Brucellosis, Diagnosis of Brucella Infection
Diagnosis of Brucella Infection
What sample is needed for brucellosis?
- It is performed on the patient’s serum.
- The serum is taken in the first week of illness and later in the 3 to 4 weeks.
- Brucella can be cultured from the blood, sputum, bone marrow, CSF, tissue, lymph node, and urine.
What are the indications for brucellosis?
- The patient has a fever of unknown origin.
- The patient has a suspected history of contact with cattle.
- The patient exhibits signs and symptoms consistent with a Brucella infection.
How will you define Brucellosis?
- It is a chronic granulomatous intracellular infection caused by small, gram-negative, aerobic coccobacilli.
- Three members of the genus Brucella produce an uncommon febrile disease known as Brucellosis (Undulant fever).
- It is a chronic granulomatous intracellular infection due to small gram-negative aerobic coccobacilli seen in:
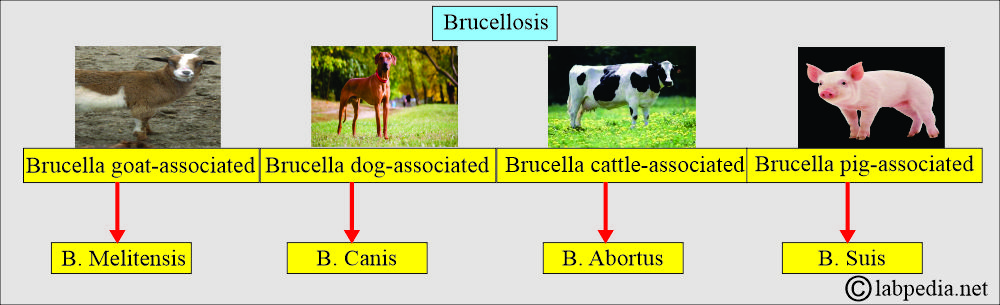
- Brucella melitensis = By goats and sheep.
- Brucella suis = By swine.
- Brucella abortus = By cattle.
- Brucella canis = By dogs.
- It spreads through infected animals or by eating contaminated animal products.
- Brucellosis (Undulant fever) is found as follows:
- Brucella suis is pig-associated.
- Brucella melitensis is goat-associated.
- Brucella Canis is dog-associated.
- Brucella abortus is cattle-associated.
How will you discuss the microbiology of Brucellosis?
- The Brucella abortus, B. Suis, B. Melitensis, or B. Canis causes brucellosis.
- Brucella is a slow-growing aerobic gram-negative coccobacillus.
- Short, slender, pleomorphic, gram-negative bacilli (coccobacillus).
- Brucella is an oxidase-positive urease variable.
