Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
What sample is needed for Alkaline phosphatase level (ALP)?
- It is done on the patient’s serum.
- A fasting sample is a better choice. Fasting for 10 to 12 hours before taking the sample is advised.
- This test can be done on a random sample as well.
- Getting good serum:
- Take 3 to 5 ml of blood in a disposable syringe or a vacutainer. Keep the syringe for 15 to 30 minutes at 37 C and then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes to get the clear serum.
- Keep the sample refrigerated as soon as you separate the serum.
- Because at room temperature level increases (up to 30% increase).
- The refrigerated sample also increases, which is slow compared to the room temperature sample.
- Testing should be done on the same day.
- Serum at 0 to 4 °C is stable for 2 to 3 days; at -25 °C, it is stable for one month.
- Perform the test as soon as possible because ALP activity increases 3% to 10% on standing at 25° C or 4 ° C for several hours.
What are the precautions for Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Storage at room temperature increases the ALP activity.
- Avoid EDTA and oxalate anticoagulants or fluoride, which decrease Alkaline phosphatase activity.
- Reject the sample in oxalate and citrate.
- If serum is left at room temperature:
- Then there is a 1% increase in 6 hours.
- 3% to 6% in 1 to 4 days.
- Even though it may increase if refrigerated the serum, which is 2%/day, the increase is slow.
- This increase may be up to 30% if the serum is left at room temperature or in the fridge.
- Recent intake of food may increase the value.
- Values may be 25% higher after taking the high-fat meal.
- Drugs that increase the level:
- Drugs like allopurinol, antibiotics, colchicine, indomethacin, fluorides, isoniazid (INH), methotrexate, nicotinic acid, methyldopa, phenothiazine, vitamin D, and probenecid can increase the alkaline phosphatase level.
- It increases after a fatty meal.
- Drugs that decrease the level:
- Drugs like fluorides, arsenal, cyanides, nitrofurantoin, and zinc salts may decrease the alkaline phosphatase level.
- Hemolysis may cause a slight increase in ALP, which is six times more abundant in the RBC than in the serum.
- Young children experiencing rapid growth, pregnant women, and post-menopausal females have a physiologically high alkaline phosphatase level.
- After I/V infusion of albumin, there may be a sometimes marked increase in alkaline phosphatase.
What are the indications for Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Alkaline phosphatase is estimated to detect diseases of the liver and bone.
- Alkaline phosphatase is the best marker for obstructive jaundice.
- ALP distinguishes obstructive and hepatocellular jaundice.
- Alkaline phosphatase is the marker:
- For hepatic metastasis.
- In parathyroid diseases.
- Vitamin D deficiency.
- Acute pain in the abdomen.
How will you define Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
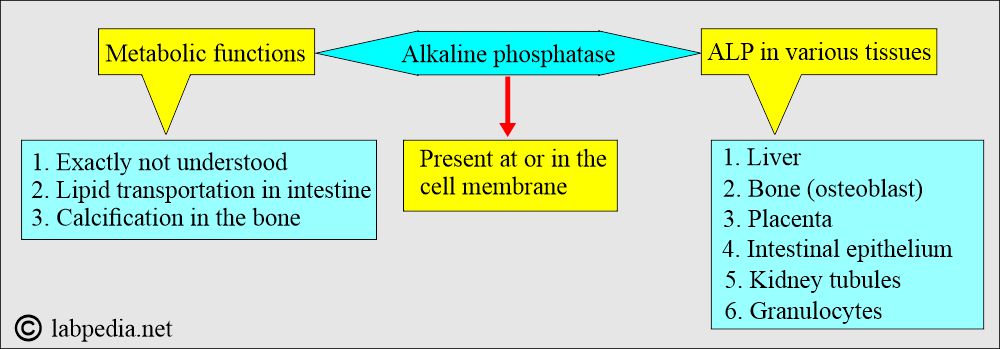
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme in various body tissues.
- It is present primarily in the liver, bones, and intestines.
- It plays a role in mineralization and other physiologic processes.
- The body contains many phosphatases, which are classified based on the pH at which they show maximum activity.
- ALP shows maximum activity between pH of 9 to 10.
- Intestinal mucosa shows the greatest activity, followed by the kidney, bone, thyroid, and liver.
- Regan isoenzymes are observed in 5% of cases with carcinoma. It is identical to the placental ALP isoenzyme.
- The bone, bile ducts, intestine, and placenta produce alkaline phosphatase.
