Tumor Markers:- Part 13 – ACTH, HCG, Calcitonin
Adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH)
What sample is needed for ACTH?
- We need venous blood to prepare the serum.
- Ask the patient not to drink or eat after midnight of the sample to be drawn.
- Do not use steroids before this test because steroids increase the ACTH.
What are the indications for ACTH?
- This test will tell the production of ACTH by the anterior pituitary gland.
- It helps to diagnose primary and secondary adrenal gland dysfunction.
What are the precautions for ACTH?
- Estrogen, glucocorticoids, and oral contraceptives can decrease the value.
- Stress, whether it is mental or physical, can increase the level.
- Obesity also increases the level.
- Physical activity also increases the level.
- Blood glucose levels also interfere with the result.
- Radioactive scans can interfere with the result.
How will you define ACTH?
- The adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a peptide hormone secreted by adenohypophysis.
- It acts primarily on the adrenal cortex, stimulating its growth and synthesis of corticosteroids.
- This hormone is also known as corticotropin, corticotrophin, adrenocorticotrophin, and adrenocorticotropin.
What is the pathophysiology of ACTH?
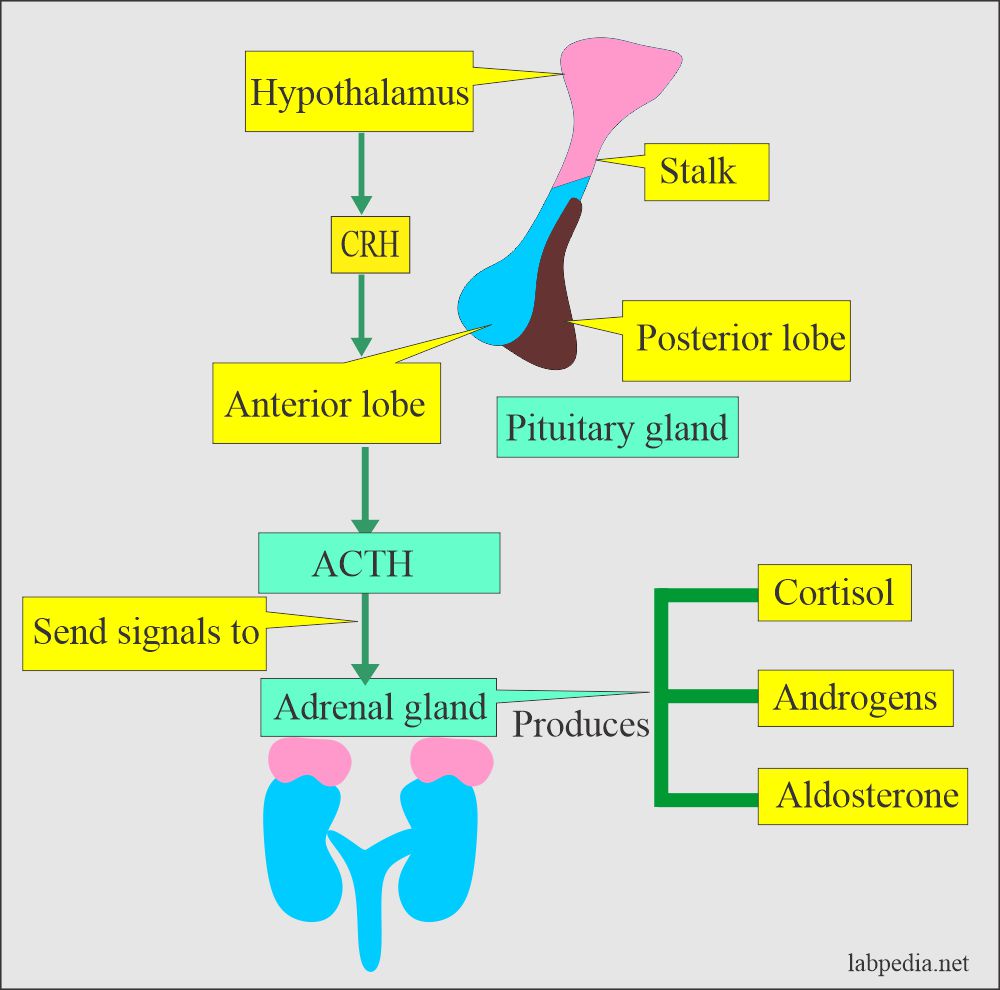
- ACTH hormone is synthesized by the anterior pituitary glands and stimulates the adrenal cortex.
