Anti-DNA, (anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies, Anti-ds-DNA Ab) and Their Significance
Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies (Anti-dsDNA)
What sample is needed for Anti-DNA?
- This test is done on the patient’s serum.
- The serum can be stored at -20 °C.
- Take 3 to 5 ml of blood in the disposable syringe. Keep the syringe for 15 to 30 minutes, then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes. This will yield a clear serum.
- Also, these anti-DNA antibodies can be detected by biopsy, e.g., of the kidney or skin.
What are the Indications for Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies?
- This is specific for the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus ( SLE ).
- This test can be used to follow up on SLE cases.
- It is indicated in the positive Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test.
What are the precautions for Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies?
- Avoid the drugs hydralazine and procainamide, which increase the DNA level.
- A radioactive scan in the last week may alter the result.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA Ab)?
- These antibodies are found in 60% to 80% of patients with active SLE.
- Anti-dsDNA is more specific for diagnosing SLE (Systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Anti-dsDNA
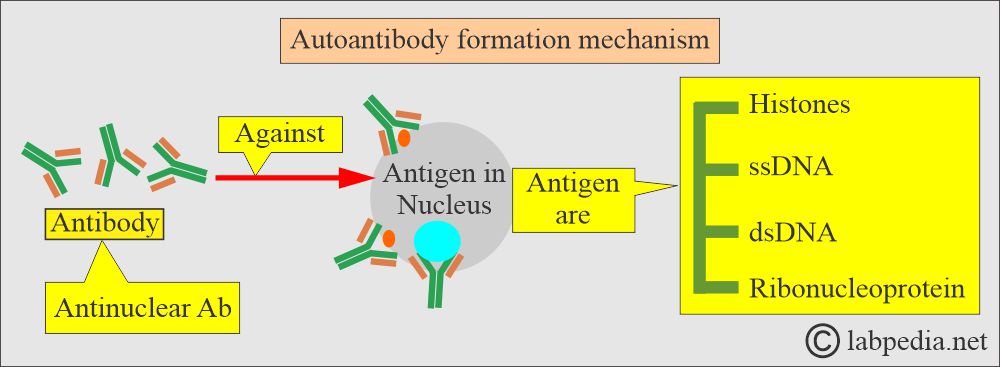
- These are a group of autoantibodies seen in autoimmune diseases.
- These antibodies are produced against antigens in the nucleus, like:
- Histones.
- Double and single-stranded DNA antigens.
- Ribonucleoproteins.
- The anti-DNA antibody is a subtype of the Antinuclear antibody (ANA).
- The most common is an antibody against the double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA, DSDNA)
- The second antibody is against the single-stranded DNA (ant-ssDNA, SSDNA) and is less sensitive and specific.
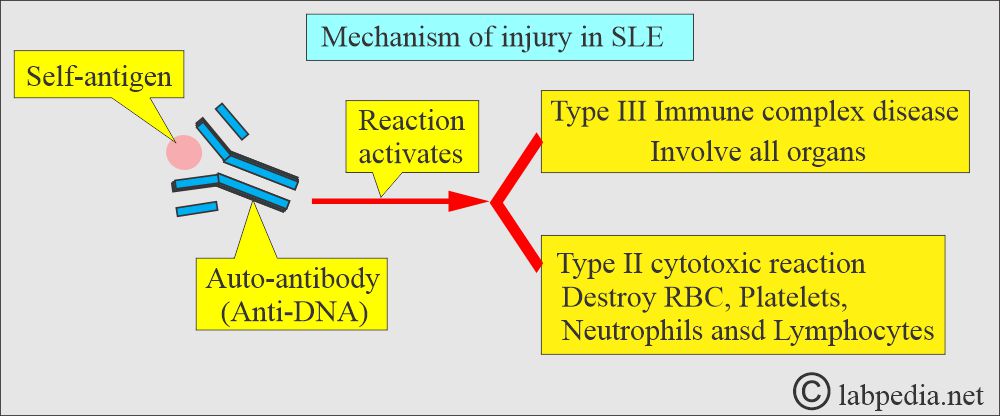
- These antigen-antibody complexes cause damage to tissue by activating the complement system.
