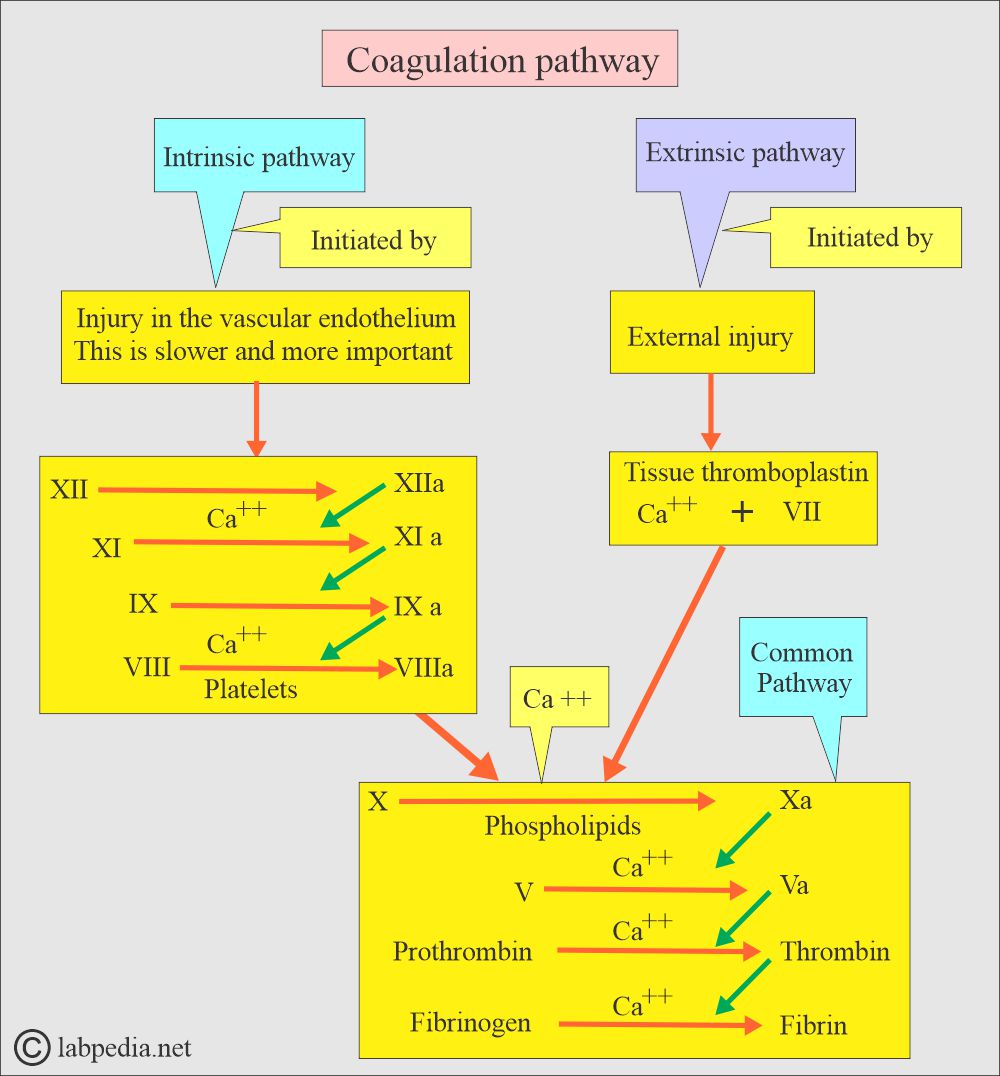
Coagulation:- part 2 – Summary of Coagulation Screening Tests
Summary of Coagulation Screening Tests
What sample is needed for Coagulation Screening tests?
- If plasma is needed, take 5 ml of venous blood and add sodium citrate as the anticoagulant.
- Perform the assay immediately or as soon as possible.
- For factors II, V, VII, and X, place the citrated plasma on ice immediately, and the sample is stable for 2 hours.
- Freeze if it is delayed >2 hours.
What are the indications for coagulation screening tests?
- Coagulation screening is done to find the cause of excessive bleeding.
- Investigation of the possible cause of the bleeding disorder.
How will you define bleeding disorders?
- Before we begin the workup of bleeding disorders, it is essential to understand two systems related to bleeding.
- Bleeding disorders may be of two types:
- Primary hemostasis, related to:
- Platelets.
- Vascular defects.
- Secondary hemostasis related to:
- Coagulation factor defects.
- Primary hemostasis, related to:
How will you differentiate primary and secondary hemostasis?
| Clinical feature | Primary Hemostasis | Secondary Hemostasis |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the Coagulation Screening tests (profile)?
1. Platelets.
2. Bleeding time.
3. Clotting time.
4. APTT.
5. PTT.
6. PT.
7. Clotting factor assay.
What are the causes of Platelet abnormality?
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenia (ITP).
- Low platelets due to:
- Drugs like chemotherapy and radiation.
- Aplastic anemia.
- Metastatic cancers.
- Viral infections.
- Certain antibiotics.
- Autoimmune diseases like SLE.
- Hypersplenism.
- Hypersplenism is due to the pooling of platelets in the spleen.
What are the conditions where you will see abnormal PTT alone?
- Bleeding due to a defect in factors VIII, IX, and XI (8, 9, 11).
What are the conditions under which you will see abnormal PT alone?
- Bleeding due to a defect in Factor VIII (8).
What are the conditions where you will see abnormal PTT + PT?
- Anticoagulant therapy.
- DIC.
- Vit. K deficiency.
- Liver diseases.
- Rarely dysfibrinogenemia.
- Rarely due to factor X, V, and II defects.
What are the conditions where you will see abnormal APTT?
- This may be due to a deficiency of abnormal coagulation factors.
- This deficiency may be in the intrinsic, extrinsic, or common pathways.
- This may be due to inhibitors.
- In case of anticoagulation therapy, such as heparin.
What are the causes of abnormal blood coagulation screening profiles?
| Coagulation tests | Result of coagulation tests | Causes of possible diseases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of Coagulation screening for bleeding disorders?
| Abnormal coagulation screening test | Cause of the disease | Possible mechanism |
|
|
Deficiency or inhibitors of:
|
|
|
Deficiency or abnormality of:
|
|
|
Deficiency or inhibitors:
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of abnormal PT, APTT, and TT?
Question 2: What does abnormal APTT and normal PT indicate?