- This is a polypeptide hormone produced by the corticotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland.
- ACTH is a tropic hormone; it binds to the adrenal cortex cells and influences their activities.
- ACTH in plasma is highest between 6 to 8 AM and lowest in the evening between 6 to 11 PM.
- ACTH secretion is increased during stress.
What is the control mechanism of ACTH?
- The hypothalamus produces corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary gland and releases ACTH.
- A high level of cortisol suppresses the CRH and ACTH.
- ACTH follows diurnal rhythem. There is a peak in the morning; then it decreases throughout the day.
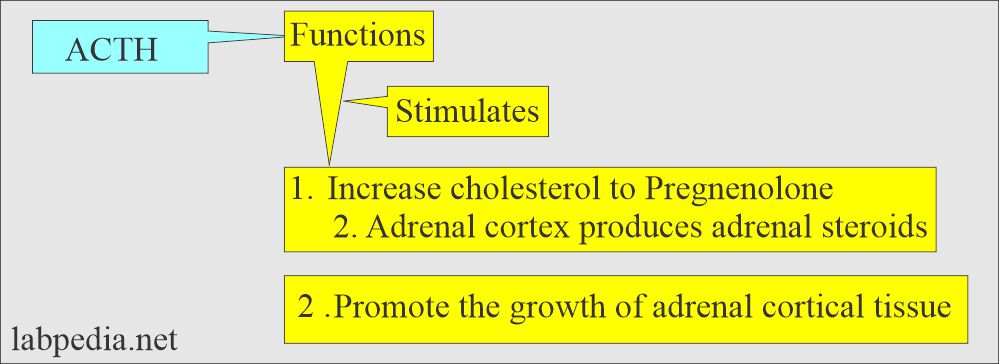
What are the functions of ACTH?
- It stimulates the adrenal cortex and promotes the production of glucocorticoids (Cortisol), mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone), and adrenal androgens.
- During stress, ACTH increases and increases cortisol production, which helps release physical or psychological stress.
- ACTH controls glucose metabolism, protein breakdown, and fat mobilization.
What is the normal ACTH level?
- AM level = <80 pg/mL (<18 pmol/L).
- PM level = <50 pg/mL (<11 pmol/L).
Another reference
- 9 to 52 pg/mL (2 to 11 pmol/L)
Another source
- 8 AM = Fasting = Adult, child, and elders = 15 to 100 pg/mL (10 to 80 ng//L).
- 4 PM = Nonfasting = 10 to 50 pg/mL (10 to 50 ng/L).
- Newborn = 10 to 185 pg/mL.
What are the causes of raised ACTH levels?
- ACTH may be raised as primary or ectopic production.
- Ectopic production from:
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung ( >200 ng/L).
- Pancreatic carcinoma.
- Breast.
- Stomach.
- Colon.
- Benign conditions are:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Mental depression.
- Obesity.
- Hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Stress.
- In primary adrenal deficiency.
- In patients with Cushing’s syndrome.
- In patients with ectopic tumors, e.g.
- Basophilic neoplasm of the anterior pituitary.
- Ectopic carcinoma of the lung.
- Addison’s disease.
- Cushing’s disease.
What are the causes of decreased ACTH?
- Secondary adrenal insufficiency is due to pituitary dysfunction, where the cortisol level is low.
- ACTH in a normal person does not exceed 50 pg/mL at its peak, and the basal level is near 5 pg/mL.
Human Chorionic gonadotropin hormone (HCG)
What sample is needed for HCG?
- Collect venous blood to prepare serum.
What are the indications for HCG?
- This test is advised to diagnose pregnancy or abortion.
- This test is also advised for the diagnosis of a hydatidiform mole.
- HCG is also advised for some cancers.
What are the precautions for the estimation of HCG?
- Avoid hemolysed, icteric, or lipemic serum.
- Excessive secretion of luteinizing hormone leads to false positive results.
- HCG-producing tumors may cause false positive results in a test conducted for pregnancy.
- Anticonvulsants, hypnotics, tranquilizers, and antiparkinsonian drugs may lead to false positive results.
- Heparine and phenothiazines may decrease HCG levels.
- May see false negative results in early pregnancy, threatened abortion, and ectopic pregnancy.
- Proteinuria and hematuria cause false positive results.
