Aldolase and Its Significance
Aldolase
What sample is needed for Aldolase?
- It is done in the Serum of the patient.
- Patients should fast for 8 hours before giving the sample.
- Take 3 to 5 ml of blood in the disposable syringe. Keep the syringe for 15 to 30 minutes, and then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes. Can get a clear serum.
- Avoid hemolysis and separate serum immediately.
- It is stable for:
- 8 hours at room temperature.
- 4 °C for 5 days.
- -15 °C for 15 days.
What are the precautions for Aldolase?
- The previous muscular injection may have increased the aldolase level.
- Hemolysis and exposure to chlorinated insecticide may increase the level.
- Hepatotoxic drugs may increase the level.
- The phenothiazine may decrease the aldolase level.
What are the indications for Aldolase?
- This test is indicated when inflammatory diseases of the muscles (myopathy) are suspected.
- To assess the severity of myopathy.
- Other tests, such as Lactate dehydrogenase, Creatinine Phosphatase, and Aspartate transferase, are advised and helpful for diagnosis, so this test is no longer recommended.
How will you define aldolase enzyme?
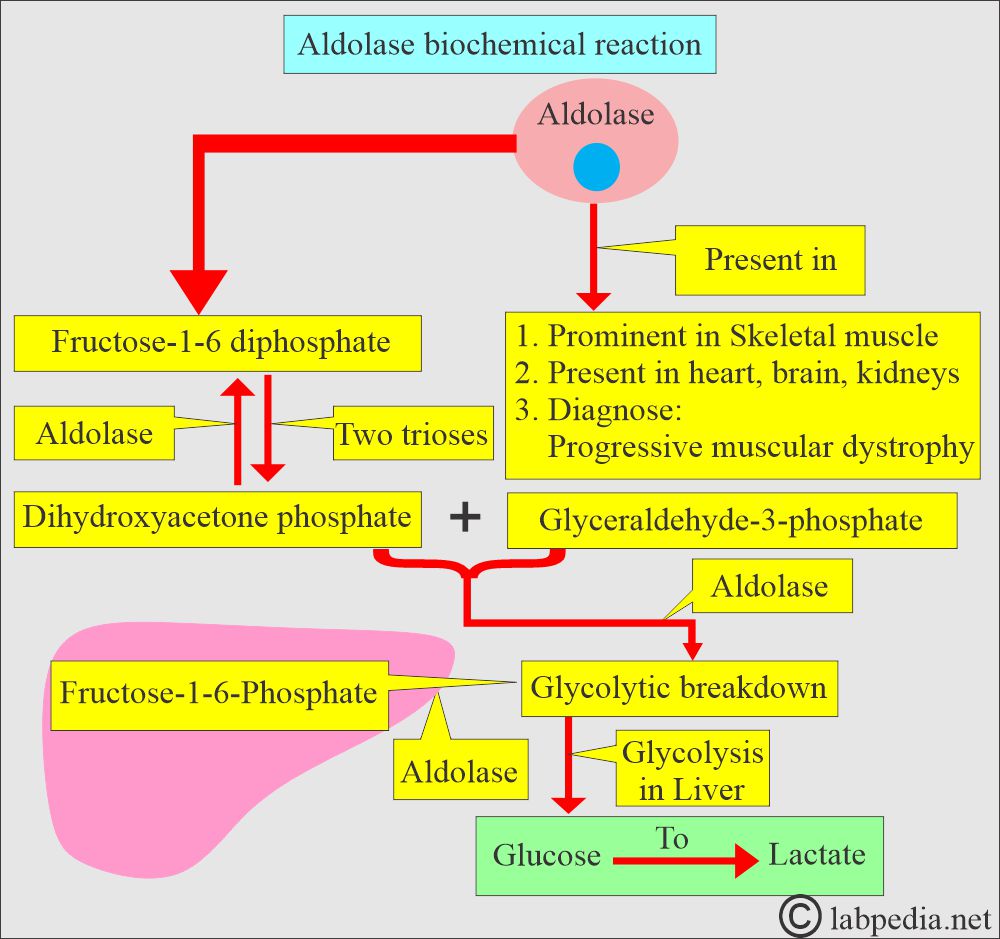
- Aldolase is a glycolytic enzyme that splits fructose-1,6-phosphatase into two triose phosphate molecules in glucose metabolism.
