Coombs’ Test:- Part 2 – Coombs’ Indirect test, Anti-globulin indirect test
Coombs’ Indirect test
What sample is needed for Coombs’ Indirect test?
- This is done on the mother’s serum.
What are the indications for the Coombs’ Indirect test?
- To diagnose the presence of antibodies in the pregnant mother’s serum.
- Detection of certain weak antigens in RBCs, like Du.
- To find weak antibodies or incomplete types of antibodies, like those found in Duffy or Kidd blood groups.
- Detection of incomplete antibodies in serum before pretransfusion screening or titration of the antibody (Cross-matching for blood transfusion).
- Detection of cold agglutinins autoantibodies.
- To diagnose autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
- To find the red cell sensitization by drugs.
- RBCs phenotyping in genetic and forensic medicine.
- To identify the syngeneic twins for bone marrow transplantation.
What are the precautions for the Coombs’ Indirect test?
- This should be done on fresh serum.
- Some of the drugs that give false-positive results are cephalosporin, antiarrhythmic, insulin, methyldopa, Dilantin, sulphonamides, and tetracycline.
- The false-positive or negative results are seen due to the following conditions:
- Clerical mistakes.
- Technical errors like not washing RBCs and failure to add reagents.
- Contamination by 5% or 10% glucose in water, but not glucose in saline, from intravenous tubing.
- Poor quality of commercial Coombs’ reagents.
What is the definition of Coombs’ Indirect test?
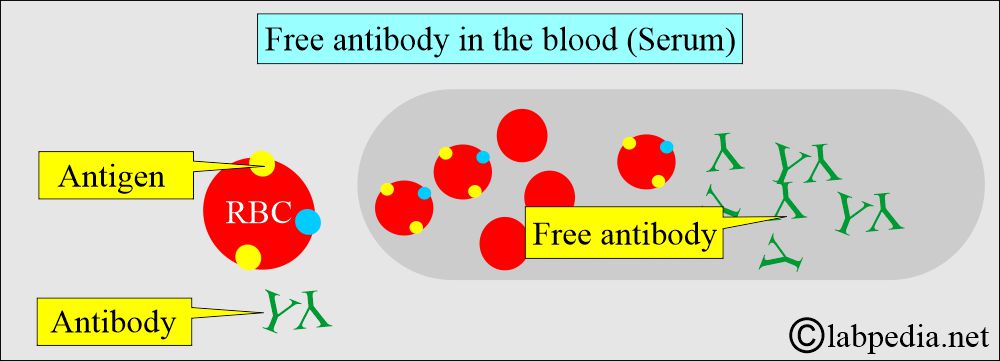
- Coombs’ Indirect test will detect free antibodies in the serum.
What is the pathophysiology of the Coombs’ Indirect test?
- The indirect Coombs’ test detects circulating antibodies in the serum, which are the free antibodies.
- The major purpose of this test is to detect if the recipient or the patient has serum antibodies other than the ABO / Rh system to RBC before receiving the blood transfusion.
- This is a test used for screening purposes in routine blood transfusions.
- This test can also diagnose other agglutinins, such as cold agglutinins, which are typically associated with Mycoplasma infections.