- When a compliment is activated, that may cause local or systemic damage.
- High titers of anti-DNA are characteristic of SLE.
- Low to intermediate levels are seen in other autoimmune diseases, chronic hepatitis, biliary cirrhosis, and infectious mononucleosis.
- Anti-DNA titer decreases with successful therapy of the SLE.
- It increases if there is a recurrence of SLE.
- It is near normal in the case of dormant SLE.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE):
What is the clinical presentation of SLE?
- These patients may have a low-grade fever.
- This patient may have persistent fatigue and weakness.
- There is muscle pain.
- There may be an arthritis-like pain in one or more joints, except for the small ones.
- There is skin sensitivity to light.
- There are butterfly rashes on the nose and cheeks.
- There is weight loss.
- There is hair loss.
- There may be numbness and tingling in the hands or feet.
- Multiple organ diseases involve the kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and central nervous system.
What are the normal values of anti-dsDNA antibodies?
Source 2
- Negative: < 70 IU/mL
- Borderline : 70-200 IU/mL
- Positive : > 200 IU /mL
Source 4
- Negative = <25 IU by ELISA
- Borderline = 25 to 30 IU
- Positive = 31 to 200 IU
- Strongly positive = >200 IU
What is the Significance of anti-dsDNA antibodies?
- Anti-DNA helps diagnose and follow up on SLE.
What is the value of DNA antibodies in various diseases?
| Anti-dsDNA Ab | Association of Anti-dsDNA antibodies for various diseases |
|
|
- The level of this antibody correlates with disease activity and the presence of kidney disease (glomerulonephritis).
- This test may be positive in chronic hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and infectious mononucleosis.
- A few drugs may give a positive test, like procainamide and hydralazine.
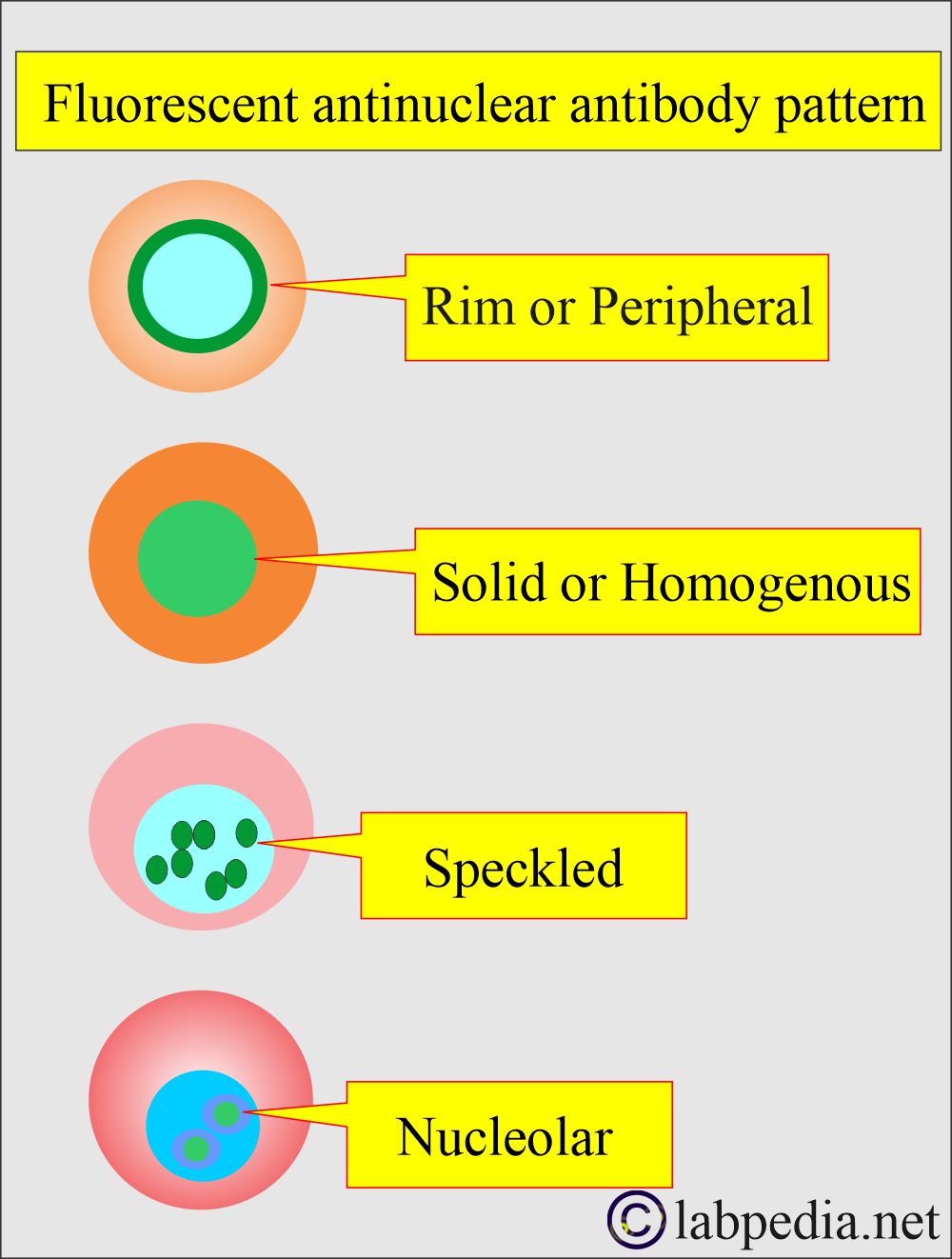
What is the pattern of Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA) on biopsy?
- This test can be done by fluorescent microscopy, revealing different patterns in various diseases in tissue biopsy.
- This ANA pattern is associated with only one autoantibody or specific disease. These patterns are:
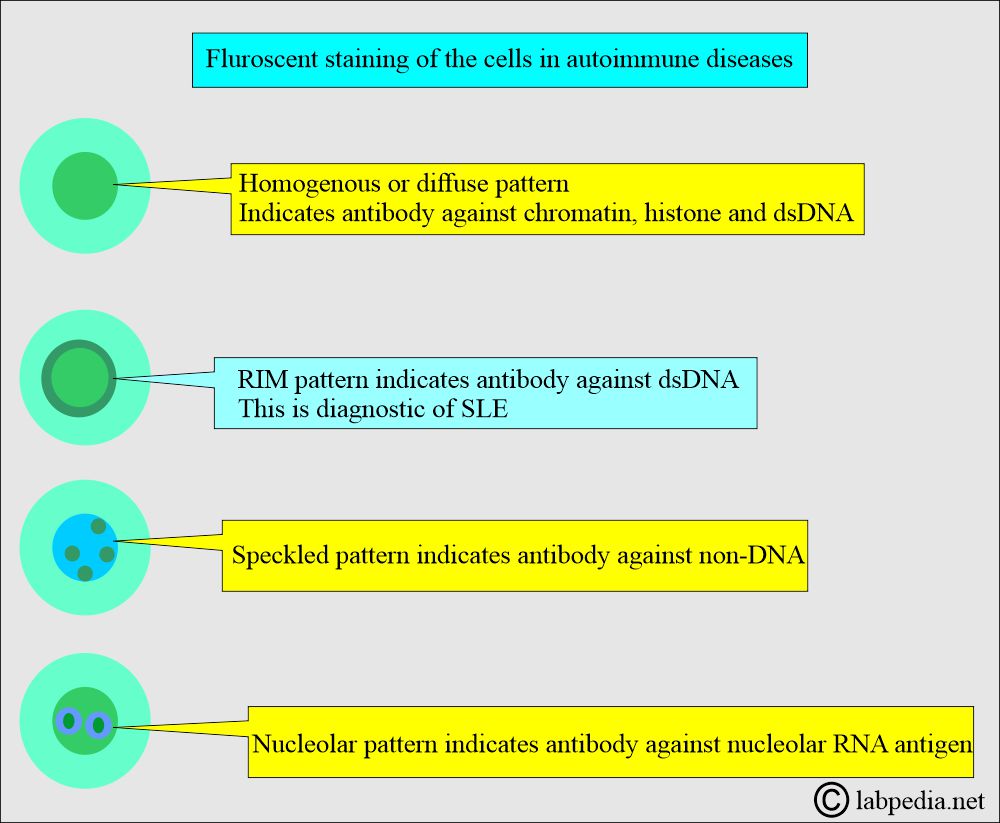
- Rim or peripheral pattern:
- This is seen at the nuclear border.