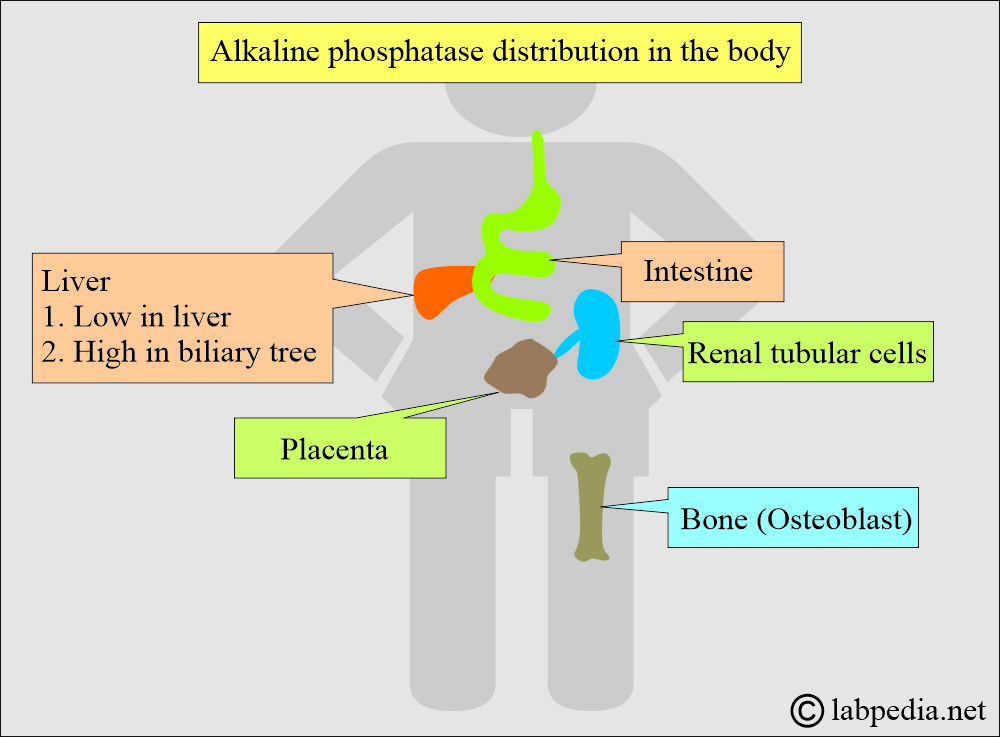
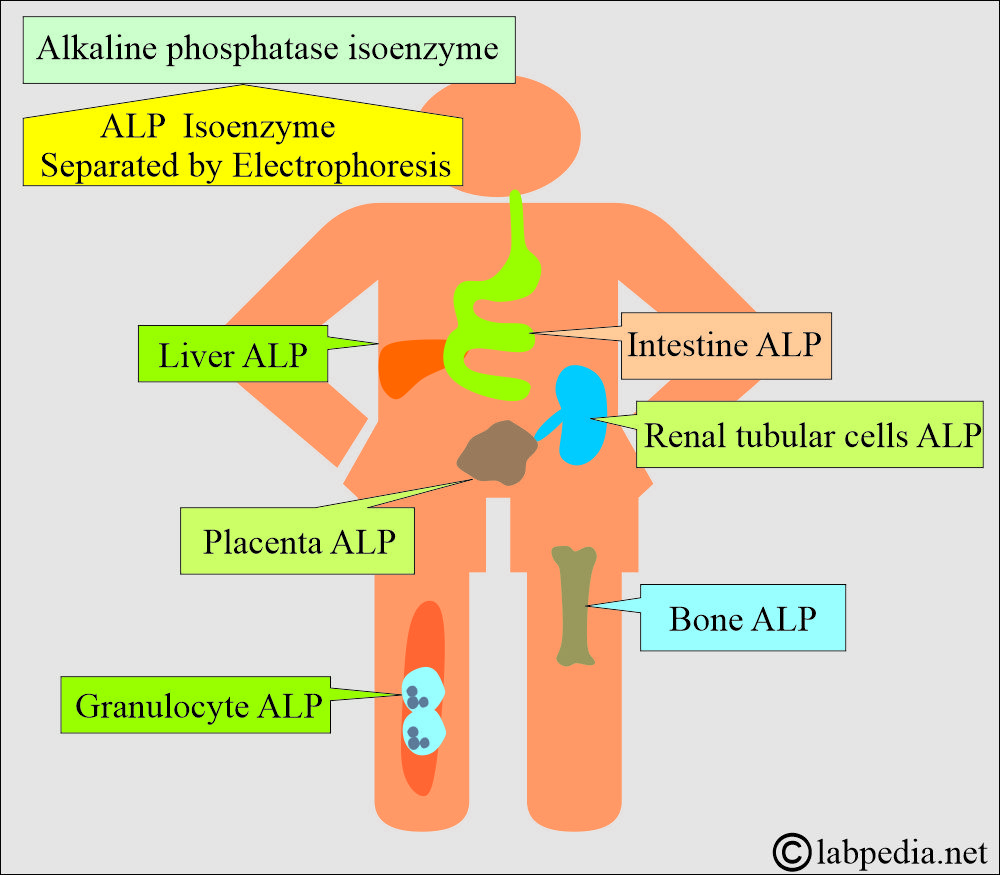
What is the distribution of the alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- This enzyme is present in the blood, and its subtypes are present in the liver, intestine, bones, and placenta.
- The maximum amount is present in the liver and biliary tree epithelium.
- The liver and the bone are two tissues for raised alkaline phosphatase levels.
