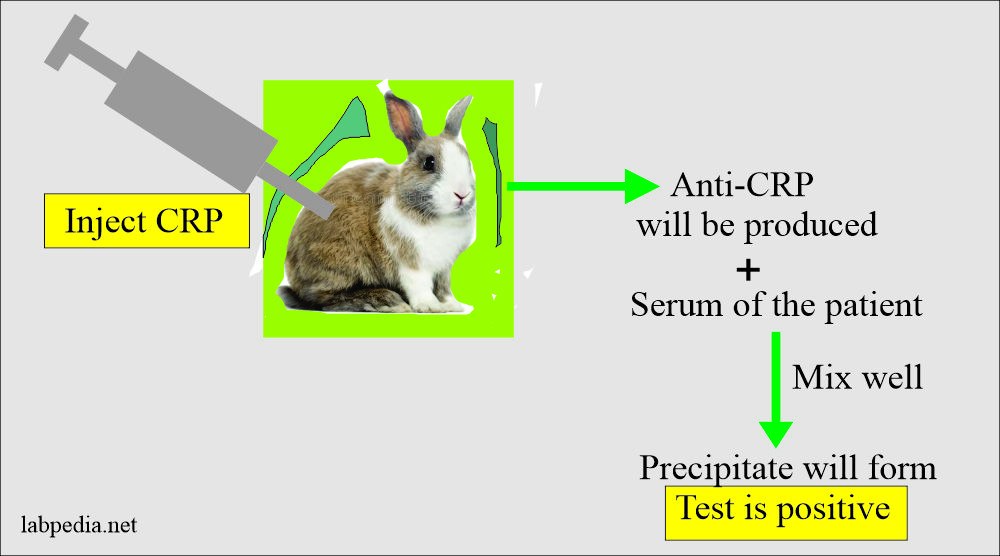
- Practically CRP is injected into the rabbit when the anti-CRP antibody is produced. Now take serum of the patient (CRP) + Mix anti-CRP. This will give precipitation.
CRP + Anti CRP = Precipitation
Causes of CRP:
- Produced in various bacterial diseases.
- Produced by injured myocardial muscle in myocardial infarction.
- Positive in acute and chronic rheumatic fever. This is a reliable and sensitive indicator of rheumatic fever. Its absence rules out a rheumatic fever.
CRP is also positive in:
- Sydenham’s Chorea.
- Myocardial infarction and negative in angina.
- Many malignancies.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Gout
- Viral infection like Viral Hepatitis.
- Bacterial Pneumonia.
- Active Tuberculosis.
- Lepromatous Leprosy.
- Acute Tonsillitis, Scarlet fever, and Mumps.
Advantage of CRP over ESR
- Raised ESR may be seen even without the presence of fever in anemia, pregnancy, nephrotic syndrome, and hypogammaglobulinemia.
- ESR may be normal in Frank’s active rheumatic fever.
CRP detection is valuable for:
- Low grade and questionable rheumatic fever.
- Follow-up and treatment of rheumatic fever.
- The differential diagnosis of coronary insufficiency (angina) and myocardial infarction