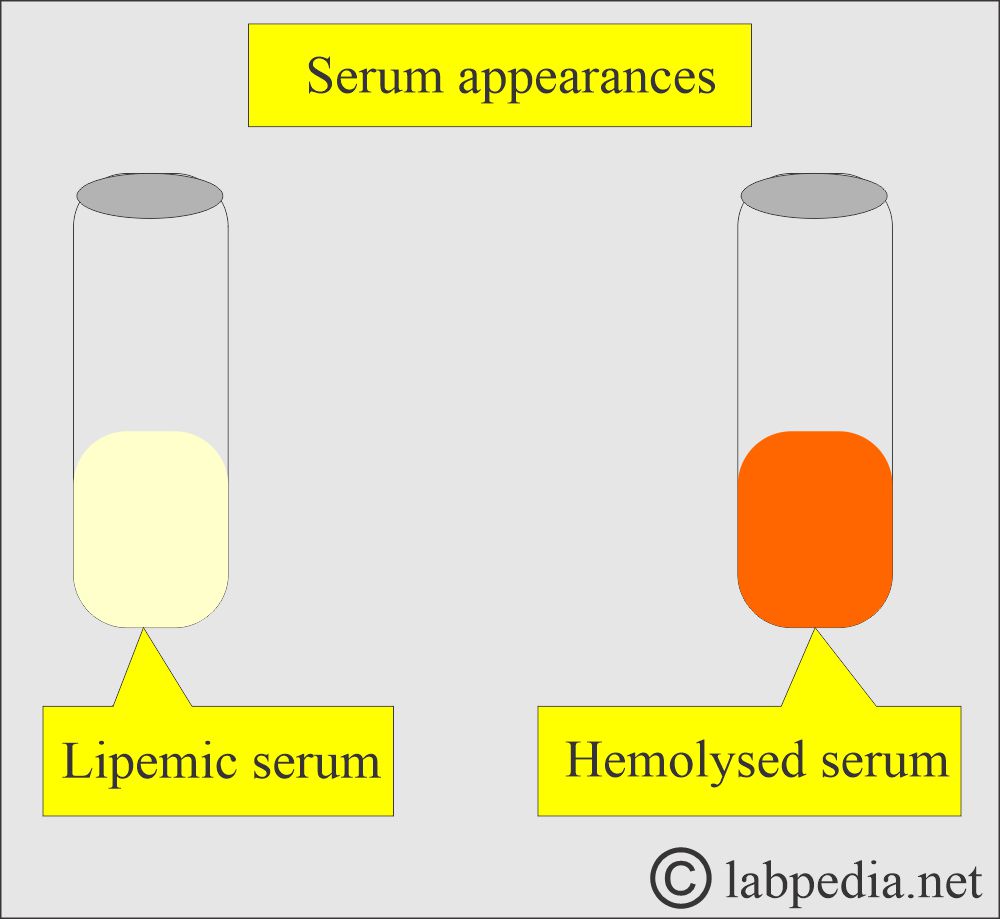
Blood samples That should be Discarded (Rejected)
Blood samples that should be discarded (Rejected)
- Whenever you encounter the following possibilities, reject the sample and attempt to obtain a fresh one.
What Blood samples should be discarded?
Hemolyzed sample:
- Serum shows evidence of hemolysis when the hemoglobin level is greater than 20 G/dL.
- Slight hemolysis does not affect most of the test values.
- Severe hemolysis causes a dilutional effect on these constituents, resulting in a lower concentration in the RBCs compared to the plasma.
- There will be a marked effect of those parameters present in high RBC concentrations compared to those in the plasma.
- Hemolysis will increase the value of:
- Aldolase.
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
- Total acid phosphatase.
- Magnesium.
- Potassium.
- Phosphate.
How will you confirm the evidence of hemolysis?
- Serum haptoglobin is <6 mg/dL.
- Increased serum potassium (K+).
- Increased acid phosphatase and prostatic acid phosphatase.
- Increased cholesterol
How to prevent hemolysis?
- Ensure that the syringe and needles are dry.
- Plastic disposable syringes are preferred.
- Avoid rough handling of the blood. Handle the blood sample carefully and gently.
- Remove the needle and then eject the blood into the tube. Blood through the needle will lead to hemolysis.
- Mix the anticoagulant gently and avoid rough handling.
- Gently transfer the blood and avoid frothing of the blood sample.