- ALP is found in many tissues, at or in the cell membrane.
- ALP is a nonspecific enzyme capable of reacting with many different substrates.
- Liver and bone ALP are predominantly found in the serum.
- Due to bone activity, children have 1.5 to 2.0 times more alkaline phosphatase than adults.
- A small amount of the ALP from the intestinal epithelium is found in the sera of blood group B or O, which are secretors of blood group substances.
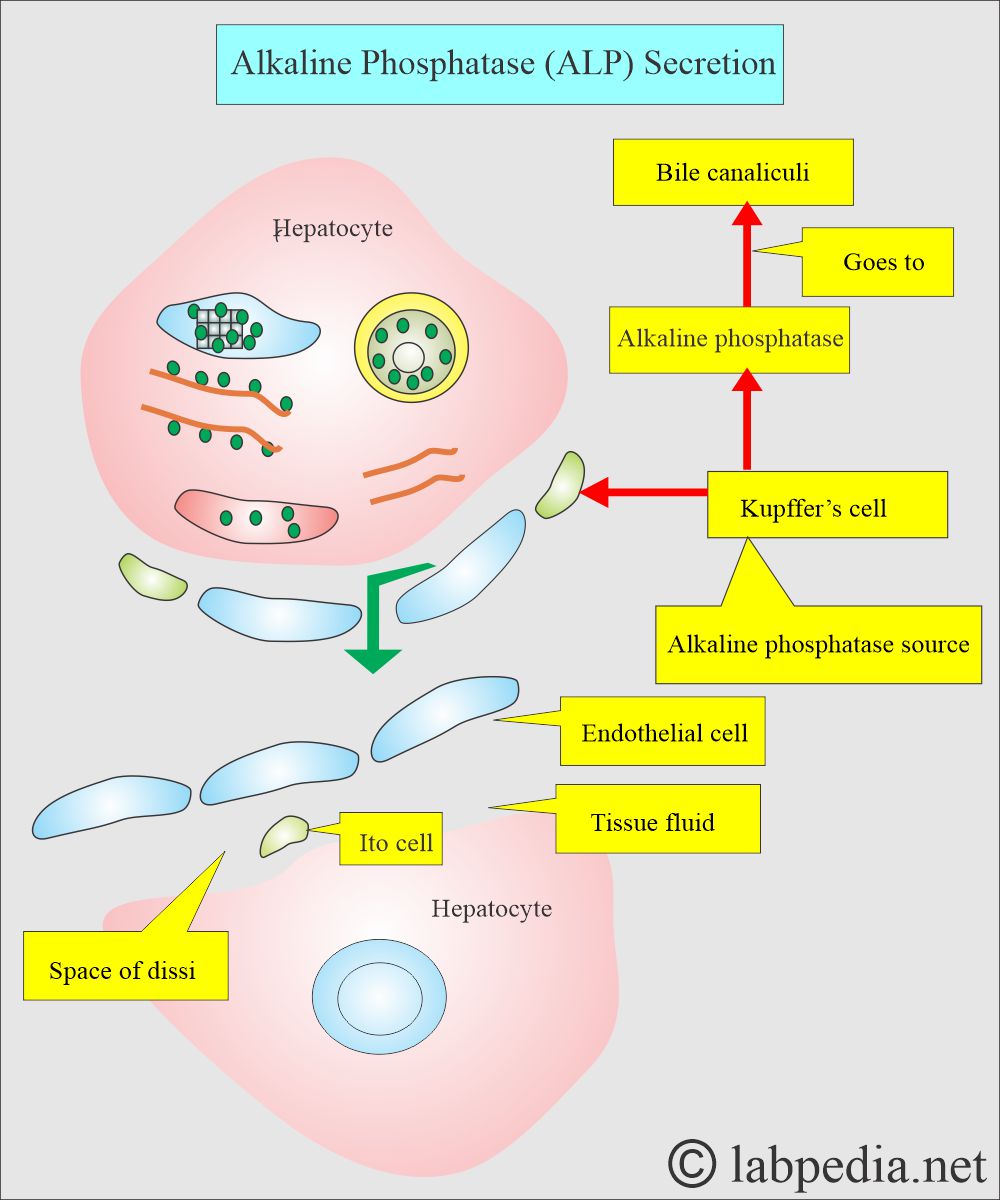
- The highest concentration is found in the liver. Within the liver, ALP is present in the Kupffer cells, which line the biliary collecting system. This enzyme is excreted in the bile. Its liver concentration is lower than that in the biliary tree.
- ALP is mainly from the liver and biliary tree and nearly up to 50% from the skeleton (osteoblastic cells).
- It is found in the intestinal epithelium and renal tubular cells and lower concentrations in leucocytes and the placenta.
- This ALP is age-dependent.
- Pregnancy can also lead to a raised level.
- Alkaline phosphatase in urine is from the renal tubule, not the plasma.
- This may be seen in renal lesions as a malignant tumor (carcinoma), nephrosis, nephritis, infarction, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
What is the effect of temperature on Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- ALP (serum) is denatured at 56 °C and stable at lower temperatures.
