Critical/Panic Values of Blood, Urine, Hormones and Serology
Critical/Panic Values
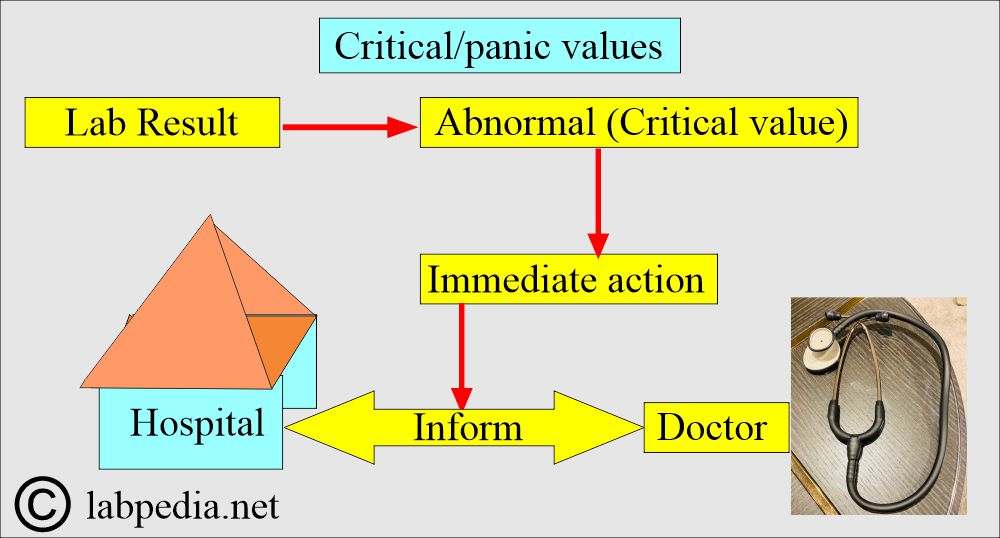
What are the Panic or critical values?
- This is the list of the critical or panic values that need immediate action.
- Critical values may indicate prompt clinical intervention and treatment.
- These critical values are also called action values or automatic call-back values.
- Should inform the hospital or the requesting doctor.
What are common Critical/Panic Values?
| Laboratory test | Normal values | High Critical or panic value | Clinical effect of high-value | Low Critical or panic value | Clinical effects of low value |
| Chemical pathology Critical/panic values |
|||||
| Ammonia | 11 to 36 µmol/L (15 to 50 µg/dL) | >40 µmol/L | Indicate hepatic damage | None | |
| Amylase | 25 to 125 U/L | >200 U/L | Indicate acute pancreatitis | None | |
| Lipase | <160 U/L | >500 U/L | Indicate pancreatitis | ||
| Arterial pCO2 | 35 to 45 mm Hg | >75 mm Hg | <20 mm Hg | ||
| Arteria pO2 (adult) | 80 to 105 mm Hg | None | <40 mm Hg | ||
| Arterial pO2 (newborn) | 60 to 70 mm Hg | >92 mm Hg | <37 mm Hg | ||
| Arterial pH | 7.35 to 7.45 | >7.59 | <7.10 | ||
| Bicarbonate (HCO3) | 22 to 26 meq/L | >40 meq/L | Respiratory issues | <6.0 meq/L | Acidosis |
| Serum chloride (Cl) | 98 to 106 mmol/L | >120 mmol/L |
Dehydration, hyperventilation, Renal tubular acidosis |
<70 mmol/L | Vomiting, Diarrhea, Diabetic acidosis |
| Blood glucose level | 65 to 110 mg/dL | >450 mg/dL | Hyperglycemiamia | <40 mg/dL | Hypoglycemia |
| Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) | 7 to 18 mg/dL | >100 mg/dL | Uremia | 2 mg/dL | |
| Serum Calcium total | 8.6 to 10 mg/L | >13 mg/dL | Cardiotoxicity, arrhythmias, and coma | <6 mg/dL | Tetany |
| Phosphorus | 2.7 to 4.5 mg/dL (0.87 to 1.45 mmol/L) | None | <1.1 mg/dL | ||
| Serum creatinine | 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dL | >10 mg/dL | Renal failure | Decreased | Renal disease, urinary tract obstruction, nephrotoxic drugs |
| Serum Potassium (K) adult | 3.5 to 5.3 meq/L | >7.0meq/L | Arrhythmia | <2.8 meq/L | Arrhythmia |
| Serum potassium (K) newborn | <8.5 meq/L | <2.5 meq/L | |||
| Serum Sodium (Na+) | 135 to 145 meq/L | >155 meq/L | Cardiovascular collapse | <120 meq/L | weakness, neurologic symptoms |
| Magnesium | 1.3 to 2.1 meq/L | > 15 meq/L | Cardiac arrest and respiratory paralysis | <1.0 meq/L | Tetany |
| Uric acid | Male= 3.5 to 7.2 mg/dL Female=2.6 to 6.0 mg/dL | High level | Gout, renal failure | Decreased level | Fanconi syndrome, Wilson’s disease, liver disease |
| CK-MB | <5% of the total or 5 ng/mL | >5% or ≥10 µg/L | Acute myocardial infarction | None | |
| Bilirubin (Total) | 0.2 to 1.0 mg/dL |
|
|
||
| Cholesterol | <200 mg/dL (adults) | >240 mg/dL | |||
| LDL-cholesterol | <100 mg/dL | >160 mg/dL | Atherosclerosis | ||
| HDL-cholesterol | 40 to 60 mg/dL | <40 mg/dL | Heart diseases | ||
| Triglycerides | <150 mg/dL | >500 mg/dL | Heart diseases | ||
| Hormones | |||||
| T4 (in adults) Total | 4.6 to 12 µg/dL | >18.0 µg/dL | |||
