Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis:- Part 5 – Abnormal Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
What sample is needed for cerebrospinal fluid analysis?
- Cerebrospinal fluid is needed for the analysis.
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows characteristic findings in various diseases.
What are the causes of the appearance of Abnormal Cerebrospinal fluid?
- Normal, clear, and colorless.
- Cloudy CSF is due to:
- Infection when WBCs are >200 /cmm.
- Hemorrhage when RBCs are >400 /cmm
- Traumatic tap.
- In the case of high proteins in the CSF.
- Oily CSF is due to the following:
- When there are radiographic contrast media in CSF.
- Yellow CSF is due to:
- It is due to the elevated level of bilirubin in jaundice.
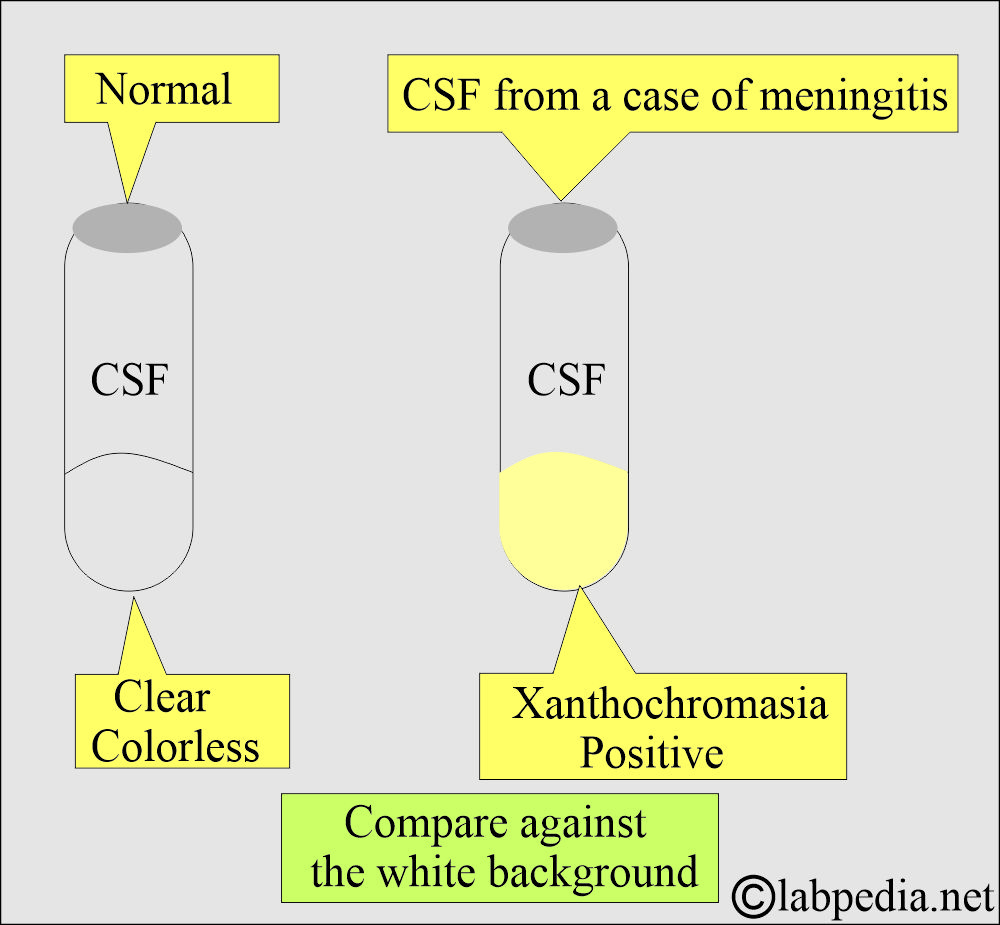
- Xanthochromic of CSF:
- The color of the centrifuged supernatant CSF is due to elevated proteins.
- Bloody CSF is due to:
- When the RBC count is >600 /cmm, and is due to hemorrhage or traumatic tap.
- The brown color of CSF is due to:
- There is the presence of methemoglobin.
- The pink color of CSF is due to:
- There is the presence of oxyhemoglobin.
- The Orange color of CSF is due to:
- This is due to the presence of carotene.
- Clotted CSF is due to:
- This is due to the increased fibrinogen, which is typically seen in a traumatic tap. It will be absent in the subarachnoid hemorrhage.
What are the causes of abnormal cell count in Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Normal values:
- RBCs in adult = 0
- RBCs in the neonates = variable
- WBCs in adults = < 5 /cmm.
- WBCs in neonates = 0 to 30 /cmm.
- When WBC >1000 /cmm:
- It is due to bacterial or fungal infections.
- When WBCs in neonates are >100 /cmm:
- It is due to viral meningitis.
- When RBCs >400 /cmm:
- It is due to hemorrhage or traumatic tap.
What are the causes of different cells in the Cerebrospinal fluid?
Adult Normal cells
- Lymphocytes = 40% to 80%
- Monocytes = 15% to 45%
- Neutrophils = 0% to 6%
Newborn Normal cells
- Lymphocytes = 5% to 35%
- Monocytes = 50% to 90%
- Neutrophils = 0% to 8%
What are the causes of increased neutrophils in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Bacterial meningitis.
- The Early stage of tuberculosis.
- Cerebral abscess.
- Tumors.
What are the causes of increased Lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Viral meningitis.
- Tuberculous meningitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome.
- Chronic alcoholism.
- Drug abuse.
- Lymphoma.
- Leukemia.
What are the causes of increased Monocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Partial treatment of meningitis.
- Tumors.
- Chronic bacterial meningitis.
What are the causes of increased Eosinophils in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Parasitic infestation.
- Fungal meningitis.
- Medications.
- Injection of dyes.
- Allergic reaction to the shunt.
What are the causes of increased Macrophagic cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Fungal meningitis.
- Tuberculous meningitis.
- Blood contamination.
- After hemorrhage.
What are the causes of tumor cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- It is due to infiltration by metastatic carcinoma.
What are the causes of increased proteins in the Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Normal CSF protein = level is 15 to 45 mg/dL
- Bacterial meningitis.
- Viral meningitis.
- Increased synthesis of immunoglobulins.
- Trauma.
- Cerebral hemorrhage.
- Contamination by peripheral blood.
- Due to any obstruction.
What are the causes of decreased protein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
- Loss of fluid due to trauma.
- Increased reabsorption with increased intracranial pressure.
What are the causes of increased Glucose levels in the CSF?
- The normal = 50 to 80 mg/dL.
- In diabetic patients with hyperglycemia.
- Traumatic puncture.
- Contamination with peripheral blood.
What are the causes of decreased levels of glucose in the CSF?
- In diabetic patients with hypoglycemia.
- Meningitis.
- Tumors.
- In the inflammatory process.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: When tumor cells are seen in CSF?
Question 2: What is the reason for the xanthochromasia?

What about a decrease in monocytes? What could that mean. I have a 90 for lymphocytes and 10 for monocytes. Total WBCs, CSF is 10.
Thank you,
This report you told is about CSF? If it is CSF, then the count is in the normal range; no need to worry about lymphocytes. Please also give H/o patient.