- The liver isoenzyme is moderately heat stable at 55° C, but the bone isoenzyme is heat-labile.
- Placental isoenzyme is stable at 65 °C but not others.
- Placenta ALP = Heat stable at 65 °C.
- Liver ALP = Moderately stable at 55 °C
- Bone ALP = Heat labile.
- The alkaline phosphatase level (ALP) is distinguished by heating. The common method is heat fractionation, where serum is heated at 56 °C for 15 minutes and finds the remaining ALP activity:
- Bone ALP activity will be only 10% to 20% of the original activity.
- The liver will retain ALP activity 30% to 50% of the original activity.
- Placenta ALP is heat stable and will contain virtually all of its activity.
- The serum will show increased activity when it is kept at room temperature.
- What is the variation of ALP at different temperatures?
- 1% when kept for >6 hours.
- 3% to 6% >1 to 4 days.
- It will increase slowly to 2% daily when kept in the fridge.
- When frozen, the activity decreases, which will recover slowly after thawing.
- In lyophilized sera used for control as a reference, it also shows increased activity:
- 50% to 100% in 24 24-hour period.
- 10% when stored at 4 °C.
- 30% when stored at 20 °C.
- Alkaline phosphatase level (ALP) enzymes require Magnesium for the reaction.
- Post-puberty ALP is mainly from the liver.
- The conditions that will stimulate bone cells lead to an increase in the level of ALP.
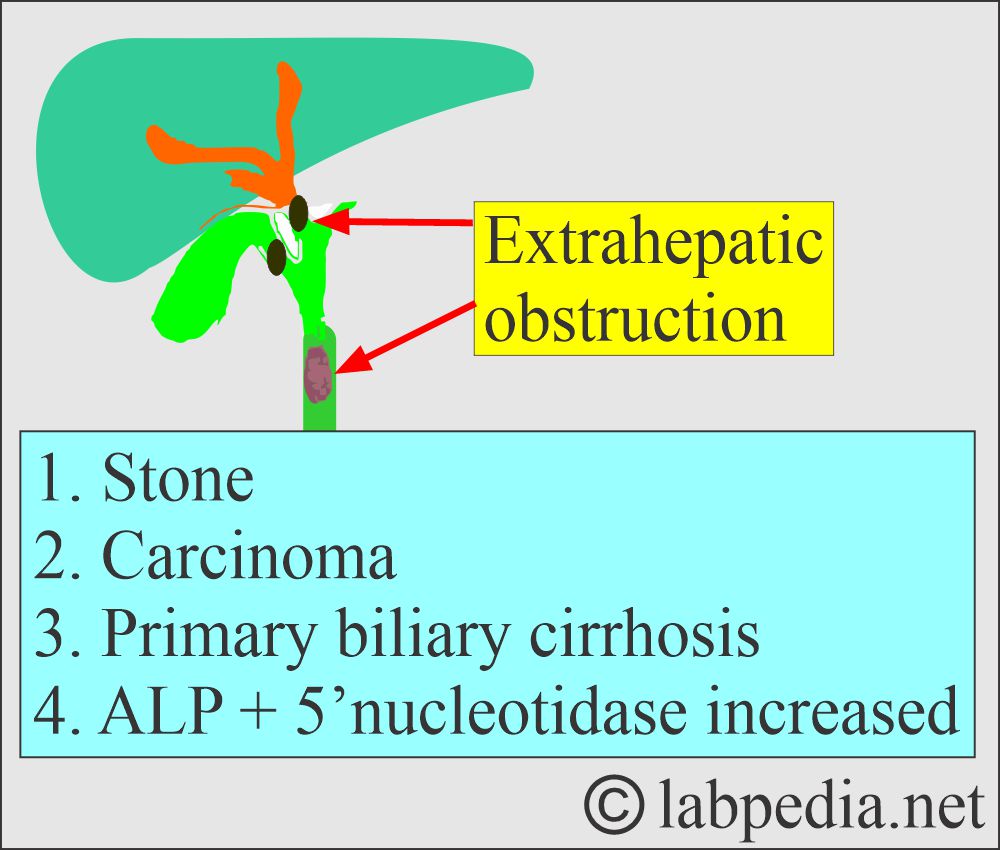
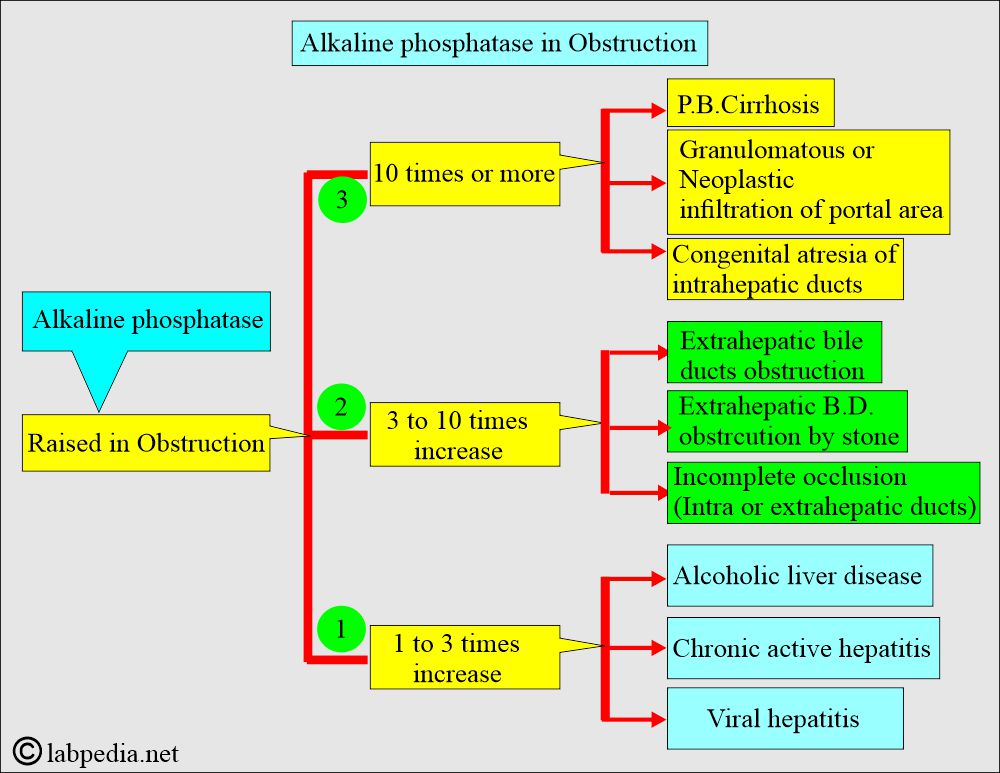
What are the effects of Obstruction on Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)?
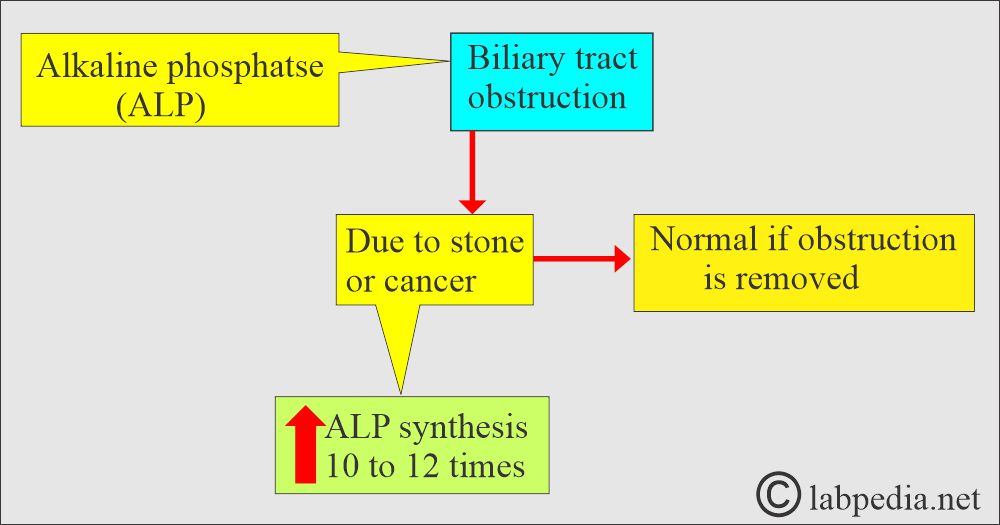