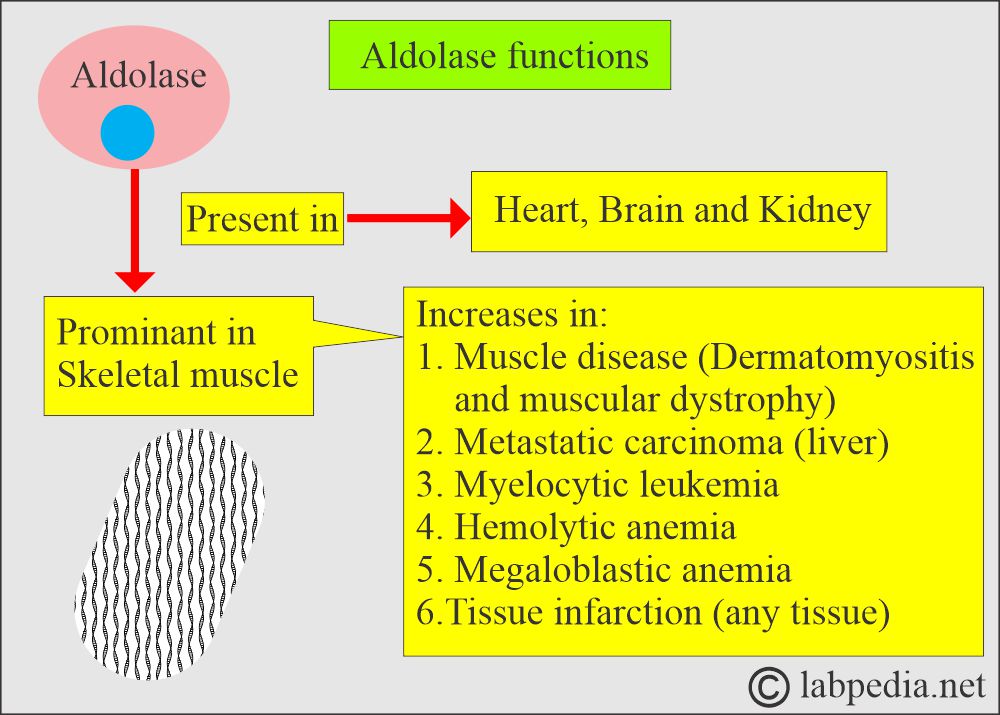
- Aldolase is present in all tissues, like the brain and kidneys, and is prominent in skeletal and heart muscles.
- Aldolase enzyme is present in the cell and the nucleus.
What is the chemical reaction of the Aldolase?
- It converts sugar to energy.
- Aldolase is described in different forms:
- Aldolase – A occurs in most of the tissues.
- Aldolase-B is seen in the liver and kidneys.
- This is a glycolytic enzyme, and it cleaves fructose – 1,6-bisphosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde – 3-phosphate.
- Fructose-1-phosphate is split into D-glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate by aldolase B, an enzyme found in the liver.
- Aldolase also takes part in glycolysis by attacking the fructose-1-6-PO4.
What is the clinical significance of Aldolase?
- For diagnosing muscular dystrophy, these tests are advised: CPK, AST, and Aldolase.
- The major use of aldolase is for the diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis.
- CPK is also raised, which is more sensitive and specific, so aldolase is not recommended.
- This is greatly increased in Duchenne-type pseudo hypertrophic muscle dystrophy compared to other muscular diseases.
