Coagulation:- part 2 – Coagulation Screening Tests and Interpretations
Coagulation Screening
Sample for Coagulation Screening tests
- If plasma is needed, take 5 ml of venous blood and add sodium citrate as the anticoagulant.
- Perform the assay immediately or as soon as possible.
- For factors II, V, VII, and X, place the citrated plasma on ice immediately, and the sample is stable for 2 hours.
- Freeze if it is delayed >2 hours.
Indications for coagulation screening tests:
- Coagulation screening is done to find the cause of excessive bleeding.
- Investigation of the possible cause of the bleeding disorder.
Definition of bleeding disorders:
- Before we start workup of bleeding disorders, we should understand two systems of bleeding.
- Bleeding disorders may be of two types:
- Primary hemostasis, related to:
- Platelets.
- Vascular defects.
- Secondary hemostasis related to:
- Coagulation factors defects.
- Primary hemostasis, related to:
Table to differentiate hemostasis:
| Clinical feature | Primary Hemostasis | Secondary Hemostasis |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Coagulation Screening tests (profile) consist of the following:
1. Platelets.
2. Bleeding time.
3. Clotting time.
4. APTT.
5. PTT.
6. PT.
7. Clotting factor assay.
Platelet abnormality is seen in the following:
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenia.
- Low due to drugs.
- Hypersplenism.
- SLE.
- (See more in Platelets)
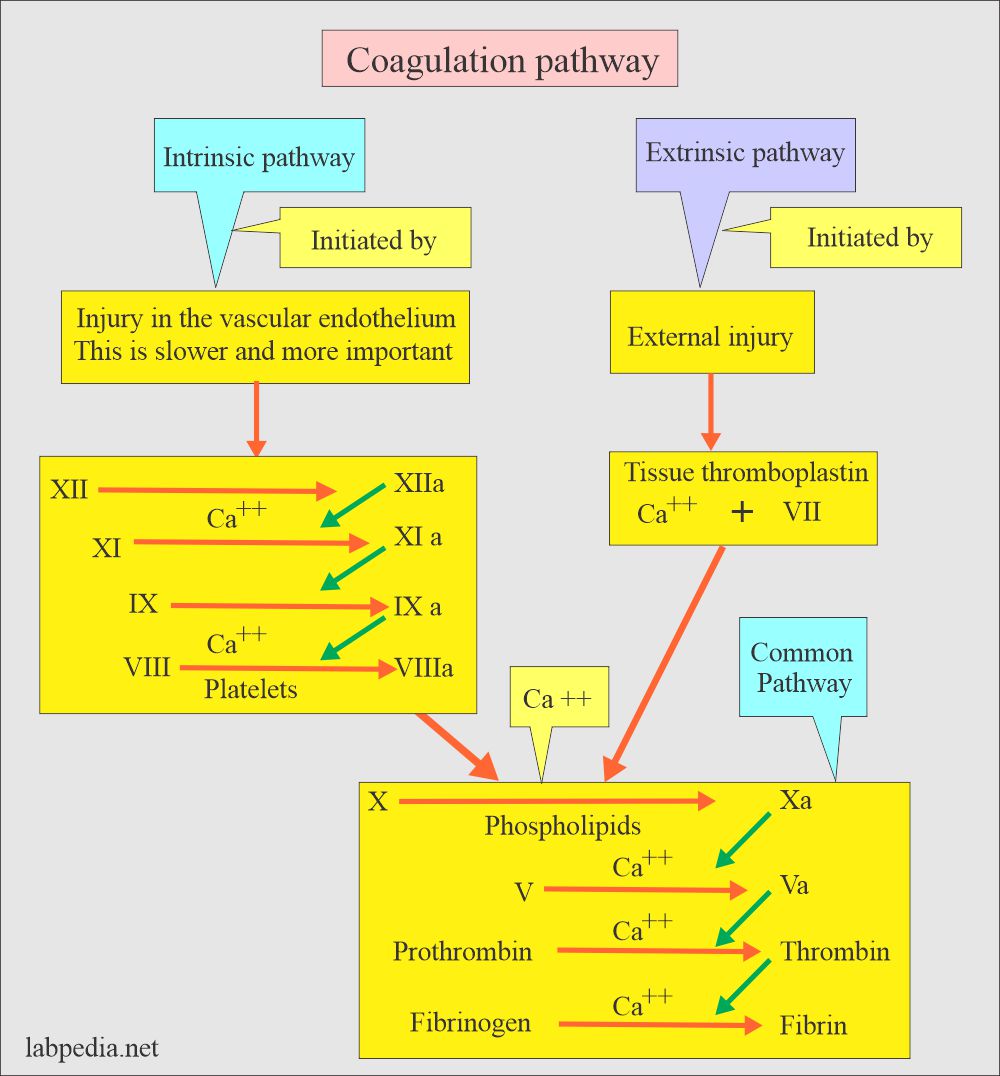
Abnormal PTT alone is seen in:
- Bleeding due to a defect in factors VIII, IX, and XI (8, 9, 11).
Abnormal PT alone is seen in:
- Bleeding due to a defect in Factor VIII (8).
Abnormal PTT + PT is seen in:
- Anticoagulant therapy.
- DIC.
- Vit. K deficiency.
- Liver diseases.
- Rarely dysfibrinogenemia.
- Rarely due to factor X, V, and II defects.
Interpretations of the blood coagulation screening profiles:
| Coagulation tests | Result of coagulation tests | Causes of possible diseases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coagulation screening for bleeding disorders:
| Coagulation screening test | Cause of the disease | Possible mechanism |
|
|
Deficiency or inhibitors of:
|
|
|
Deficiency or abnormality of:
|
|
|
Deficiency or inhibitors:
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of abnormal PT, APTT, and TT?
Question 2: What does abnormal APTT and normal PT indicates?