Pregnancy:- Part 2 – Beta-HCG Level, β-HCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
Beta-HCG Level
Sample for Beta-HCG Level
- This test is done on the serum or urine of the patient.
- Can save serum at 2 to 8 °C for 24 hours for total HCG.
- For more time, keep serum at -20 °C.
- Freshly voided urine first-morning sample is preferred and centrifuge at 900 x g for 10 minutes.
- Can store urine at 2 to 8 °C for 48 hours.
- β- HCG serum is stable for 7 days at 2 to 8 °C. For longer periods, freeze it at -20 °C.
Indications for Beta-HCG Level
- To diagnose the pregnancy.
- To monitor the high-risk pregnancy.
- Diagnose ectopic pregnancy.
- Screening of Down syndrome.
- Used as a tumor marker.
- HCG level is also used to monitor the therapy and progress of the disease.
- This can be used as a marker for placental and germ cell tumors.
Precautions for Beta-HCG Level
- Negative tests if done in the early stage of pregnancy. This is a false-negative result.
- Avoid a sample of hematuria and proteinuria which gives the false-positive test.
- Hemolysis in the urine gives the wrong result.
- Maybe negative in the diluted urine, so a morning sample is preferred because it is concentrated urine.
- Taking a history of drug use, like diuretics and promethazine, may give a false-negative result.
- Drugs like anticonvulsants, tranquilizers, and hypnotics give a false-positive result.
- Radioisotope administered in the last week may affect the result.
Pathophysiology of Beta-HCG Level
- The HCG is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 37,900 D higher carbohydrate portion as compared to other hormones, and it is made of two subunits:
- Alpha (α).
- Beta (β).
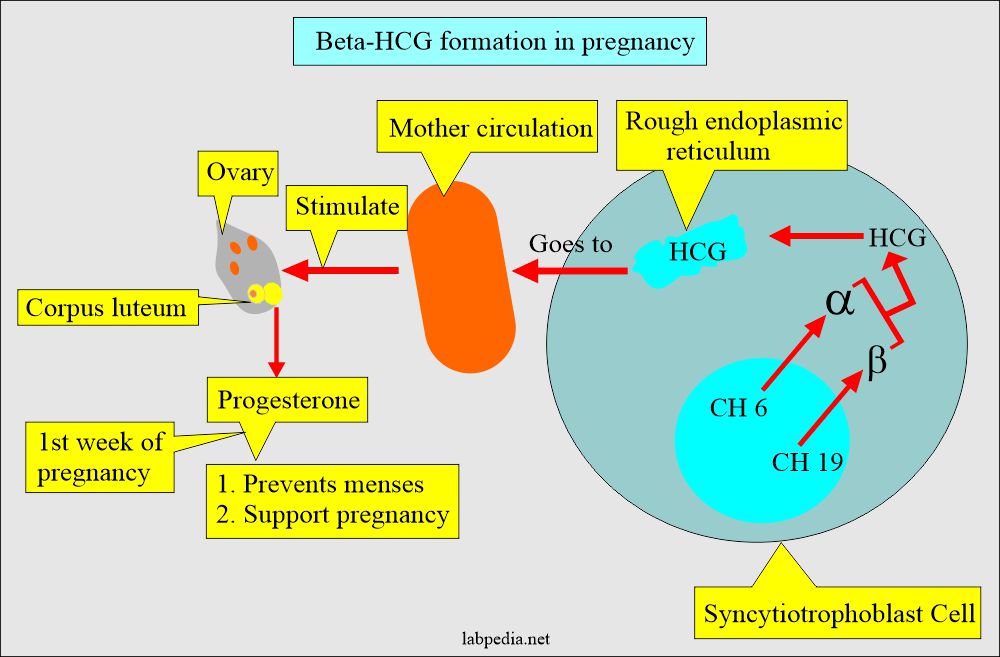
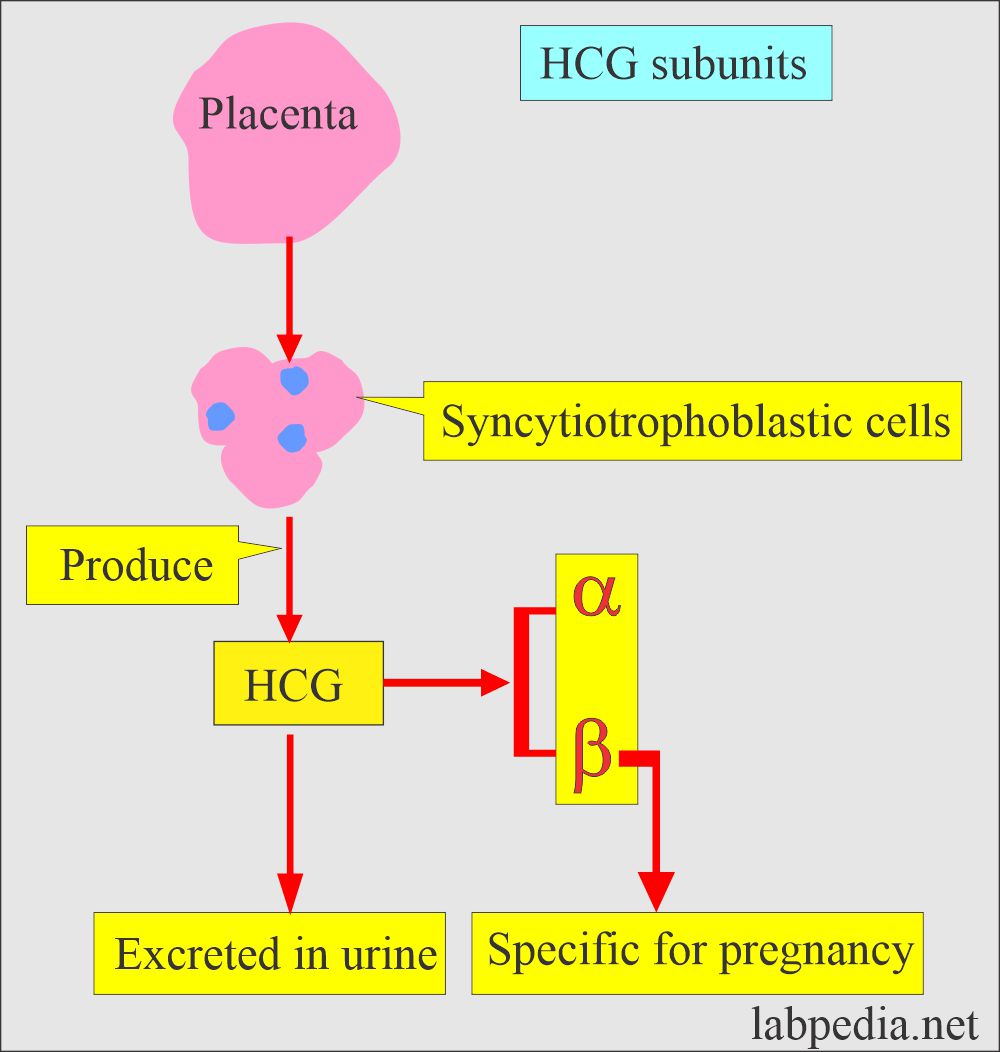
- The HCG is produced by the placental syncytiotrophoblastic cells.
- Chromosome 6 codes for the α-subunit, and Chromosome 19 codes for the β-subunit.
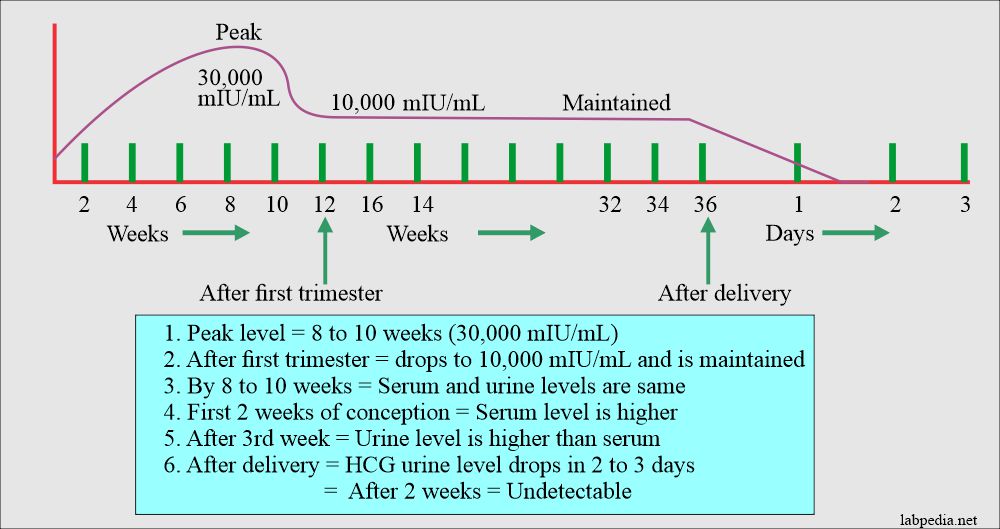
- The peak of the β-HCG is 6 to 8 weeks.