- Diuretics and promethazine may cause false negative urine tests.
How will you define human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) hormone?
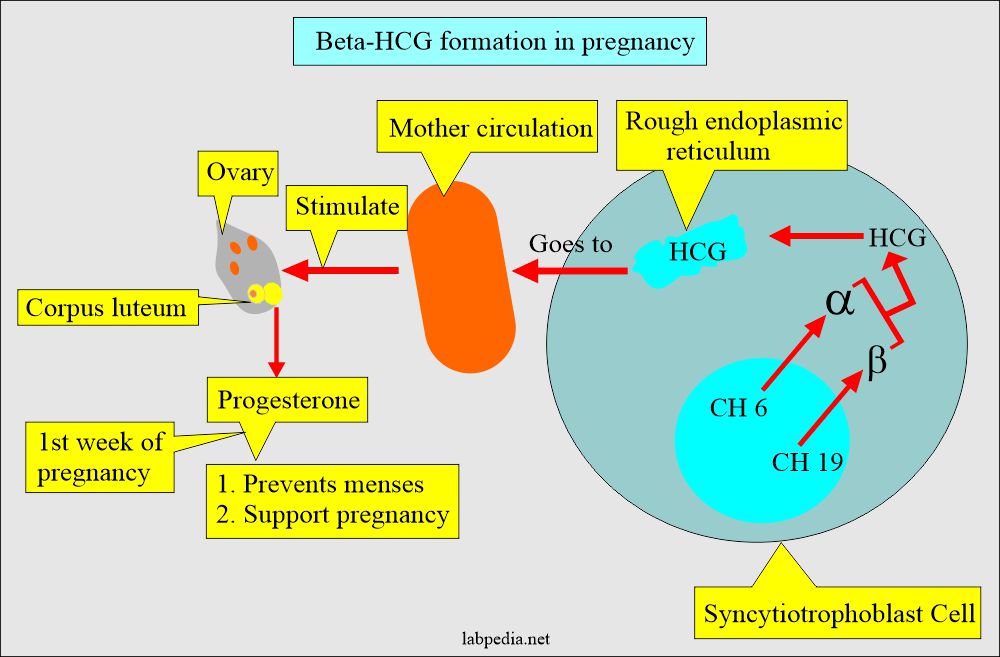
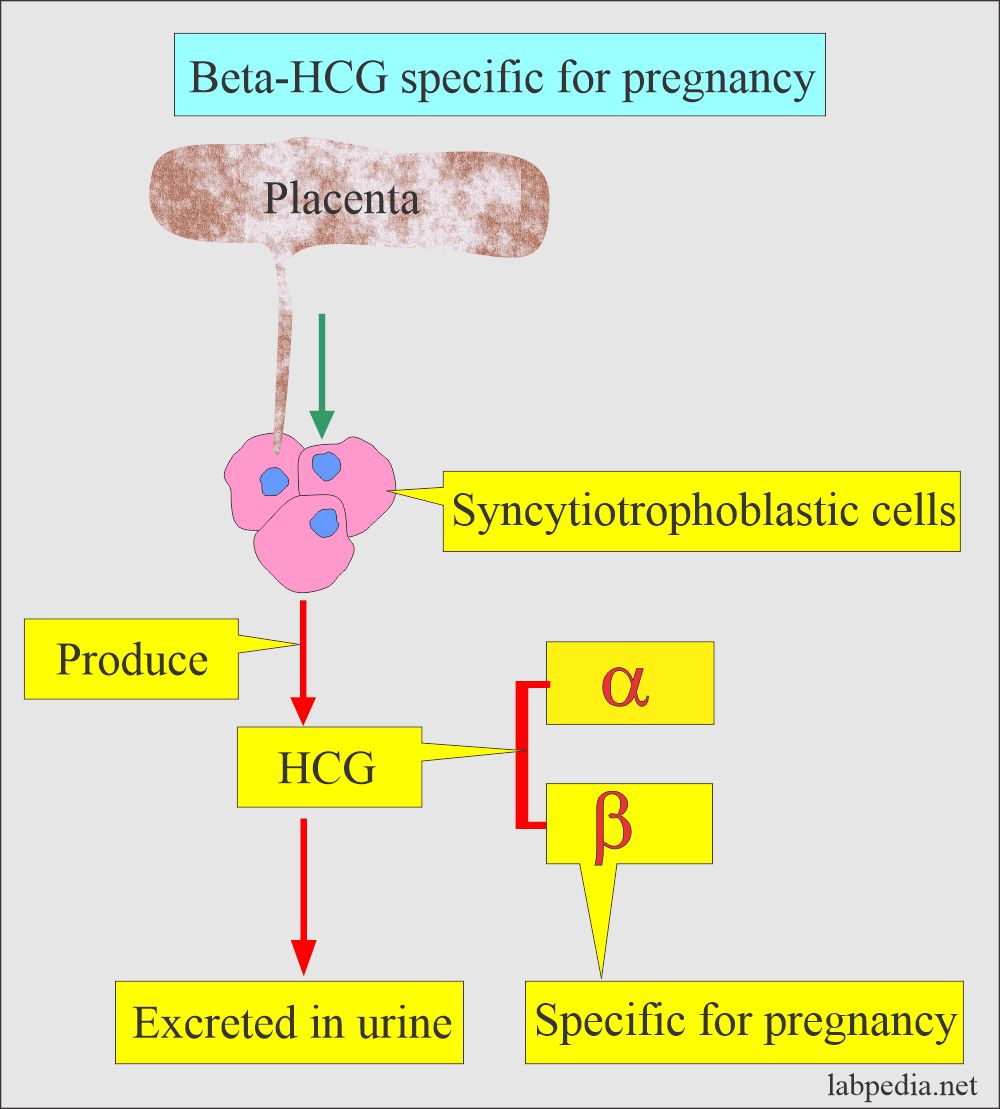
- Chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the placenta’s syncytiotrophoblast cells during pregnancy.
- HCG has a vital role in the maintenance of the pregnancy and the development of the fetal parts.
What is the structure of the HCG hormone?
- This is also called Chorionic gonadotropin.
- This is a glycoprotein secreted by the syncytiotrophoblastic cells of the placenta.
- This consists of two subunits:
- α- HCG:
- It is shared with other glycoproteins like LH, FSH, and TSH.
- β-HCG:
- It is unique to HCG and provides biological properties.
- α- HCG:
What are the functions of HCG?
- It maintains the pregnancy.
- It helps in fetal development.
- It stimulates the fetal testes to produce testosterone hormone, which will help in male differentiation.
- It suppresses the mother’s immune system against the fetal tissue.
What is the normal HCG?
- Male and nonpregnant females serum = Negative or <5 mIU/mL.
- Urine = Negative in males and nonpregnant females.
- Pregnant women:
- Serum = 0 to 14 weeks of gestation = 100mIU/mL (rising level).
- Urine = First trimester = up to 500,000 IU.
- Second trimester = 10,000 to 25,000 IU.
- Third trimester = 5,000 to 15,000 IU.
What are the causes of raised HCG levels?
- Elevated HCG level is seen in:
- Trophoblastic disease (level is usually >one million IU/L).
- Germ cell tumors and non-seminomatous tumors of the testis (there is a moderate increase).
- Reported in melanoma and carcinoma of the breast, GIT tumors, lung, and ovary.
- The presence of HCG in seminoma indicates another component of choriocarcinoma.
- Also raised in benign conditions like:
- Cirrhosis.
- Duodenal ulcer.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Pregnancy.
Calcitonin
What sample is needed for the Calcitonin level?
- Please get venous blood to prepare the serum.
- A fasting sample is needed.
- Heparinize and chill the sample immediately.
- If the test is not performed immediately, then freeze the sample.
What are the precautions for Calcitonin levels?
- Calcitonin is usually raised in pregnancy at term and in the newborn.
- Avoid gross lipemia and hemolysis.
What are the indications for Calcitonin?