- The liver ALP is increased in biliary obstruction when its excretion is impaired.
- In intrahepatic obstruction, the ALP level increases less than in biliary tract obstruction, which may go up to 2.5 times.
- Extrahepatic obstruction may reach 10 to 12 times the upper limit and is normal when a surgical obstruction is removed.
- In the case of infectious hepatitis, there may be a moderate elevation or even normal.
What is the effect of bone activity on alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- The stimulus that increases bone activity causes an increase in the ALP level.
- Elevated levels indicate liver or bone diseases.
- Bone alkaline phosphatase is produced by the osteoblasts of the bone and not by the osteoclasts.
- The ALP level rises during active bone formation, such as in infants, children, and adolescents. So, their level is three times the norm compared to adults.
- Bone alkaline phosphatase indicates bone-forming activity.
What are the activators of the Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Magnesium, Cobalt, and manganese.
- The exact ratio of Mg²/Zn² is important to avoid the displacement of the Mg² to get optimal activity.
- Zinc is a constituent metal ion.
What are the inhibitors of the Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Alkaline phosphatase level (ALP) inhibitors are:
- Borate
- Phosphate.
- Cyanide
- Oxalate.
How will you divide Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Isoenzymes?
- The ALP is divided into isoenzymes based on the following:
- Acrylamide gel Electrophoresis.
- Characteristic inactivation by heating.
- Incubation and inhibition by the urea.
- Inhibition by L-phenylalanine.
