Bilirubin:- Part 2 – Conjugated (Direct) Bilirubin, Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia
Conjugated (Direct) Bilirubin
What sample is needed for the Conjugated (Direct) Bilirubin?
- This test is performed on the patient’s serum.
- A random sample can be taken.
- This is ideal if the patient has consumed only water for 4 to 8 hours before the sample.
- The sample is stable at 4 °C for 3 days.
- Protect the sample from the light because bilirubin is photo-oxidized (photosensitive).
What are the precautions for Conjugated (Direct) Bilirubin?
- Avoid hemolysis and lipemic serum, as these can yield a false result.
- Medication that will increase the total bilirubin level, such as:
- Anabolic steroids.
- Antibiotics.
- Antimalarial drugs.
- Chlorpropamide.
- Methotrexate.
- Antihypertensive drugs, such as methyldopa.
- Oral contraceptives.
- Antituberculous drugs like rifampin.
- Medications that will decrease the bilirubin level, such as:
- Penicillin.
- Caffeine.
- Barbiturates.
- Exposure of the sample to sunlight or ultraviolet light may decrease the level.
How will you define the facts about the conjugated bilirubin?
- Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is usually due to hepatocellular injury or cholestasis, intrahepatic or extrahepatic.
- Early diagnosis and management are carried out to prevent complications.
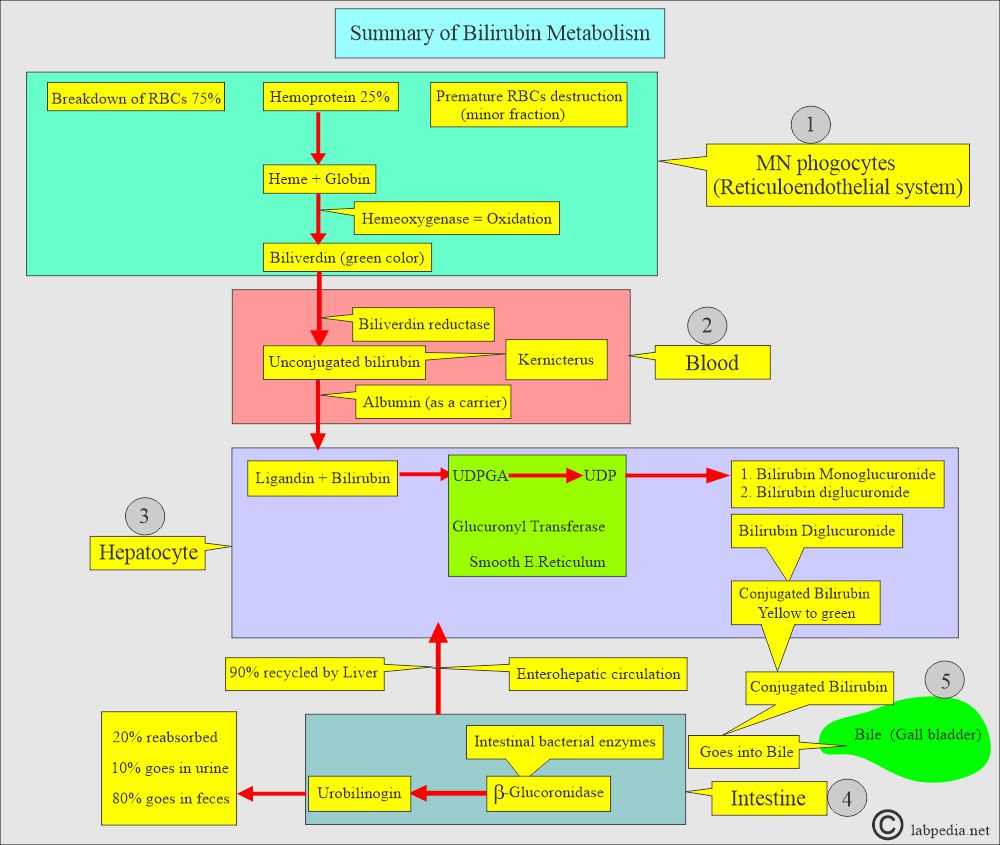
- Bilirubin is a yellow to green pigment of bile derived from the porphyrin structure of hemoglobin.
- Excessive bilirubin within cells and tissues causes skin jaundice (Icterus) or yellowness.
- Bilirubin estimation is a type of liver function test.
- Clinically, jaundice appears when the bilirubin level exceeds 2 mg/dl.
- Direct bilirubin dissolves in water (water-soluble) and is synthesized in the liver from indirect bilirubin.
- The one-minute van den Berg reaction is called a direct reaction, and the bilirubin reaction is called direct bilirubin or conjugated bilirubin.
- While bilirubin reacts in 30 minutes (with the help of alcohol), it is referred to as indirect or unconjugated bilirubin.
What is the Mechanism of Hyperbilirubinemia?
- Destruction of the RBCs, like hemolytic jaundice.
- Diseases affecting the metabolism and excretion of bilirubin in the liver.