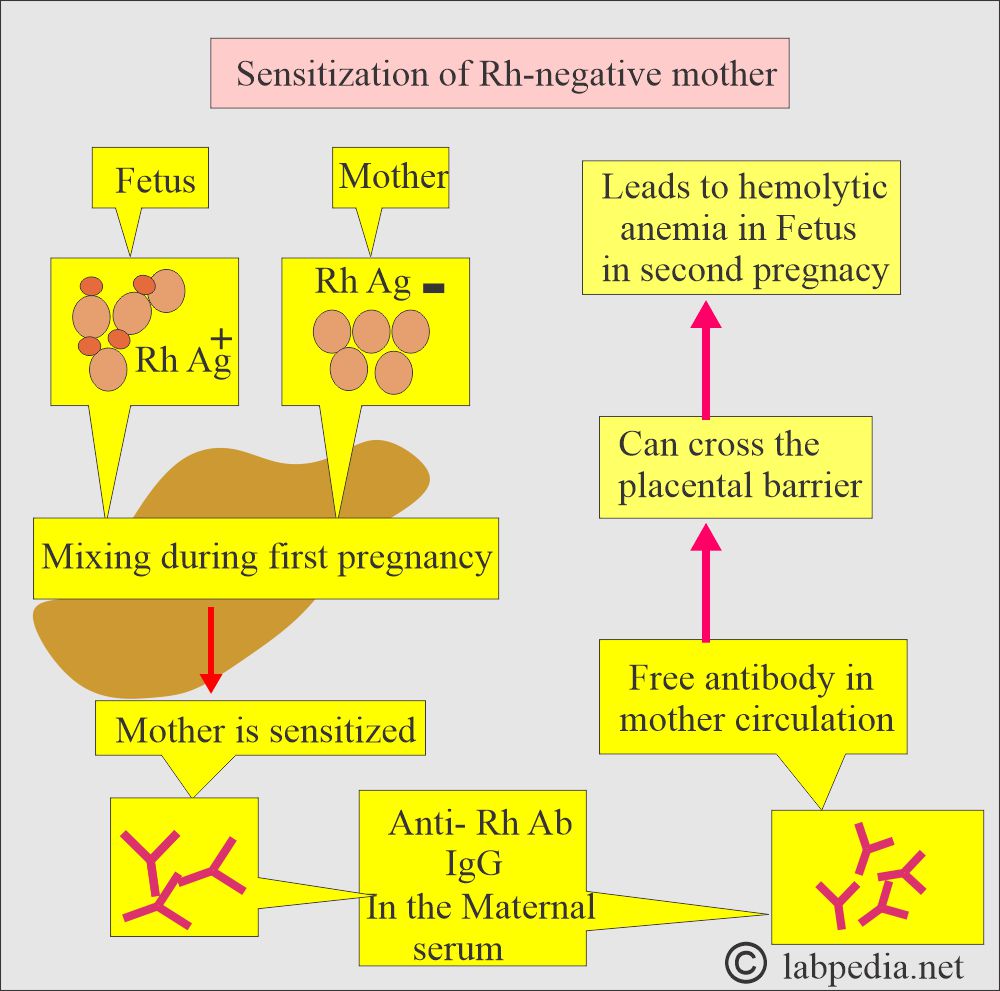
- Circulating antibodies against RBC may be seen in the Rh-negative mother who is carrying an Rh-positive fetus.
- There is a mixing of the feto-maternal blood during the first delivery.
- When fetal blood enters the mother’s circulation, Rh-positive fetal blood will sensitize the mother, and IgG-type antibodies are formed.
- These antibodies can cross the placental barrier and enter fetal circulation.
- In the second pregnancy, a Type II cytotoxic reaction will destroy the fetal RBCs and lead to hemolytic anemia.
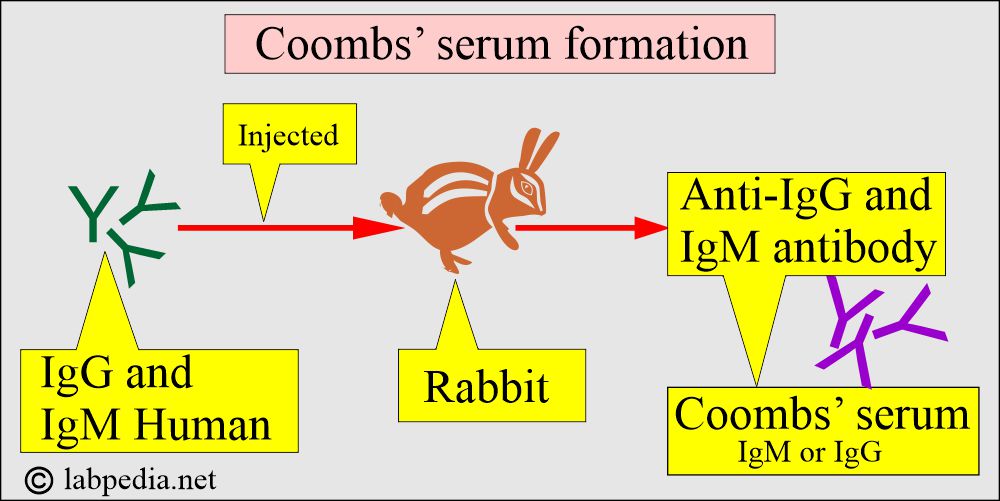
What is Coombs’ serum?