- Brucella is nonmotile.
- These are non-sporing.
- Culture media:
- Enriched medium such as glucose serum, liver infusion broth, or agar.
- Small transparent colonies develop after several days of incubation at 37 °C in aerobic conditions.
- CO2 is needed for the growth of B. abortus.
- There is growth in selective buffered charcoal yeast extract and Thayer-Martin medium.
- Brucella canis is very rare and is typically contracted through exposure to dogs.
What are the characteristic features of the Brucella organism?
| Characteristic features | B. abortus | B. melitensis | B. suis | B. canis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Growth in: | ||||
| Basic fuchsin |
|
|
|
Positive |
| Thionine |
|
|
|
Positive |
| Methyl violet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
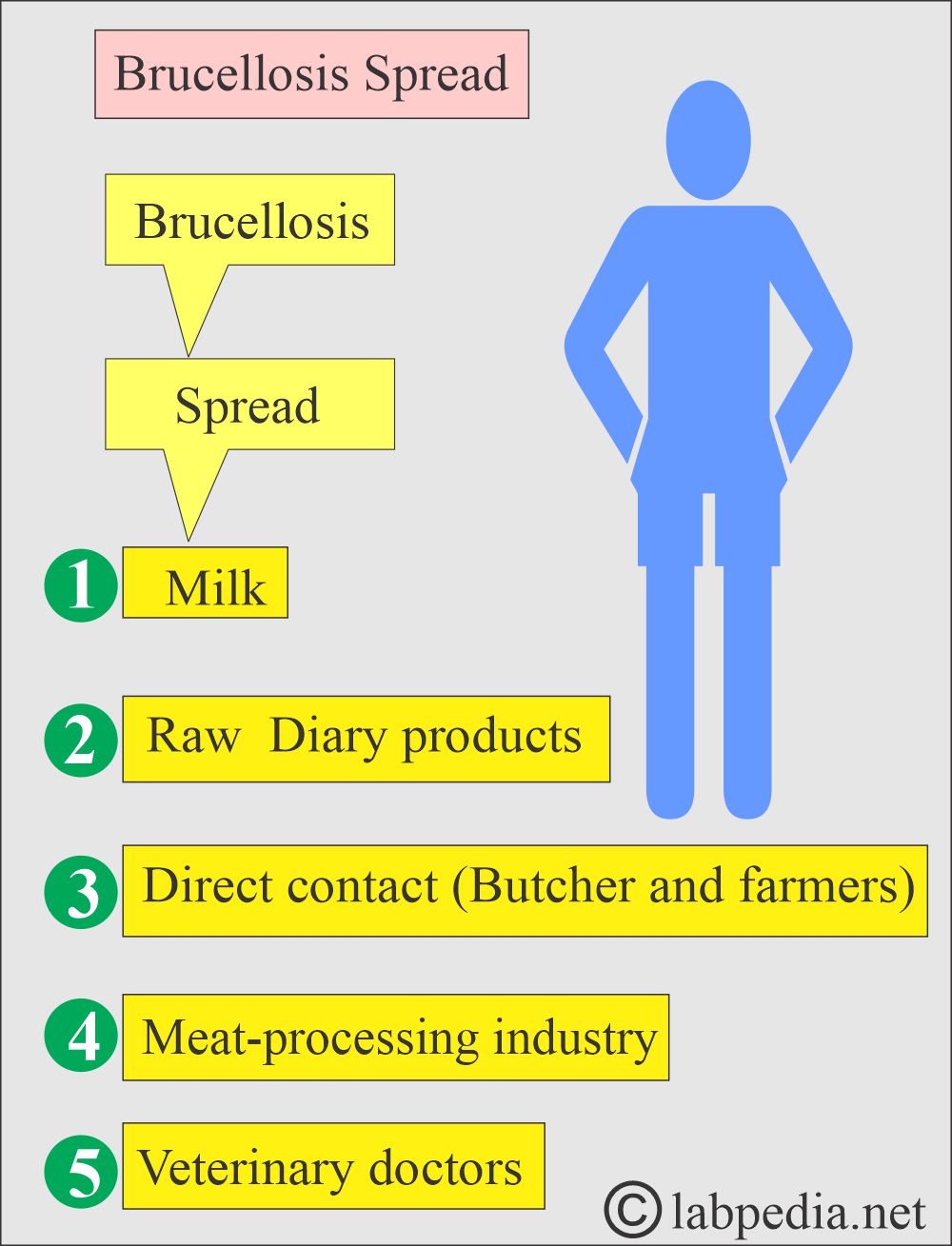
What is the mode of spread of Brucellosis?
- It is by ingesting contaminated milk and milk products, especially goat milk.
- Their milk is also contaminated when sheep, goats, cows, or camels are infected with these bacteria.
- These names are based on infected animals.
- Brucella is primarily transmitted through unpasteurized milk or raw dairy products.
- Direct puncture of the skin of butchers and farmers. These bacteria can enter through the skin and mucous membranes.
- Brucella can penetrate the skin, conjunctiva, lungs, and GI Tract.
- Brucella can spread through inhalation.
- Brucella also spreads among meat industry workers, especially with swine (pigs).
- Veterinarians and dairy farmers are also at risk.
- Penetration is followed by the lymphatics spread.
- There is facultative intracellular growth in the macrophages.
- It also involves the organs.