- Before taking blood, ensure the skin is dry and clean.
- If you apply sterile petroleum on the heel, it will prevent the spread of blood.
- Collection of the heel prick blood, when collected in a heparinized plastic tube or a siliconized glass tube, will prevent hemolysis.
- In the event of a delay (1 to 3 hours), store the blood in the refrigerator at 4 °C to 10 °C.
- If there is the possibility of cold agglutinins, store the blood at 37 °C in a water bath.
- Avoid freezing blood because, upon thawing, RBCs can lead to hemolysis.
- Hypotonic solutions can cause hemolysis of the blood, so try to prepare an isotonic solution.
Lipemic serum:
- Serums with lipemic appearance will affect chemistry tests like:
- Phosphorus.
- Creatinine.
- Total protein.
- Calcium.
- ALT (Alanine aminotransferase).
- Ultracentrifugation can remove the effect of lipemia.
What is the impact of Lipemia?
- Decreased sodium (Hyponatremia).
- Decreased potassium (Hypokalemia).
- Increased chloride (Hyperchloremia).
What blood Samples are to be rejected?
- The sample for CBC is unsuitable if it contains clots or is hemolyzed.
- If there are microclots that are not suitable for Cell counting, it will give a low count.
- If there is an insufficient blood sample.
- If the sample is not labeled.
- If there is a discrepancy between the sample and the request form.
- If the blood sample is insufficient in quantity.
- Poor handling of the sample when there is the effect of light.
- The sample was collected at the wrong time.
- If there is contamination of the sample.
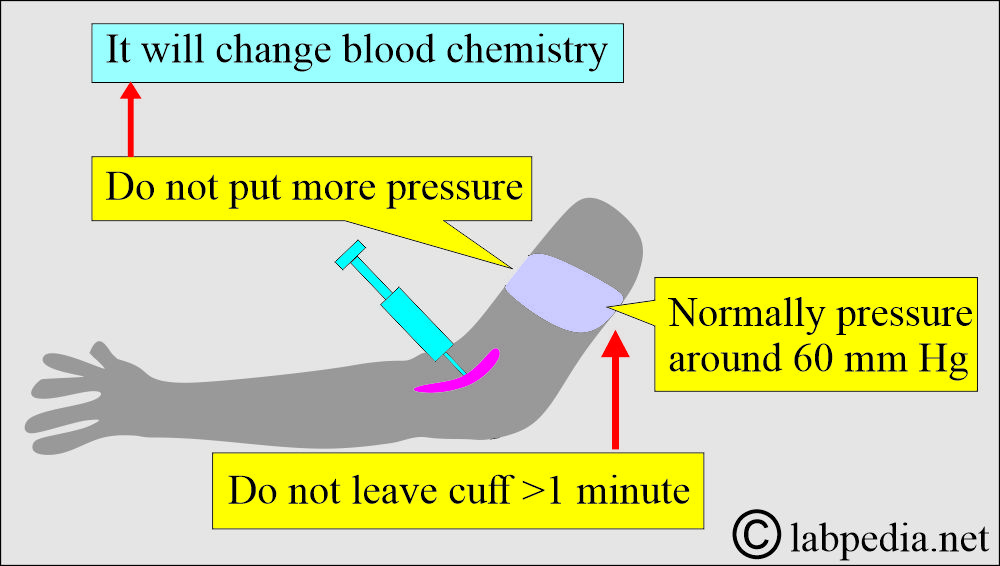
What are the changes in the blood/serum when the vein is pressurized too much?
- Most of the time, the tourniquet applies pressure to the vein, making it more prominent.
- When a blood pressure cuff is used, the pressure is typically around 60 mmHg.
- Never leave the Velcro pressure cuff on for more than one minute; it can alter blood chemistry even for a short period.
When the cuff is applied for 1 to 3 minutes, what changes will appear in blood chemistry?
| Parameters | Increase in concentration | Decrease in concentration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the importance of a Blood sample?
- The blood sample near the tourniquet has the same composition as the circulating blood.
- Use the first sample for critical values, such as serum calcium.
- The first tube may show a 5% increase in the protein level, while the third tube shows a 10% change.
- In the case of slight trauma to the skin, the enzymes (SGOT) may increase.
- In the case of stress, the patient’s body increases the production of growth hormone and cortisol.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the effect of lipemia on sodium?
Question 2: What is the best test to find hemolysis evidence?