Chapter 32: Common Serological Tests, Widal test, Rheumatoid factor (RA factor)
February 12, 2021Elementary Immunology
COMMON SEROLOGICAL TEST
Some of the standard serological tests are discussed.
Widal test
Principle: This test is advised for antibodies in patients’ serum against Enteric bacilli to diagnose enteric or typhoid fever.
Sample
The serum of patients is needed.
Procedure:
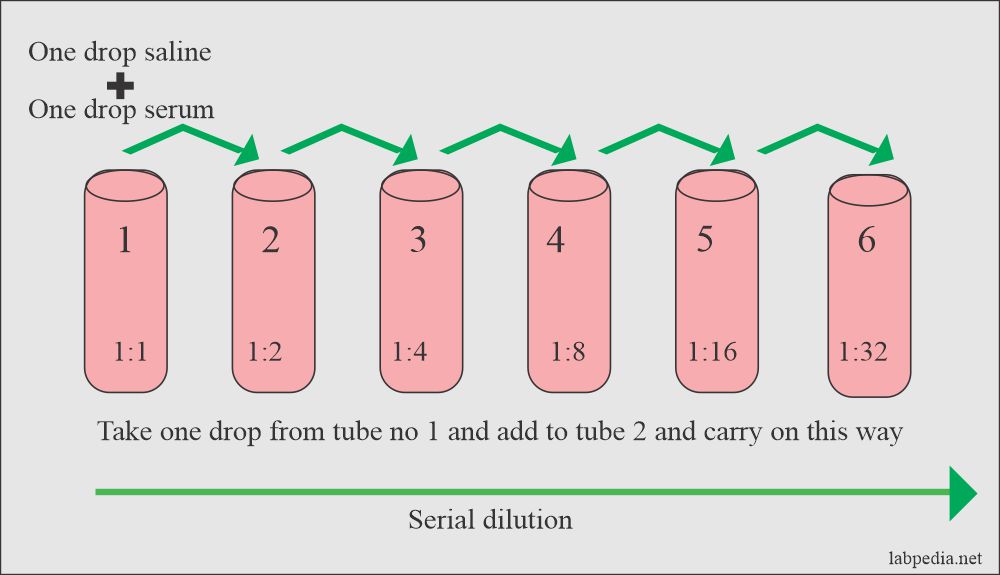
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
This can be done by:
- Slide method
- Tube method
Antigens
Salmonella groups A, B, C, D, and E and Paratyphi A, B, C.
Salmonella Typhi antigens are:
- O-Antigen (Somatic Antigen):- These are 0-17 groups. 95% fall in group A, B, C, D, and E.
- O-Ag rises in 50% of the cases by the first week. It disappears in 6-12 months. This is diagnostic for acute infection.
- H-Antigen (Flagellar Ag).
- H-Ag rises slowly and disappears after many years.
- V1-Virulence antigen. This is also a surface antigen. this is used to find the carrier state.
Precautions
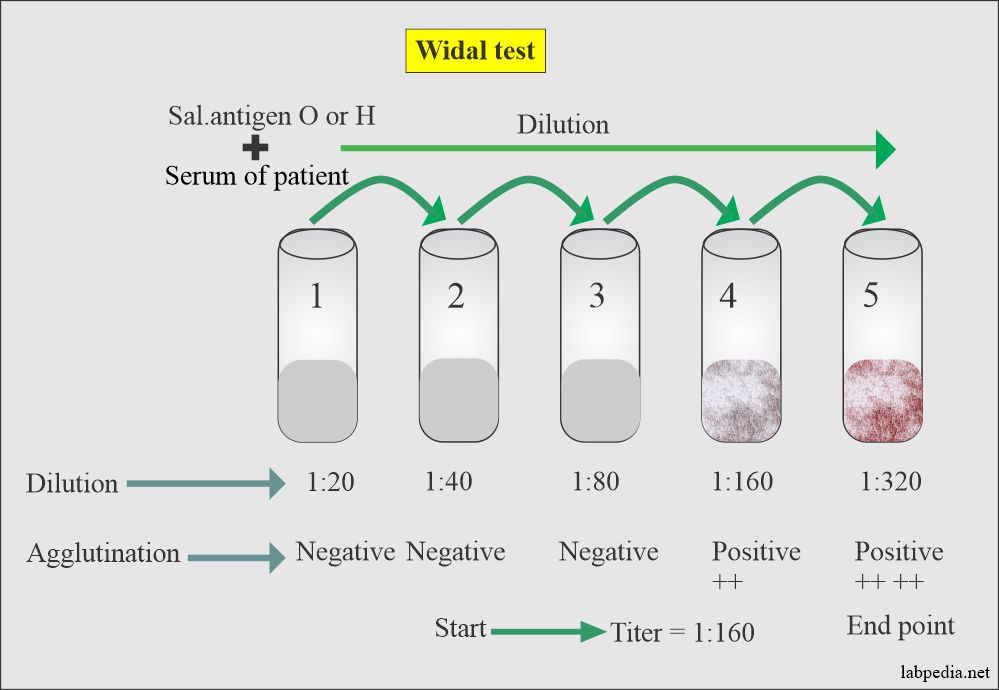
- No value if done before 7 days of the onset of fever. Two or preferably more tests are done every 3-5 days to see a rising titer.