What are the isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase and their characteristics?
| Isoenzyme of ALP | Effect of heat/urea | Effect of L-phenylalanine | Electrophoresis (anodal mobility) |
| Bone | Positive (+++) | Negative | 2 (++) |
| Liver and biliary (ALP1) | Positive (+) | Negative | 1 |
| Intestinal | Positive (+) | Positive (+++) | 4 (++++) |
| Placenta | Negative | Positive (+++) | 3 (+++) |
| Regan (Oncofetal placental ALP) | Negative | Positive (+++) | 3 (+++) |
How would you discuss the Liver Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) isoenzyme (ALP1)?
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is formed by the liver and biliary tract epithelial cells.
- This is derived from the epithelial cells of the biliary tract.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) increases in:
- Active liver disease.
- Biliary tract obstruction, whether intrahepatic or extrahepatic.
- Whether mild or severe diseases.
- Whether it is a localized disease or extensive involvement of the liver.
- 50% of the liver and biliary ALP is inactivated by heat.
- The normal route of elimination is the excretion of bile into the intestine.
- This fraction moves fastest on electrophoresis, followed by bone, placenta, and intestinal fractions.
- This is moderately heat-stable.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) will be raised in:
- Extrahepatic common bile duct obstruction.
- Biliary tract obstruction.
- Biliary tract obstruction due to liver cell injury.
- Liver space-occupying lesions like tumors, granulomas, and abscesses.
- Uncommon conditions are primary biliary cirrhosis.
- An alkaline phosphatase (ALP) raised level is seen in:
- 5% of patients with viral hepatitis.
- 5% of the patients with active alcoholic cirrhosis.
- 13% to 20% of the patients with infectious mononucleosis.
- 75% to 80% of the metastatic tumors of the liver.
- 100% of the cases are biliary tract obstruction, except for partial or intermittent obstruction.
How would you discuss the Bone Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) isoenzyme (ALP2)?
- Bone is the second most common cause of raised Alkaline phosphatase (ALP).
- Osteoblast produces a large amount of Alkaline phosphatase (ALP).
- The heat inactivates 90% of the bone isoenzymes.
- This increases due to osteoblastic activity and is normally elevated in children and people over 50.
- An alkaline phosphatase (ALP) raised level is seen in:
- Children at growing age will have high-level ALP.
- Adults with healing fractures of the bone have raised levels of ALP.
- Paget’s disease leads to a very high level, 10 times or more the upper limits of the normal.
- ALP is raised in metastasis to the bone, myeloma, and metabolic bone diseases like rickets, hyperparathyroidism, and osteomalacia.
- Deficient levels of this bone ALP are seen in the metabolic disorder of hypophosphatasia.
- To differentiate the origin of Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), whether from bone or liver diseases, advice:
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Mostly, GGT is not raised in bone diseases.
- 5-nucleotidase.
- Serum electrophoresis is difficult but more reliable.
How would you discuss the Intestinal Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) isoenzyme (ALP)?
- It is ∼25% of the normal sera.
- This depends upon the blood group and the secretor status of people.
- Blood groups B or O secretors are more likely to have this isoenzyme. In this group, ALP will increase after 2 hours of the meal.
- This will lead to false positives in nonfasting individuals, particularly Lewis positive type B and O secretors.
- After the ingestion of the meals, the ALP will increase by 30% for 2 to 12 hours.
- A fasting ALP level is indicated.
- This is inactivated by heat.
- This will be raised in inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis and regional enteritis.
- This isoenzyme may lead to abnormal values in a non-fasting sample.
How would you discuss the Placental Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) of placental origin starts to rise by the end of the first trimester and reaches a peak (up to 4 times the normal) by the third trimester.
- The rise in the second and third trimesters will be both placental and bone origin.
- 60% is of placental origin.
- Placental ALP appears in the 16th to 20th week of gestation. Then it keeps increasing, two times the normal at the time of labor.
- It disappears 3 to 6 days after the delivery.
- It disappears 3 to 6 days after the delivery.
- Bone-derived alkaline phosphatase persists longer and may be seen for more than 6 weeks of the infant.
- Placental ALP is not inactivated by heat. It tolerates moderately high temperatures without decomposition and loss of activity.
- This is usually seen in a pregnant mother’s blood, which is placental in origin.
- This may increase pregnancy complications, like hypertension, preeclampsia, and threatened abortion.
- It is lower in diabetic than in non-diabetic pregnancies.
- This oncofetal form of placental ALP is also known as Regan isoenzyme, after the patient in whom it was first described.
How would you discuss the Renal Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Renal tubular cells have ALP activity that is normally excreted in the urine.
- It does not reach the serum in pathological conditions.
- The sloughed renal cells may cause an artificial false-positive result on the new immunoassay screening procedure.
How would you discuss the Granulocytes Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- ALP in the granulocytes does not raise the serum ALP level.
- This is helpful as a marker for granulocytic maturity in leukocytosis.