- While α-HCG keeps on increasing.
- HCG stimulates the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone in the first week of pregnancy.
- Progesterone:
- Prevents menses.
- It supports pregnancy.
- The α- subunit is the same for all the glycoproteins, Like LH, FSH, and TSH, while the β-unit is unique for HCG.
- Molecular weight is around 14,900, with 10,200 for protein and 4700 for carbohydrate.
β-subunit (Beta HCG) level
- The β-subunit is specific for HCG.
- The molecular weight of the β-subunit is 23,000 for proteins, 16,000, and 700 for carbohydrates.
- The ratio of α-subunit to β-subunit increases two-fold between the first and third trimesters.
- The HCG and its β-subunit can detect early pregnancy, which is present in the blood and urine. This is excreted by the kidneys.
- β-HCG sensitivity can detect pregnancy as early as 6 to 10 days after the oocyte implantation.
- The amount is the same in the urine and serum by one month.
HCG (HUman chorionic gonadotropin)
- HCG will appear in the pregnancy as early as 10 days after conception and is found in the serum and urine.
- HCG plays an important role in maintaining the functions of the corpus luteum during the first week of pregnancy until the luteoplacental shift of progesterone production has occurred.
- HCG also promotes steroidogenesis in the fetoplacental unit and plays an important role in stimulating the fetal testicular secretion of testosterone.
- The human fetal testes have specific binding sites for HCG.
- The maximum level of fetal testosterone in the fetus occurs around the peak level of HCG secretion during the pregnancy.
- In the first few weeks of pregnancy, its level rises where the serum level is higher than the urine level.
- This blood test detects beta-HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), a hormone normally produced during pregnancy and in some cancers.
- The intact molecule of HCG is more specific for pregnancy.
- After delivery, the HCG level falls rapidly in the first 2 to 3 days and is undetectable after 2 weeks.
- The persistence level of HCG means trophoblastic disease. It needs the workup of the patient.
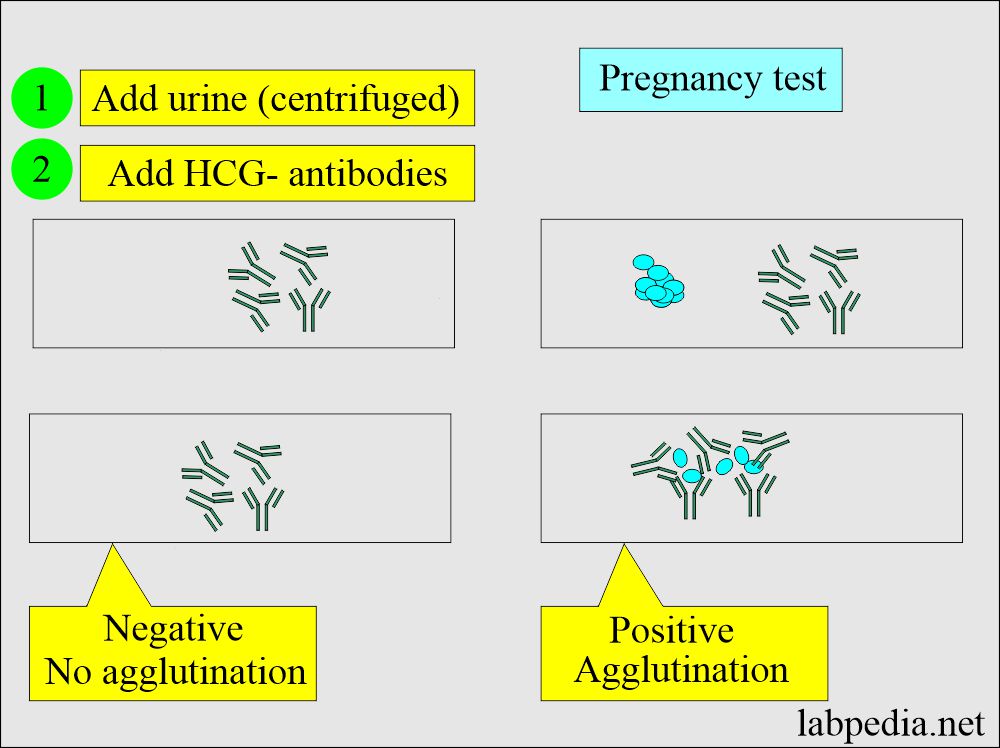
HCG was detected by the following methods (Pregnancy tests):
- Biological method where the urine was injected into a rabbit (1920). Now it is obsolete.