- It is prepared by injecting IgG immunoglobulin (an antibody) into a rabbit, and then from its serum, the anti-IgG antibody is separated, which is called Coombs’ serum.
What is the principle of the Coombs’ indirect test?
- It detects free antibodies (free antibodies) in the blood (serum).
What is the procedure of Coombs’ indirect test?
- This test is done in the serum.
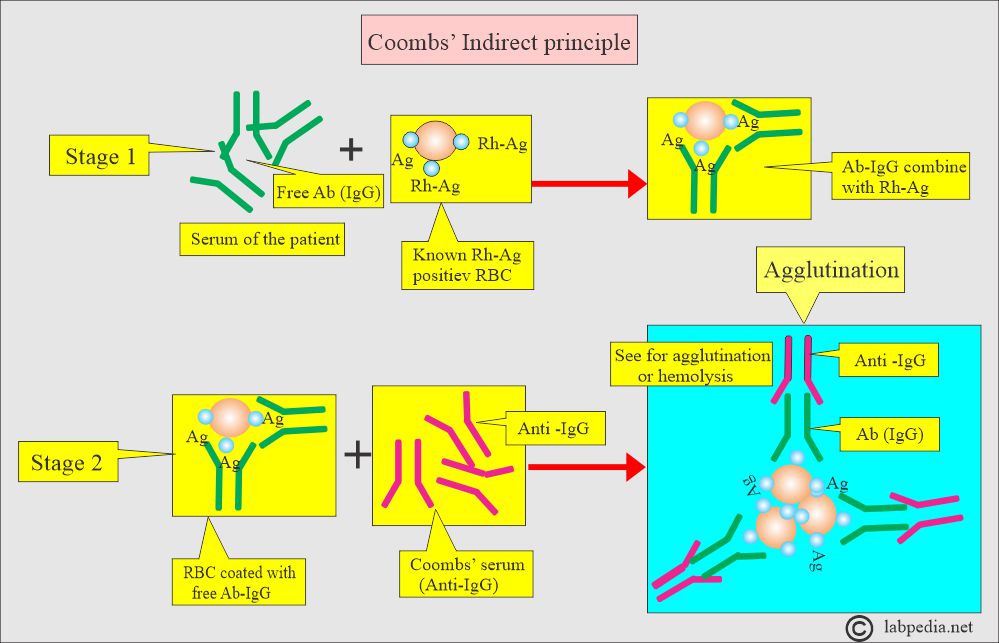
- Add recipient serum (patients) to known blood O cells (donors’ RBCs or screening cells) in a test tube.
- Mix well and incubate for 15 to 30 minutes at 37 °C.
- Centrifuge for 15 seconds at 3400 rpm.
- Observe for agglutination or hemolysis.
- Wash the RBC three or four times with saline.
- Add a large amount of saline and decant completely.
- Now add Coombs’ serum and again centrifuge.
- Mix well.
- Centrifuge at 3400 rpm for 15 seconds.
- See for agglutination.
- If the test is positive, then you will see clumping or agglutination.
- In the event of negative results, examine the sample microscopically.
How will you report Coomb’s indirect test?
| Grade of the reaction | Degree of agglutination |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the normal value of Coombs’ indirect test?
- Negative, and there is no agglutination.
What are the causes of a positive Coombs’ indirect test?
- Incompatible blood transfusion.
- Mother has anti-Rh antibodies.
- Erythroblastosis fetalis.
- Acquired hemolytic anemia.
- Due to drugs and cold antibodies.
What is the difference between the direct and indirect Coombs’ test?
| Lab parameter | Coombs’ direct test | Coombs’ indirect test |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of the Coombs’ test in pregnant mothers?
- A positive indirect Coombs’ test indicates sensitization of the mother by a previous Rh-positive fetus.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is a type of antibody in the Coombs' indirect test?
Question 2: How is Coombs' serum made?


I would like to asked what are the possible causes of false positive and false negative of Indirect Coomb’s Test?