- Obstructions like gallstones or pancreatic tumors, and certain drugs like:
- Chlorpromazine and phenothiazine derivatives.
- Estrogen hormones.
- Halothane is an anesthetic drug.
- It is raised in the hepatic and post-hepatic types of jaundice.
What is the fate of conjugated bilirubin?
- After conjugation in the liver, it is secreted into the bile.
- On demand, bile is secreted into the intestine.
- In the intestine, some of this is reabsorbed, and the rest is excreted into the stool as stercobilinogen or in urine as urobilin.
What are the normal Values of Conjugated (Direct) Bilirubin?
- Total bilirubin = 0.3 to 1.0 mg/dL (5.1 to 17.0 mmol/L)
- Direct bilirubin = 0.1 to 0.3 mg/dL (1.0 to 5.1 mmol/L)
- Indirect bilirubin (total bilirubin minus direct bilirubin level) = 0.2–0.7 mg/dL
Another source, Total bilirubin level
| Age | Premature mg/dL | Full-term mg/dL | Adult mg/dL |
| Cord blood | <2 | <2.0 | |
| 0 to 1 day | <8.0 | 1.4 to 8.7 | |
| 1 to 2 days | <12.0 | 3.4 to 11.5 | |
| 3 to 5 days | <16.0 | 1.5 to 12.0 | |
| 5 days to 60 years | 0.3 to 1.2 | ||
| 60 to 90 years | 0.2 to 1.1 | ||
| >90 years | 0.2 to 0.9 |
What are the causes of a raised level of direct bilirubin (Conjugated bilirubin)?
- Gallstones.
- Gallbladder tumors.
- Inflammatory scarring or obstruction of the extrahepatic ducts.
- Extensive liver metastasis.
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Rotor syndrome.
- Drugs may cause cholestasis.
| Clinical presentation | What is the etiology |
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of raised direct and indirect bilirubin?
- Hepatocellular disease.
- Hepatitis (viral disease).
- Cirrhosis.
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
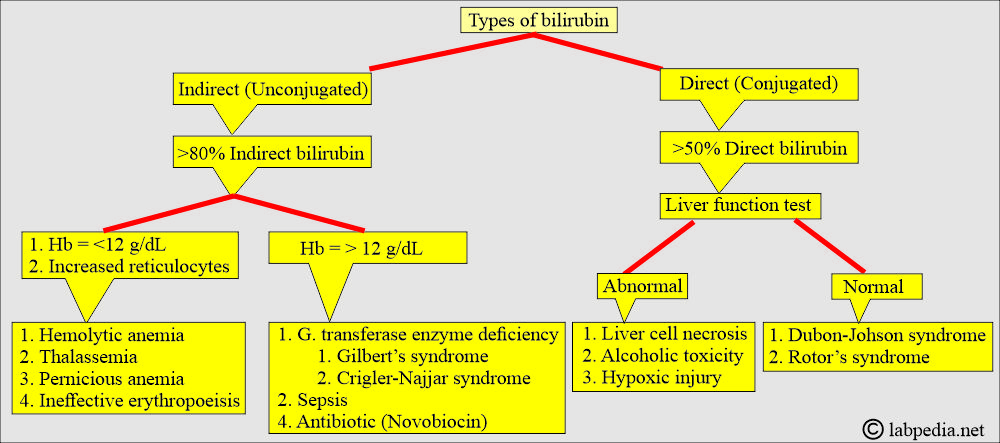
When will you see raised conjugated bilirubin (Direct) <20%?
- Hemolytic diseases.
- Gilbert syndrome.
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome.
When will you see a Conjugated bilirubin (Direct) level of 20% to 40%?
- Suggestive of hepatocellular injury (disease).
- Bilirubin metabolism abnormalities, such as:
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Rotor’s syndrome.
- It excludes extrahepatic obstruction.
When will you see a Conjugated bilirubin (Direct) level of 40% to 60%?
- Hepatocellular injury.
- Extrahepatic obstruction.
When will you see a Conjugated bilirubin (Direct) level greater than 50%?
- It is seen in extrahepatic obstruction.
- It excludes hepatocellular injury.
How will you discuss the differential diagnosis of Bilirubin?
What are the panic values?
- Total bilirubin in infants >15 mg/dL will require phototherapy.
- A total bilirubin level in infants exceeding 20 mg/dL requires a blood transfusion.
- Untreated infants will get kernicterus, which may lead to permanent brain damage.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: At what bilirubin level is phototherapy needed?
Question 2: What is the basic defect in Gilbert's syndrome and Crigler-Najjar syndrome?
Please see more details on bilirubin, Total part 1.

Hello Thanks for the info.
At times we find crazy results. How or when does d.bilirubin be higher than Total bilirubin? Even after running controls and are normal. Help, I find it hard to comprehend.
Please see the link below, which may solve your issue>
https://labpedia.net/bilirubin-part-1-total-bilirubin-direct-and-indirect-bilirubin-classification-of-jaundice-neonatal-jaundice/
Thanks
Welcome, Thanks for your encouraging comments.