- Many people without the disease have agglutinin in low titer.
- The immunized person will also show agglutinin (antibodies).
- There will be a significant rise after 7-10 days.
- The anamnestic reaction will show negative results in low dilution and will be positive in high dilution.
- The test has to be done with a battery of antigens.
- The slide test is suitable for screening, but confirmation should be done by tube method.
Interpretation
- The history of patients and discussions with physicians will be helpful.
- A single test is not diagnostic.
- In a vaccinated case, antibodies may be present. So a significant level is a four-fold rise in O-Ag or at least O Ag is > 1:80.
- Antibiotic use prevents the rise in antibody levels.
Negative Result
- When there is no agglutination
- Blood was drawn early before 7 days.
- A negative test does not rule out an enteric fever.
Positive Result
- Indicate infection.
- In-person with a history of vaccination.
- A high titer of H-Ag indicates recent/past disease or vaccine.
Rheumatoid Factor (RA Factor)
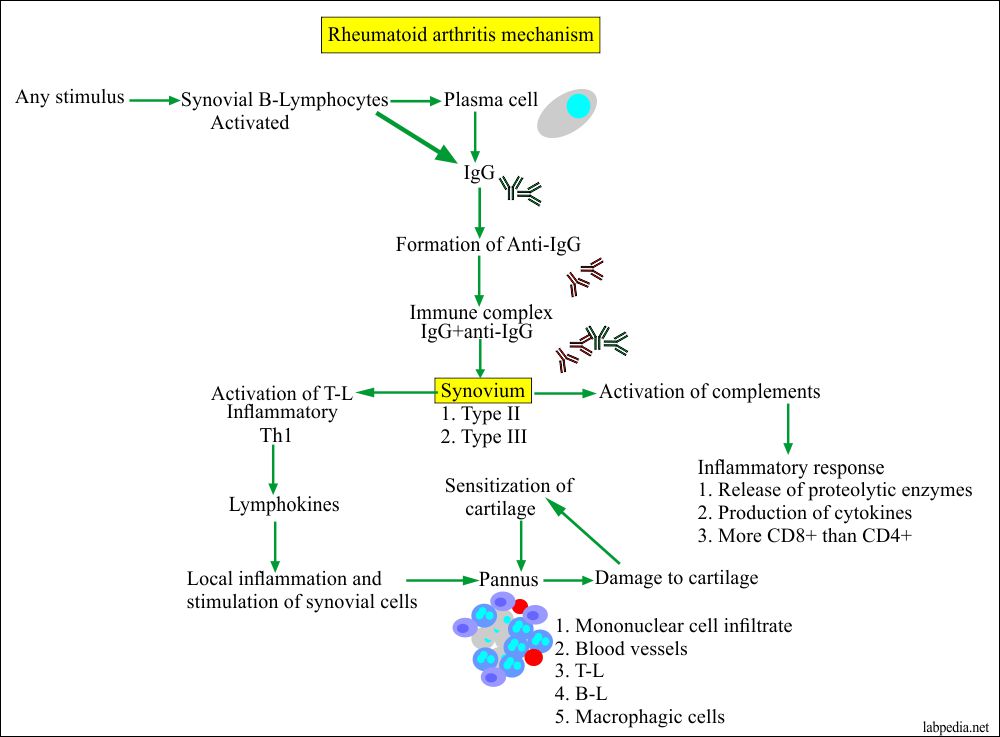
- Pathogenesis:
- The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown. Related factors are:
- Genetic factors are important.
- Hormonal factors.
- Psychosomatic factors.
- There are pieces of evidence of immunologic factors involved in the articular and extraarticular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Some belief in infections but is not established.
- In the USA, RA is among the most prevalent chronic conditions.