| T4 (in newborn) | >18.0 µg/dL | <3.5 µg/dL | |||
| Hematology Critical/panic values | |||||
| Hemoglobin (Hb) |
Male = 10 to 17 g/dL Female = 11.5 to 15.5 g/dL |
>20 g/dL | Polycythemia | <7 g/dL | Anemia |
| Hematocrit (Hct) |
Male = 39% to 49% Female = 33% to 43% |
>60 vol% | <20 vol% | ||
| Platelets count (adult) | 130,000 to 450,000/cmm | >1,000,000/cmm | Thrombocytosis | <50,000/cmm | |
| Platelets count (pediatric) | >100,000/cmm | Thrombocytosis | <20,000/cmm | Thrombocytopenia | |
| White blood cells (WBC) | 3100 to 9000/cmm | >30,000/cmm | Leucocytosis | <2000/cmm | Leucopenia |
| Fibrinogen | 200 to 400 mg/dL | >700 mg/dL | <100 mg/dL | ||
| Prothrombin time (PT) | 11 to 14 seconds | >30 seconds | None | ||
| INR | 1.0 to 1.5 | >4.5 | Bleeding tendency | ||
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) | 25 to 38 seconds | >100 seconds | None | ||
| CD4+ lymphocytes | 500 to 1000 cells/cmm | <500 cells/cmm | |||
Critical/Panic Values
| Urine Critical/panic values | ||
| Parameters | Interpretations | |
| Black or brown urine | Blood | |
| Red urine (negative occult blood) | Porphyria | |
| Blood-positive (negative RBCs) | Myoglobinuria | |
| Glucose | Strongly positive for:
|
|
| Abnormal crystals |
|
|
| Urine culture | Colony count >50,000/mL | |
| Serology Critical/panic values | ||
| high-sensitivity CRP | >3.5 mg/L | Acute inflammation = >10 mg/L |
| Coomb’s test | Positive direct and indirect | |
| Serum test | Positive for:
|
|
| Blood crossmatch | Positive | |
| Rh-positive baby in Negative mother | Immediate report for Rh-Gham (Rh-IgG) | |
| Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Critical/panic values | ||
| Parameters | Low value | High value |
| Glucose | <80% of the blood value | |
| Protein | None | >45 mg/dL |
| White blood cells | None | >10/cmm |
| Special stain for bacteria | positive | Positive |
| Malignant cells | Positive | Positive |
| Microbiology (Bacteriology) Critical/panic values | ||
| Parameters | Result | |
| Gram stain | If positive on any body fluids | |
| Blood cultures | Positive | |
| AFB stain | Positive from any site | |
| Antigen detection | Positive | |
| India ink preparation from CSF | Positive | |
| Bone marrow smear | positive for:
|
|
| Surgical biopsy material | Positive for pathogenic bacteria | |
| Respiratory culture | Positive for pathogenic bacteria | |
| Antigen detection | Positive for:
|
|
| Bronchial washings |
|
|
| Stool culture | Positive for:
|
|
| Amniotic fluid critical/panic values | ||
| Parameters | Result | |
|
This may be:
|
|
| Bilirubin level | It is due to hemolytic disease of the newborn | |
| Lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio | <2.0 | |
| Chromosomal abnormalities |
|
|
| Metabolic disorders |
|
|
Note: You may find some differences in the normal values in different books and references.

Save to my account
You can subscribe to labpedia.net.
Thanks a lot, I appreciate so
Thanks.
Useful values. Please review pediatric thrombocytosis value.
Critical values for pediatric group are the same as adult values.