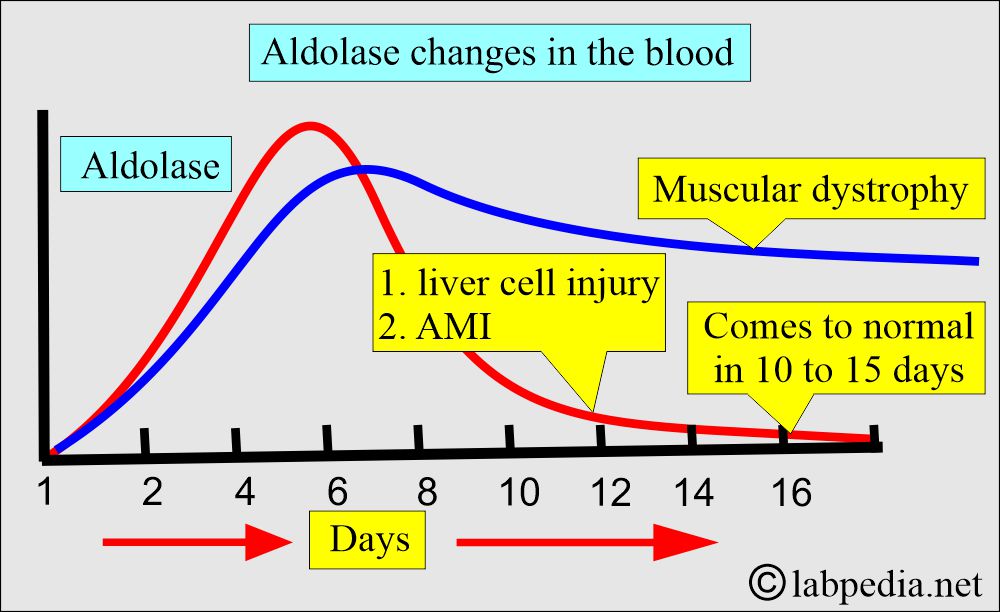
- It is high in the early stage.
- But it falls as the disease progresses.
- There is a 10 to 15 times increase over the normal level.
- This is raised in dermatomyositis and limb-girdle dystrophy.
- Normal values are seen in poliomyelitis, myasthenia gravis, and multiple sclerosis, where the origin of the muscle disease is neurogenic.
- It is usually normal in cirrhosis and obstructive jaundice.
- The aldolase pattern is like ALT, and it comes to normal in 10 to 15 days.
- This has the main interest in the primary disease of skeletal muscles.
- If the muscle disease is due to neurological causes, aldolase will be normal.
What are the normal Aldolase levels?
- Adult = 1.0 to 7.5 U /L
- Newborn = 4 x adult level
- Values are double in early childhood and then slowly fall to a normal level by 18 to 20 years of age.
- Children 10 to 24 months = 3.4 to 11.8 U/L
- child 25 months to 16 years = 1.2 to 8.8 U/L
Another source
- Adult = 22 to 59 mU/L at 37 °C (SI unit)
- Child = Approximately 2 times the adult value.
- Newborn = Approximately 4 times the adult value.
Another souArce
- Adult/elderly = 3.0 to 8.2 U/dL (22 to 59 mU at 37 °C).
- Levels are slightly higher in men than women due to increased muscle mass.
- Newborn = 2 to 4 times the adult level.
- Child = Approximately twice the adult result.
Another source
- Maternal serum = 9.5 (7.0) U/L
- Fetal serum = 23.2 (9.4) U/L
What are the causes of increased Aldolase levels?
- Cell destruction like Acute myocardial infarction (5 to 8 times the normal).
- Burns.
- Acute Hepatitis (Viral or toxic). It is raised in the early stage of viral or toxic hepatitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of muscles (Myopathy).
- Raised in skeletal muscle disease or injury.
- Raised in Muscular Dystrophy. It is raised in pseudo hypertrophic muscular dystrophy (as the CPK is also raised).
- Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy.
- Trauma involving the muscles.
- Carcinoma of the prostate (about 6 times the normal).
- Cancer involving the lung, breast, liver, GIT, or genitourinary system.
- Myelocytic leukemia (about 6 times the normal).
- Megaloblastic and hemolytic anemia (about 10 to 13 times the normal).
- In neoplastic diseases like carcinomatous metastasis to the liver, lung, breast, genitourinary system, melanoma, and CNS tumors.
- This may be raised in eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome.
- Trichinosis.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Gangrene.
- Melanoma.
What are the causes of decreased Aldolase levels?
- Hereditary fructose intolerance.
- This may indicate late muscular dystrophy.
What are the causes of normal Aldolase levels?
- Neurogenic muscle atrophy.
- Cirrhosis (or maybe slightly increased).
- Obstructive jaundice (or maybe slightly increased).
- This test is nonspecific and is not commonly requested except for follow-ups on muscle diseases.
- This is also not recommended because the CPK level is raised in all these conditions where aldolase is raised.
What is the importance of the treatment at the aldolase level?
- The increase in the level reflects the intensity of the disease, and one can measure it serially to determine the effect of corticosteroid treatment.
- CK is considered the test for muscular diseases.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the main function of Aldolase enzyme.
Question 2: What is the level of aldolase in neurogenic muscular atrophy?