How will you summarize Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes classification and differentiation?
| Basis for classification | Isoenzyme liver | Isoenzyme intestine | Isoenzyme bone | Isoenzyme placenta | Isoenzyme Renal |
| Amount of ALP |
Present in the serum | Present in the serum in inflammatory GI tract diseases | Present in the serum | Trace amount found in serum | Excreted in urine |
| Heat stability | Stable at 56 °C for 30 minutes, more than bone | Disappear at 56 °C within 15 minutes | Disappear at 56 °C within 10 minutes | Stable at 65 °C for 30 minutes (Regan 15 to 15% cases of cancers) | |
| Chemical inhibition | By urea but low by L-phenylalanine | Strong by L-phenylalanine | Strong by urea but low by L-phenylalanine | Resistance to urea but strong inhibition by L-phenylalanine | |
| Electrophoresis | Most anodic | Cathodic to the bone fraction | Intermediate | Migrate with the placenta or bone fraction | Renal isoenzyme is more cathodic and slower |
| Gene arrangement | Similar to the liver, the short arm of chromosome 1 | Product of unique gene long arm of chromosome 2 | Similar to the liver, the short arm of chromosome 1 | Different Chromosome 2 | Similar to the liver, the short arm of chromosome 1 |
What are the functions of alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- The exact metabolic function of ALP is still not known.
- The main function is to remove the phosphate group from the proteins and other molecules.
- These are necessary for the hydrolysis of organic phosphate and are important for digestion and mucosal absorption.
- ALP is associated with lipid transport in the intestine.
- The second role is in the osteoblastic tissues. The metabolic activity of the osteoblasts is associated with ALP activity.
- ALP is also associated with the calcification process of the bone.
- ALP is beneficial in distinguishing various bone diseases and hyperparathyroidism when combined with serum calcium and X-rays.
- Alkaline phosphatase is called Alkaline because its function is seen between a pH of 9 to 10 and best at a pH of 9.0.
What are the normal Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) values?
- Value varies according to the kit and methodology used.
- As Alkaline phosphatase level (ALP) exists in various tissues, isoenzymes may be advised in the case of raised levels.
- If this value is found on two separate test results >6 months apart, at least a 1.5-times increase is suggested for further patient workup.
Source 6
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source 4
Male
- 1 to 12 years = <350 U/L
- 12 to 14 years = <500 U/L
- >20 years = 25 to 100 U/L
Female
- 1 to 12 years = <350 U/L
- >15 years = 25 to 100 U/L
- ALP is slightly higher in males than in females. It rises in females after middle age.
- There will be a biliary disease if = ALP is raised and + 5′-nucleotidase is raised.
- If ALP raised + 5′-nucleotidase is normal, then think about other causes.
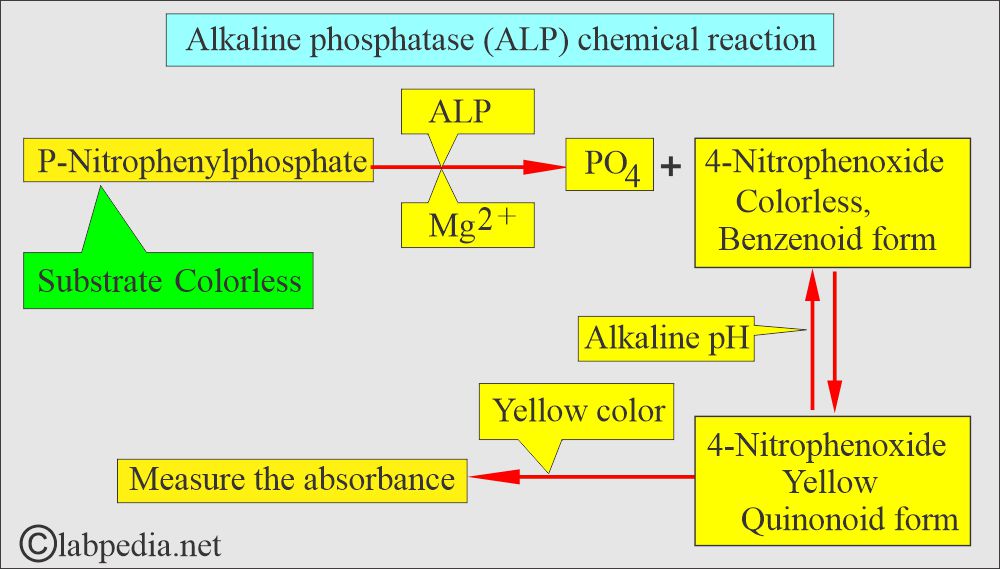
What is the principle of the Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) chemical reaction?
- Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme of the hydrolase class that catalyzes orthophosphate cleavage from orthophosphoric monoesters under alkaline conditions.
- There is colorless substrate p-Nitrophenyl phosphate (4-nitrophenyl phosphate), and by the action of ALP enzyme converted to p-Nitrophenol (4-nitro phenoxide, benzenoid form) is colorless, changed to 4-nitophenoxide, is the quinonoid form which is a yellow color in alkaline medium.