- This is thought to be produced against several nucleoproteins, including sNP, Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), and histones.
- A high titer of ANA (1:160 or greater) with the rim strongly suggests SLE.
- If the ANA antibody titer is low, then it is not helpful to diagnose SLE.
- Solid or homogeneous pattern:
- This is seen throughout the nucleus.
- This is the second most common ANA pattern.
- ANA can produce this pattern against dsDNA, ssDNA, sNP, and histones.
- This pattern is most frequently seen in SLE but is not diagnostic.
- This may be seen in other rheumatoid-collagen diseases.
- The ANA titer is usually <1:160 in diseases except for SLE.
- Speckled pattern:
- There are small fluorescent dots throughout the nucleus.
- There is no involvement of the nucleoli.
- This is the most common ANA pattern.
- The ANAs are produced against acidic nuclear proteins ENA (Sm and RNP), SS-A and SS-B, histones, and scleroderma-70 (Scl-70).
- It is seen in 25% of SLE cases.
- ANA against Sm strongly suggests SLE, while ANA against RNP suggests mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD).
- ANA against SS-B suggests Sjögren’s disease, and ANA against Scl-70 suggests scleroderma.
- Nucleolar pattern:
- This is only seen in the nucleolus, which has several irregular shapes and sizes.
- This pattern is due to ANA against the nucleolar ribonucleic acid (RNA, 4- 6s RNA).
- It suggests scleroderma in 55% to 90% of the cases when the titer is high.
- The low titer is found in SLE and other collagen diseases.
- Rim or peripheral pattern:
What is the pattern of immunofluorescence staining in various autoimmune diseases?
| Disease | Nuclear Pattern |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLE nuclear pattern
- Anti-double-stranded DNA antibody (anti-dsDNA) is more specific than simple anti-DNA antibodies.
What are the various cytoplasmic and nuclear protein positivity in SLE?
| Test parameters | Positivity in SLE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of increased anti-DNA antibody levels?
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Other autoimmune diseases.
- Biliary Cirrhosis.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
Question and answer:
Question 1: Which antibody is specific for SLE?
Question 2: Which immunofluorescent shape is specific for SLE?

Ok👌
Thanks.
Thank you Dr. Riaz for this great article.
If possible, Could you please help me with this multiple choice question?
Most common ANA pattern associated with SLE:
a. Rim b. Speckled c. Homogenous d. Nucleolar
From what I got, the answer is Speckled?
Please correct me if I’m mistaken.
Rim is more specific.
Thanks for the great article Dr.Riaz. After having positive ANA test, my doctor did dsDNA test on me, but the way I got the test result is different, not in IU measurement. The report says normal value: <1:10 titer. My value is 1:160. How do I convert it to IU?
Thank you.
I think no need to convert into IU, because the test report is positive.