- In most of the studied population is 1% to 2%.
- This disease (RA) has three distinct stages:
- The development of synovitis by the primary etiological factors.
- This is followed by immunologic manifestations that will initiate the initial inflammatory reaction.
- There is a transient inflammatory reaction in the synovium which, leads to the proliferative destructive process.
- Age:
- This may be seen at any age.
- Initially, this disease was seen among the ages of 30 to 50 years.
- Older age groups and overweight people are prone to arthritis.
- Sex:
- Females are 2 to 3 times more prone than males to develop RA.
- Signs and symptoms:
- This is a chronic, usually progressive inflammatory disorder of the joints.
- This disease may be:
- Mild illness of brief duration.
- This may be progressive destructive polyarthritis associated with systemic vasculitis.
- RA usually starts with fatigue, anorexia, weakness, generalized aches, and pain.
- Stiffness of the joints appears after weeks to months.
Mechanism of damage to cartilage and bone: The damage to the cartilage takes through the immune complexes.
Diagnosis:
- Rheumatoid factor is used to diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- This factor consists of a group of immunoglobulin reacting with the Fc region of IgG. This may be IgM, or IgG, or IgA.
- RA factor is present in:
- Blood
- Joint fluid
- It first appears in the joint fluid then in the blood.
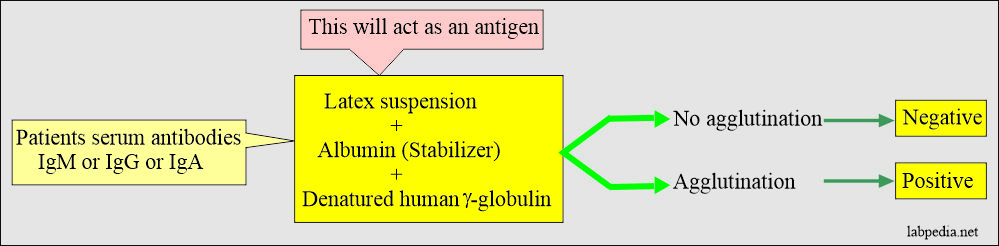
Principle
- These antibodies “RA” factor is identified by agglutination reaction.
- The rheumatoid arthritis agglutination test is based on the reaction between patients’ antibodies in the serum. This is known as a rheumatoid factor that will react with the antigens derived from gamma globulins.
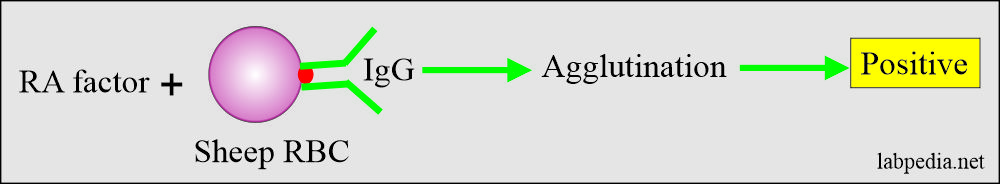
- Haemagglutination: When sheep RBC are coated with IgG-Ab are used. Now add serum of patients, and this will give agglutination.
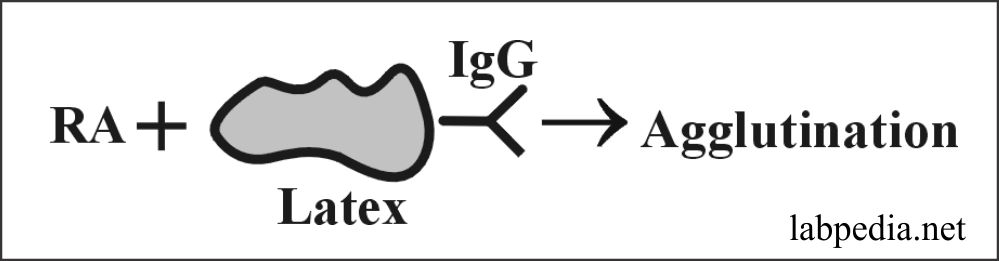
- Latex particles are coated with IgG, and then serum is added, and this will show agglutination.
Limitations
- 70-90% of the cases are positive for rheumatoid arthritis.
- A negative result does not rule out rheumatoid arthritis.
- The false-positive test may be seen in:
- 71% Rheumatic fever.
- 30-40% SLE.
- 12% Gout
- RA factor may be positive in tuberculosis & syphilis.
- False Positive may also be seen in old age, liver disease, SBE, chronic lung disease & syphilis.