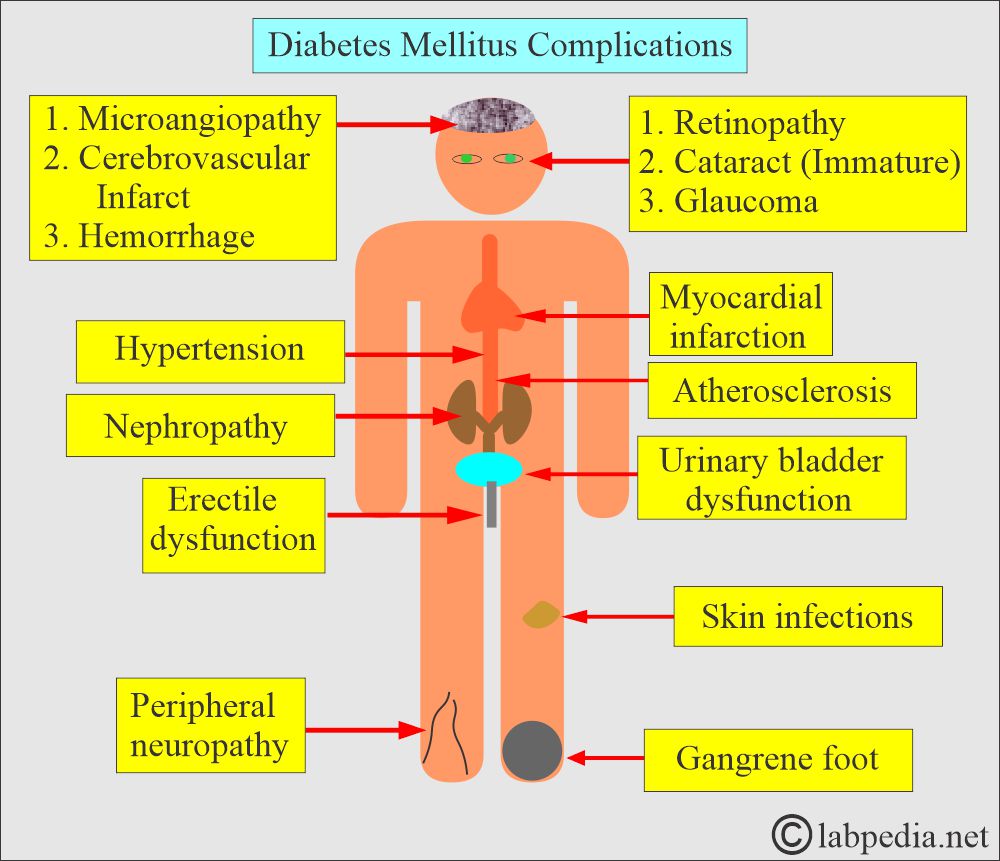
Diabetes Mellitus complications
Diabetes Mellitus Complications
- There are diabetes mellitus complications in patients who do not take care of themselves.
- Patients who do not control their blood glucose levels may have complications.
Diabetes Complications are:
Acute complications:
- Low blood glucose levels that is more common in Type 1 diabetes than type 2.
- These are primarily associated with insulin use.
- It may be seen in the use of sulfonylurea and meglitinide medicines.
- Ketone bodies formation:
- These are also common in type 1 diabetes mellitus than in type 2.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis may be seen in children with type 1 diabetes.
- Ketone bodies may be seen in children with type 1.
- In the case of ketones, patients on oral hypoglycemic agents should be shifted to insulin.
- Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state:
- It is seen when blood glucose rises to a dangerous level.
- This will lead to dehydration and changes in mental functions.
- It may be seen in:
- Infections.
- Medication.
- Substance abuse.
- Undiagnosed diabetes mellitus.
- Treatment:
- This is an emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Chronic complications:
- Hypertension associated with diabetes mellitus:
- More than 1/3 of the youth with type 2 DM had hypertension.
- It usually appears after 4.5 years of the diagnosis of DM.
- There are more chances for diabetic nephropathy.
- Abnormal lipids:
- Children/adolescents with type 2 DM may have decreased HDL (good cholesterol).
- These patients have increased LDL (bad cholesterol).
- Also, there is an increase in triglycerides.
- Advised that yearly screening is needed.
- Microalbuminuria:
- It refers to protein in the urine (proteinuria).
- It is mainly seen after 4.5 years of the diagnosis of DM in 16.6% of the youth.
- Advise screening for microalbuminuria every year.
- Retinopathy:
- Eye screening is needed every year to find retinopathy.
- It is done with dilated eyes.
- This is an early diabetes complication.
- It is found that 13.7% of the youth have type 2 DM and had retinopathy after 4.5 years post-diagnosis.
- Obstructive sleep apnea:
- It is seen in patients who are overweight.
- It is seen with snoring and long breathing pauses when sleeping.
- The patient becomes restless, has a morning headache, and feels sleepy during the day.
- Advise the sleep study.
- Erectile dysfunction:
- When DM is present for a long time, it may lead to erectile dysfunction.
- Microvascular complications:
- Diabetic retinopathy.
- Diabetic nephropathy.
- Diabetic neuropathy.
- Macrovascular complications:
- Stroke.
- Coronary artery disease.
- Peripheral arterial disease, like poor leg circulation, may be a risk of amputation.
- Increased risk of infections:
- Diabetic foot ulcer and infection.
- Delayed wound healing.
- Gum disease.
- Risk for pneumonia.
Prevention and control of the complications:
- Stricket blood glucose control.
- You can check blood glucose by pricking your fingers or using the Libra sensor 3 plus or another CGM system.
- Regular check-up of the eyes, foot examination, and kidneys.
- Avoid smoking.
- Adopt a healthy diet.
- Do regular exercise.
- Do take the medications as prescribed by the doctor.