Ectopic Pregnancy and Its Diagnosis
Ectopic Pregnancy
What Sample is needed to diagnose Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Patient serum is required for Beta-HCG testing.
- Biopsy of the fallopian tube or ovarian tissue for surgical pathology will show placental villi and trophoblastic cells.
How will you define Ectopic Pregnancy?
- This is defined as the product of conception implanted outside the uterine cavity.
- Or implantation of the fertilized ovum in a location other than the uterus.
What is the incidence of ectopic pregnancy?
- Ectopic pregnancy is the most common cause of death in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- In the majority of cases,>95% occur in the fallopian tubes.
- Rest occurs in the ovary, cornua, and abdomen
What is the Pathophysiology of Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Ectopic pregnancy is a gynecological issue because of the differential diagnosis.
- This is the implantation of the fetus outside the usual place of the uterine cavity.
- This may be seen in 1% of pregnancies.
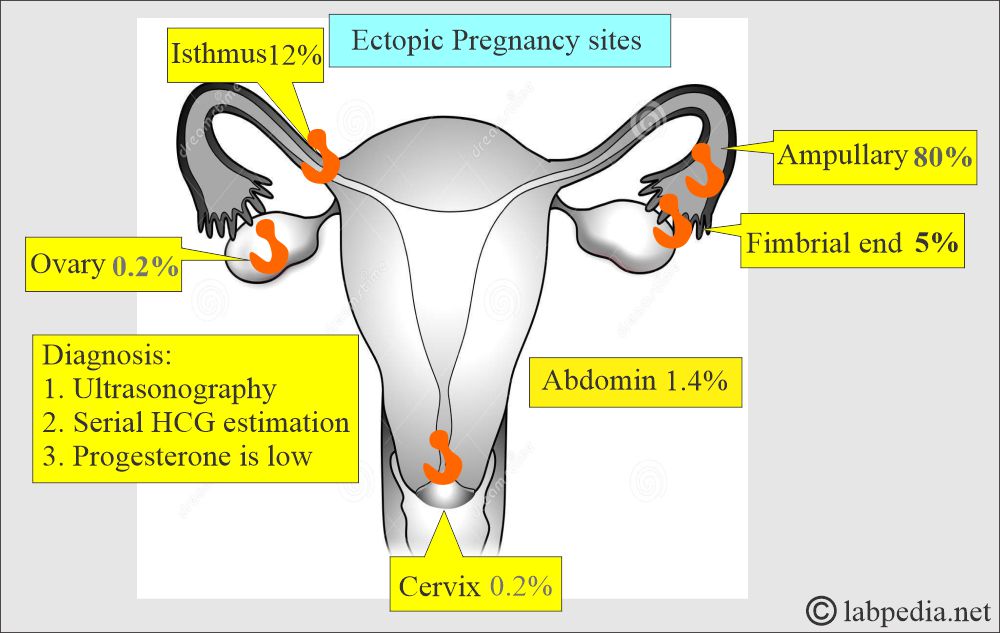
- The most common site is:
- The ampullary part of the fallopian tube is 80%.
- The isthmic portion of the fallopian tube is 12%.
- The fimbria of the fallopian tube is 5%.
- The abdomen is 1.4%.
- The ovary is 0.2%.
- The cervix is 0.2%.
| Ectopic pregnancy site | What % percentage can occur |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- The most common site is the fallopian tubes, also called a tubal pregnancy.
- There is a chance of ectopic pregnancy in 1 out of 50 pregnancies.
- The hormonal changes are the same as in a normal pregnancy.
- There is a cessation of the menstrual cycle.
- There is an elevation of the serum and urinary placental hormone.
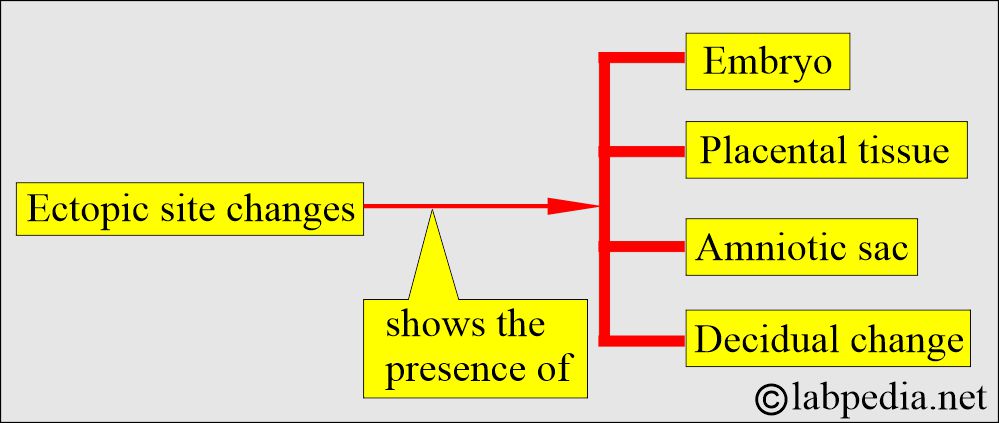
- 50% of the cases show hypersecretory and decidual changes.
- The surgical biopsy material takes many sections, particularly from the blood clot.