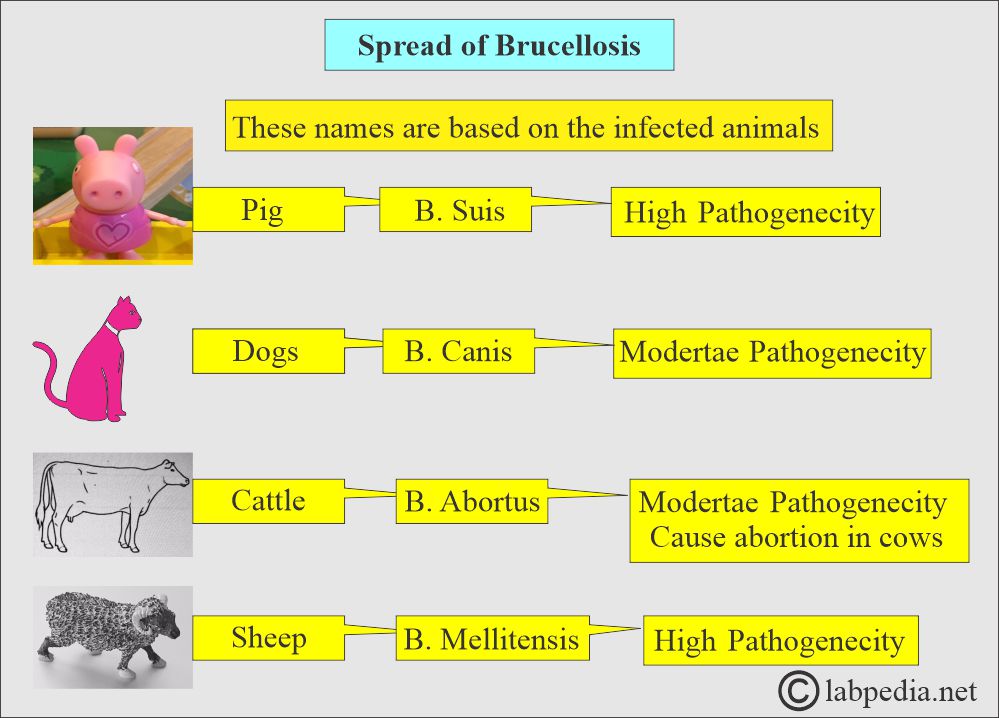
What are the types of Brucella?
- There are the following types of Brucella:
- Brucella abortus is sourced from cattle and exhibits moderate pathogenicity.
- Brucella melitensis is sourced from sheep, and these are highly pathogenic.
- Brucella Canis is sourced from dogs and has moderate pathogenicity.
- Brucella suis is a source in pigs, and these are highly pathogenic.
What is the antigenic structure of Brucella?
- These Brucella antigens are classified into :
- Surface antigens.
- Cytoplasmic antigens.
- Virulence-associated structures.
- Three species share two antigens, A and M, which are O-polysaccharide antigens present on the smooth polysaccharides (L-LPS) of Brucella.
- B. melitensis contains an excess of M antigen.
- B. abortus and suis contain an excess of A antigen.
- Monospecific antisera can be prepared and used for identification.
What are the clinical Signs and Symptoms of Brucellosis?
- This may be the acute or insidious onset of the symptoms.
- The acute or insidious onset of signs and symptoms characterizes this multisystem disease.
- There may be fever, chills, and night sweats.
- The fever peaks in the evening and slowly returns to normal by morning.
- Undulant fever (wavy pattern of the fever) is characterized by a slow rise in temperature during the day, declining at night.
- There is undue fatigue.
- There is anorexia and weight loss.
- There may be a headache and arthralgia.
- 25% of the patients develop single-joint arthralgia.
- There may be pain in muscles, joints, or the back. Myalgia may be the first symptom.
- Sometimes there is lymphadenopathy. But most lymph nodes are not enlarged.
- Approximately 20% of patients may exhibit splenomegaly.
- Some patients may develop pneumonia.
- If not treated, then these patients may have:
- Arthritis.
- Recurrent fever.
- Swelling of the scrotal area and testes.
- Depression.
- Chronic fatigue.
- May develop endocarditis.
- Splenomegaly and hepatomegaly are common findings.
- Spondylitis is also common.
- These symptoms may last months to years, but the outcome is not fatal.
- Laboratory findings due to involvement of various organs:
- Liver >50% have increased LDH, SGOT, and SGPT>
- CNS has been involved <7% of the cases.
- The principal cause of death is due to endocarditis and involvement of the aortic valve.
What are the complications of brucellosis?
- The patient may develop endocarditis.
- There may be arthritis and osteomyelitis.
- The infection of the testes gives rise to epididymal orchitis.
- CNS involvement may lead to meningitis or encephalitis.
- Inflammation of the liver and spleen leads to splenomegaly and hepatomegaly.
- Relapses occur within the first year in about 10% of the cases.
How will you prevent Brucellosis?
- Please avoid the following:
- Use of unpasteurized milk and dairy products (cheese, ice cream).
- When handling animals, use preventive measures such as gloves.
How will you diagnose Brucella Infection?
- WBC count is usually normal or decreased. There may be decreased WBC with relative lymphocytosis.
- There is mild anemia. There may be anemia in <75% of the cases with the localized type of disease.
- There is relative lymphocytosis.
- ESR may be increased in <25% of the cases.
- There is thrombocytopenia in <20% of the cases.
- Liver function tests are abnormal.
- B. melitensis infection is more severe, giving higher AST, ALT, and LDH, and may give rise to thrombocytopenia.
- By serological test detecting the Brucella antibodies.
- A skin test with brucellergin is available, but a positive result only indicates exposure to the organism and does not prove active disease.