- An immunological method like agglutination inhibition test (AIT).
- β-HCG is a better test to detect pregnancy after 18 days of conception in the urine.
- After the monoclonal antibody, the detection of the pregnancy improved, and now pregnancy can be detected 3 to 7 days after conception.
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA).
- This is reliable and sensitive to detect the β-HCG subunit of HCG.
- The best sample is the blood for RIA, but urine can also be used.
- RIA can detect pregnancy before the first missed cycle.
- Radioreceptor assay (RRA).
- This test is done on the serum and is very sensitive and accurate.
- 90% to 95% positive after 6 to 8 days of conception.
- This test is very useful if someone wants to terminate the pregnancy; also good for the infertile couple anxious for the confirmation of pregnancy.
- This can detect the minute amount of HCG secreted in the ectopic pregnancy.
- This test is helpful in monitoring spontaneous abortion.
- Home test kits are based on the immunometric or immunochromatographic technique.
- The detection limit is 50 IU/L.
- Their clinical specificity is 77% to 100%.
- While their clinical sensitivity is 31% to 100%.
- The high number of false-negative results is difficult to understand in the literature.
- False-positive 1% results in urine are due to the following:
- Protein.
- Drugs.
- Bacteria.
- RBCs.
- White blood cells.
- False-negative results occur because the test usually does not detect levels at a concentration of less than 25 to 50 IU/L.
-
- Cold reagents, high temperatures, and extreme pH give a false result.
-
If serum HCG is positive (raised):
- If there is no pregnancy, it means the placenta is not properly implanted in the uterus, then it may indicate:
-
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Miscarriage.
- Testicular cancer.
- Trophoblastic Tumor.
- Hydatidiform mole.
- Ovarian cancer.
- If the urine test is negative but clinically indicates pregnancy, then repeat the test within 1 to 2 days.
- A urine test may be negative when the serum is positive for HCG.
The normal level of HCG and Beta-HCG
Source 2
- Qualitative test = negative (positive in pregnancy)
- Men = < 5.0 mIU/mL
- Non Pregnant women = < 5.0 mIU/ mL
- another reference
- normal = <2 ng/mL
- Urine = > 25 mIU/ ml suggests pregnancy.
- β- HCG normal value = <2 ng/mL
Source 4
- Men = <5.0 mIU/mL.
- Nonpregnant women = <5.0 mIU/mL.
- Pregnant women:
| Level of HCG | mIU/mL / IU/L |
| At implantation | 10 to 50 |
| 1 week of gestation | 5 to 50 |
| 2 weeks of gestation | 50 to 500 |
| 3 weeks of gestation | 100 to 10,000 |
| 4 weeks of gestation | 1080 to 30,000 |
| 6 to 8 weeks of gestation | 3500 to 115,000 |
| 12 weeks of gestation | 12,000 to 270,000 |
| 13 to 16 weeks of gestation | up to 200,000 |
| 17 to 40 weeks of gestation | Gradual fall to 4000 |
- mIU/mL to IU/L = the conversion factor is 1.
HCG level during pregnancy:
HCG level in pregnancy:
- HCG is detectable after 6 to 8 days of the delivery when the level is around 10 to 50 mIU/mL.
- The HCG doubles every two days until the concentration is 1200 mIU/mL around 10 weeks.
- Then double every three days between 1200 to 6000.
- Now double every 4 days above 6000 till the peak is near the end of the first trimester and is around 100,000.
- 10 to 20m weeks is the peak level of 150,000 to 200,000mIU/mL
- 2nd and 3rd trimester is 10,000 to 50,000 mIU/mL.
- By the second trimester, the peak level is 10,000 (800 ng/mL).
- 20 mIU/mL or less during the first week of pregnancy suggests ectopic pregnancy.
- A sudden fall from the plateau indicates threatened abortion.
The increased HCG level is seen in the following:
- Pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- A hydatidiform mole of the uterus.
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus.
- Seminoma of the testes.
- Germ cell tumor of the ovary and testes ( choriocarcinoma, embryonal cell carcinoma, and teratoma ).
- Nonendocrine tumors:
- Bronchogenic carcinoma.
- Hepatoma.
- Lymphoma.
The decreased HCG level is seen in the following:
- Therapeutic abortion.
- Incomplete abortion.
- Dead fetus.
Please read Part 1 for more details.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Can you get a false positive pregnancy test in urine?
Question 2: Where you can see a decreased level of HCG?