- Try to find the placental villi to confirm the ectopic pregnancy.
What is the Pathogenesis of ectopic pregnancy?
- Ectopic pregnancy is caused by:
- Infection or scar formation of the fallopian tubes, which block the tube, is seen in almost 50% of cases.
- Due to previous surgery, there may be scarring.
- Adhesion due to previous surgery on the fallopian tubes or pelvic area.
- Endometriosis may also block the passage of the ovum.
What are the Predisposing factors for ectopic pregnancy?
- If there is a previous H/O of ectopic pregnancy.
- Patients with H/O infertility are more prone to ectopic pregnancy.
- If there is a H/O of gonorrhoeal or chlamydial infection.
- If there is an H/O intrauterine device application.
- In the case of H/O endometriosis.
- More chances in cases of in vitro fertilization pregnancy.
- If it is tubal damage from infections or disease.
- In case there is H/O smoking.
- In the case of a previous H/O miscarriage.
What are the complications of ectopic pregnancy?
- Intratubal hematoma is also called hematosalpinx.
- There may be an intraperitoneal hemorrhage.
- Death of the ovum.
- The tubal rupture and hemorrhage of the ectopic pregnancy lead to a fatal outcome.
- There is severe abdominal pain.
- The patient may go into shock.
- Immediate surgery can save a life.
- 13% of these ectopic pregnancies may lead to maternal death.
- If the diagnosis is not made in time, it leads to the fetus’s death and endangers the pregnant lady’s life.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy?
- Most of the time, its diagnosis is missed.
- Usually, there is abdominal pain. This may vary and be seen in 97% of the cases.
- There may be vaginal bleeding (spotting). This abnormal bleeding is seen in 75% of the cases.
- Menstruation is delayed in these ladies in 75% of cases.
- Adnexal tenderness on palpation is seen in 90% to 95%.
- Also, a unilateral adnexal mass is present in 50% of cases.
- Fever is seen in about 5% of the cases.
- A hypovolemic shock may be the presenting symptom in 14% of cases.
- The following signs and symptoms suggest an emergency surgical procedure:
- Severe tenderness.
- If there is abdominal rigidity or guarding.
- If there is a hypovolemic shock.
- 25% of ectopic pregnancy patients show three classic presentations:
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Adnexal mass.
- Sometimes, patients suspicious of ectopic pregnancy have threatened abortion, pelvic inflammatory disease, rupture of corpus luteal cyst, bleeding ovarian cyst, and dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
How will you diagnose an ectopic pregnancy?
- Three important symptoms are:
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- An adnexal mass.
- Hemoglobin <10 g/dL is reported in about 40% of ectopic pregnancy cases.
- Increased total white cells (leucocytosis) may be present in about 50% of cases.
- The pregnancy test has variable sensitivity. Urine and serum pregnancy tests have sensitivities of 500 to 1000 mIU/mL.
- A positive pregnancy test is not diagnostic of ectopic pregnancy. It will indicate only a raised HCG level.
- Advise beta-HCG to confirm the pregnancy.
- β-HCG levels range from undetectable to 200,000 IU/L, depending on the size and viability of the trophoblastic cell mass.
- Follow the normal dynamics of the HCG level. This will be disturbed in the ectopic pregnancy.
- Normally, it increases every 48 to 72 hours until it reaches 10,000 to 20,000 IU/mL.
- It should be further evaluated if an abnormal rise in the β-HCG level is <66% higher than the original values.
- Serial HCG levels are estimated to differentiate ectopic pregnancy from normal.
- If the HCG level does not rise at least 66% in 48 hours, or the HCG level falls in this period.
- If there is a failure to double (increase) the HCG level in 24 hours, at 4 to 8 weeks of gestation, it occurs:
- In 66% of ectopic pregnancies.
- In 85% of the spontaneous abortions.
- In 15% of normal pregnancies.
- But you can see the rising rate of 15% in ectopic pregnancies.
- Ultrasound is the most helpful tool.
- A transvaginal ultrasound is more sensitive.
- Progesterone and HCG both predict abnormal pregnancy rather than advising a single test of HCG.
- Ectopic pregnancy:
- In 97% of cases, Progesterone is <12.6 ng/mL and HCG is <3000 IU/L.
- Normal pregnancy has progesterone >12.6 ng/mL and HCG >3000 IU/L.
- Progesterone level >25 ng/ mL will ensure intrauterine pregnancy without further laboratory tests (nearly 97%).
- A progesterone level <5 ng/mL strongly suggests an abnormal pregnancy.
- Progesterone values are limited because in 85% of pregnancies, they range from 5 to 25 ng/mL.
- Values between 5 and 25 ng/mL are intermediate.
How will you Treat Ectopic Pregnancy?
- The first line of management is surgical laparoscopy.
- Medically gives methotrexate I/M.
How will you do a Follow-up of ectopic pregnancy?
- After removing the ectopic pregnancy, the HCG level remains typically detectable for four weeks.
- Monitor HCG levels to ensure there is no residual trophoblastic tissue.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How will you diagnose ectopic pregnancy?
Question 2: How will you treat the ectopic pregnancy case?

What about syncobal attacks at ectopic pregnancy?
Dear Your question is not clear to me. Please elaborate your question.