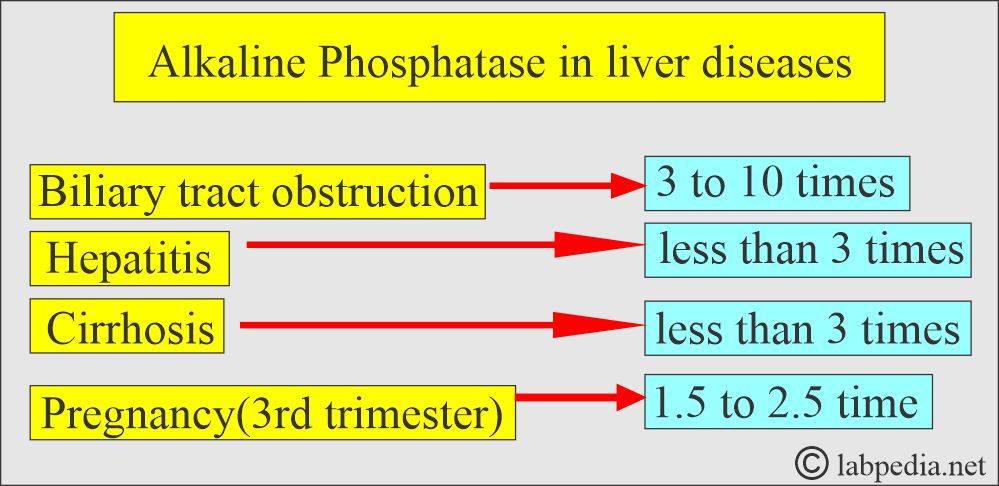
How will you differentiate Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in liver diseases?
- In the absence of bone disease or pregnancy, markedly raised Alkaline phosphatase ( around 10 times ) is the best obstructive liver pathology marker, like gallstones obstructing the biliary tract.
- Also, advise on 5’nucleotidase, which will be raised in case of biliary disease. If it is normal, then search for other causes of raised ALP.
- 1 to 2 times raised levels may be seen in various liver parenchymal diseases like Hepatitis and Cirrhosis.
- In extrahepatic obstruction due to stones and cancer, ALP increases 3 times the normal.
- In the case of complete obstruction, ALP may be raised 10 to 12 times.
- In the case of intrahepatic obstruction, ALP rises but less than in the case of extrahepatic obstruction.
- In the case of infectious diseases, ALP rises but <3 Times.
- In pregnancy, the average increase in ALP is 1.5 times the normal limit between 16 to 20 weeks, and it persists till labor.
- After labor, ALP comes to normal within 3 to 6 days.
- This may be raised in pregnancy complications like hypertension, Eclampsia, pre-eclampsia, and threatened abortion.
- To confirm the hepatobiliary origin of ALP, advise γ-GT or 5-nucleotidase.
- ALP is a sensitive marker for hepatic metastasis. If there is hepatomegaly without jaundice, it indicates metastatic liver disease.
What causes mildly raised levels of Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- Metastatic diseases of the liver.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Biliary Cirrhosis.
- Intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholestasis.
- Gilbert’s syndrome.
- Chronic alcohol ingestion.
- Diabetes mellitus and diabetic hepatic lipidosis.
What are the causes of raised Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in bone diseases?
- It is increased in bone diseases like Paget’s disease, healing fractures, Rickets, pregnancy, and childhood.
- Metastatic bone tumors.
- Osteogenic sarcoma.
- Osteomalacia ( while in osteoporosis, ALP is normal ).
- There is a higher level of ALP in children and infants, and it is 3 times the adult level.
How will you summarize Alkaline phosphatase in bone diseases?
Diseases |
ALP increased |
Explanation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of raised alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
- It is also raised in old age and pregnancy.
- Hodgkin’s disease.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Amyloidosis.
- Pulmonary and myocardial infarction.
- Hyperthyroidism (with a raised level of calcium).
- Chronic renal failure.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- ALP is increased during the last trimester of pregnancy and falls to normal within 3 to 6 days (postpartum).
- Hyperparathyroidism.
What are the causes of decreased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels?
- Malnutrition.
- Hypothyroidism (Cretinism).
- Milk-alkali syndrome.
- Celiac sprue.
- Scurvy (vitamin C deficiency).
- Gross anemia.
- Deposition of radioactive material in the bone.
- In hypophosphatemia.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Nutritional deficiency of zinc or magnesium.
- Theophylline therapy.
- Estrogen therapy in postmenopausal females.
- Wilson’s disease.
How will you summarize raised levels of Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)?
| Level of raised Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | Causes of raised Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: When Alkaline phosphatase level (ALP) is raised in bone diseases?
Question 2: What is the significance of Alkaline phosphatase level (ALP)?


very helpful information.concise and compact.
Thanks for the encouraging remarks
nice and comprehensive information, thanks a lot.
Thanks.
Very well written article on ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE
Thankyou Dr Riaz and team
Thanks for your appreciation.
token of thanks sir
Thanks.
THANKS