- Culture for Brucellosis:
- Multiple blood cultures are necessary when a high agglutination titer is present.
- Blood culture. This is positive in 30% to 40% of the cases.
- Blood culture for B. abortus needs 10% CO2.
- Blood culture must be kept for at least four weeks.
- About 70% are positive.
- Bone marrow:
- Bone marrow culture may be positive when blood culture and serologic tests are negative.
- Bone marrow culture has more positivity.
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination.
- Sputum.
- Food specimen.
- Biopsy and culture of affected tissue and organs.
- On biopsy, one may see a nonspecific granuloma, suggesting the diagnosis of Brucellosis.
- By immunofluorescent demonstration of the organism in the clinical specimens.
- Serology values:
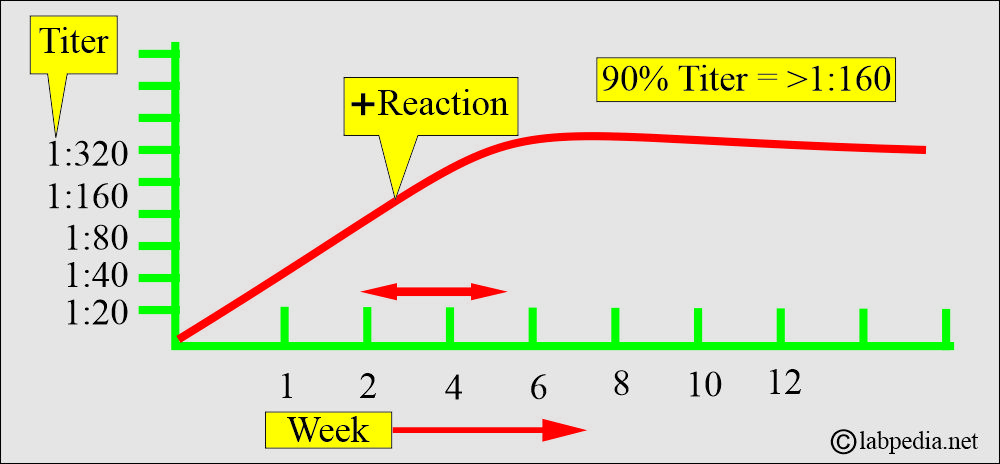
- Test results greater than 1:80 are suspicious for brucellosis. The serologic tests become positive during the second to the third week of illness.
- 90% of the patients have a titer of ≥1:160.
- The rising titer is diagnostic.
- False-negative results are rare.
- In chronic localized brucellosis, the titer may be negative or ≤1:200.
- These tests remain positive for a long time after the infection is cured.
- EIA is the method of choice to detect specific IgM and IgG antibodies.
- A failure to decline the titer indicates an incomplete response to treatment.
- With a high titer, multiple blood cultures are positive.
What are the normal serological values for Brucellosis?
- Source 1
- This test detects the presence of antibodies against the Brucella antigen.
- Borderline cases 1: 160. Ninety percent of patients have this titer. The agglutination reaction becomes positive during the second to third weeks of illness.
- Significant level = >1:160
- Highly suggestive of active infection = > 1: 320.
- The rising titer is of diagnostic significance.
- In chronic localized brucellosis, the titer may be negative or <1:200.
- False-negative results are rare.
- False-positive serological tests are seen with tularemia, cholera vaccination, or after the Brucellin skin test.
- Source 2
- A rising titer ≥ 1:160 suggests infection, either past or present.
- A single titer of 1:160 or 1:320 may be suggestive of Brucellosis, if there are clinical S/S of brucellosis.
- It can prevent the prozone phenomenon by diluting the serum ≥1: 1280.
- Antibody levels decrease within 3 months or with the use of antibiotics, but persist at low levels for years, especially in chronic infections.
- The antibody titer may persist for 1 to 2 years after recovery.
How will you perform a Skin test for the diagnosis of Brucellosis?
- Brucellergen (these are killed bacteria) is injected into the skin.
- After 24 to 48 hours, it shows a reaction greater than 5 mm.
- A definitive diagnosis requires the isolation of the organism through blood culture or a tissue sample.
- Real-time PCR is more specific.
How will you treat brucellosis?
- These bacteria are sensitive to a combination of tetracycline and streptomycin. This combination is the choice of treatment.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significant level of brucellosis?
Question 2: What are the sites for the culture of brucellosis?


Excellent
Thanks.
Assalamualaikum sir
My brucella test shows antibodies >1:80
Sir what is your advise
Please repeat the brucella antigen titer after ten days; if the titer is the same, then no need to worry. If it is 1:320, then it is brucellosis.