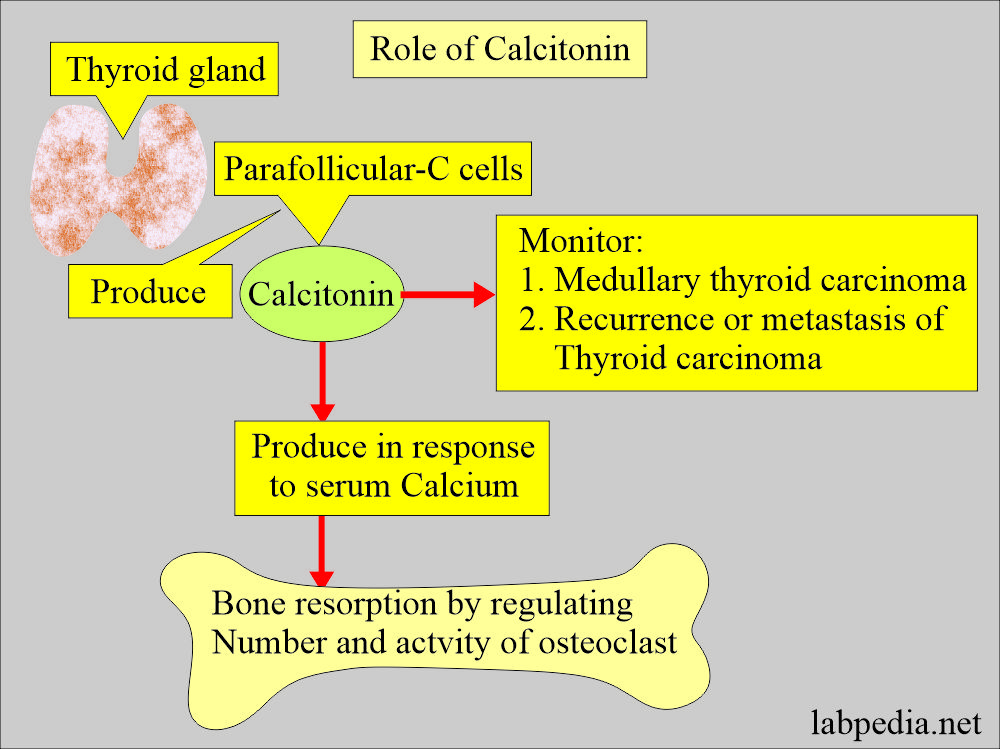
- It is advised for the diagnosis of recurrence of medullary carcinoma.
- It is also advised in metastases after the removal of the primary tumor.
- Calcitonin is advised with basal value after the surgery to see complete removal.
How will you define Calcitonin?
- This is a polypeptide with 32 amino acids.
- This is produced by the parafollicular C cells of the thyroid.
- The serum half-life is 12 minutes.
- In a normal person, it is <0.1 µg /L.
- There is circadian variation in the calcitonin level, and the peak level is after lunchtime.
What is the mechanism of calcitonin on bone?
- Calcitonin acts directly on osteoclasts to decrease bone-resorbing activity and leads to a decrease in calcium levels.
- Calcitonin inhibits bone resorption by regulating the number and activity of the osteoclast.
- This is produced in response to increased serum calcium levels. This response is directly related to calcium levels.
- Calcitonin helps monitor disease after treatment.
- It inhibits the release of calcium from the bone and lowers serum calcium.
What is the normal Calcitonin level?
Source 2
- Basal (plasma)
- Male = ≤19 pg/mL (≤19 ng/L)
- Female = ≤14 pg/mL (≤14 ng/L)
- Calcium infusion (2.4 mg/kg)
- Male = ≤190 pg/mL (≤190 ng/L)
- Femal = ≤130 pg/mL (≤130 ng/L)
- Pentagastrin injection (0.5 µg/kg)
- Male = ≤110 pg/mL (≤110 ng/L)
- Female = ≤30 pg/mL (≤30 ng/L)
Another source
- Male = <8pg/mL,
- Female = <6 pg/mL.
What are the causes of increased Calcitonin?
- A basal fasting level of calcitonin may be increased in patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, even in the absence of a palpable mass.
- Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. The level is >2000 pg/mL and is always associated with medullary carcinoma.
- A level of 500 to 2000 pg/mL generally indicates medullary carcinoma of the thyroid but is also seen in renal failure or ectopic production of calcitonin.
- A level of 100 pg/mL to 500 pg/mL should be interpreted carefully, and the provocative test should be performed; if the repeat test after 1 to 2 months is abnormal, thyroidectomy should be advised.
- Myeloproliferative disorders.
- Carcinoid tumor.
- Lung cancers.
- Breast cancer.
- Kidney tumor.
- Liver tumor.
What are the causes of increased Calcitonin levels in nonmalignant conditions?
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
- Pulmonary disease.
- Pancreatitis.
- Hyperparathyroidism.
- Paget’s disease of bone.
- Pregnancy.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Newborn.
- Chronic renal failure.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of calcitonin in the diagnosis?
Question 2: In which condition ACTH is raised?