Tumor Markers:- Part 2 – Tumor Markers for Various Organs and Monoclonal Antibody
Tumor Markers for various organs
- There are specific markers for diagnosing tumors from the various organs in the human body.
Markers For thyroid tumors:
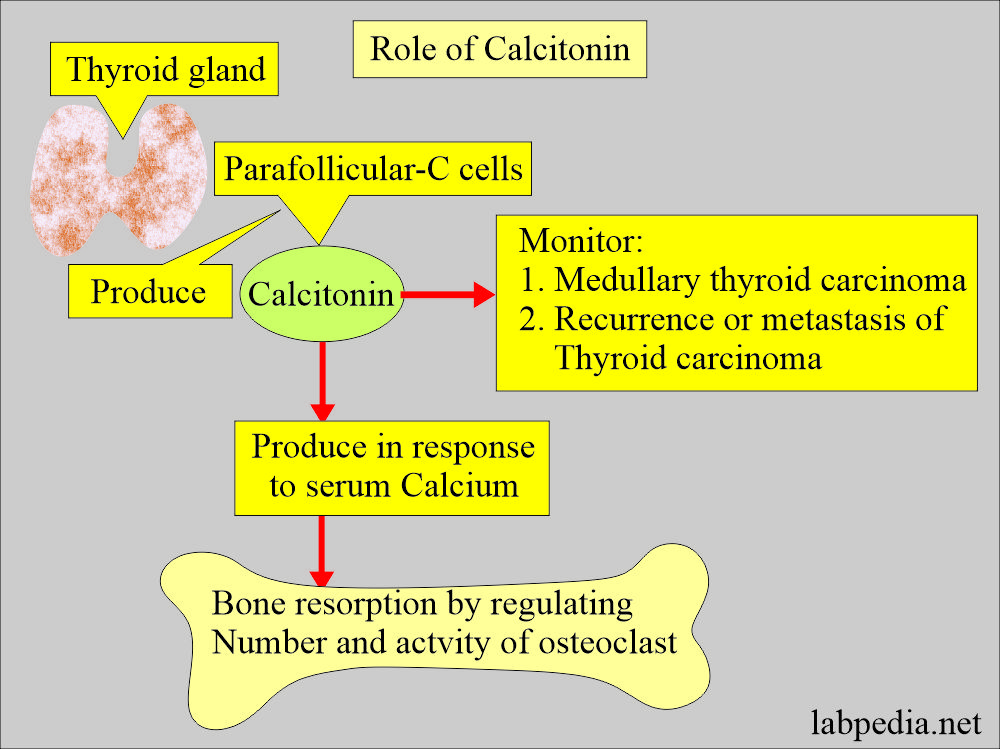
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma:
- Calcitonin.
- CEA may be elevated in some cases.
- Papillary and follicular carcinoma:
- Thyroglobulin.
- Anti-thyroglobulin antibody.
Markers For breast tumors:
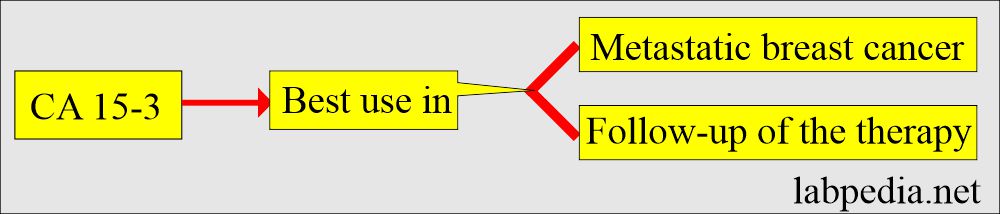
- CA 15-3.
- CA 27.29
- CA 549.
- ER/PR receptors.
- HER2/neu.
- CK-BB.
- BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 mutation.
- CEA may be elevated in metastatic cancer.
Markers For Testicular tumors:
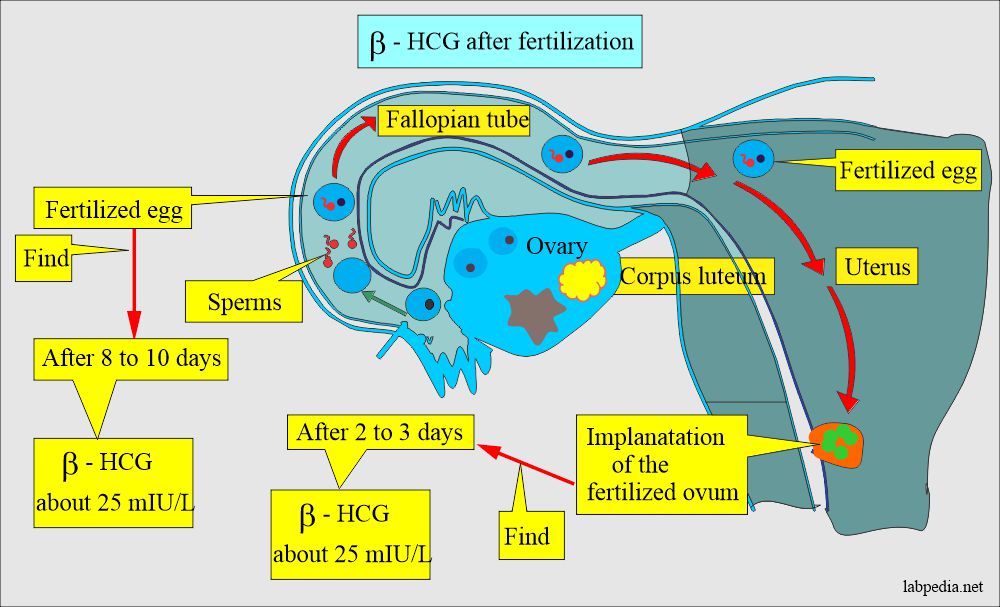
- HCG (β-HCG).
- AFP.
- Calcitonin.
- LDH.
- Placental alkaline phosphatase
Markers For Prostatic tumors:
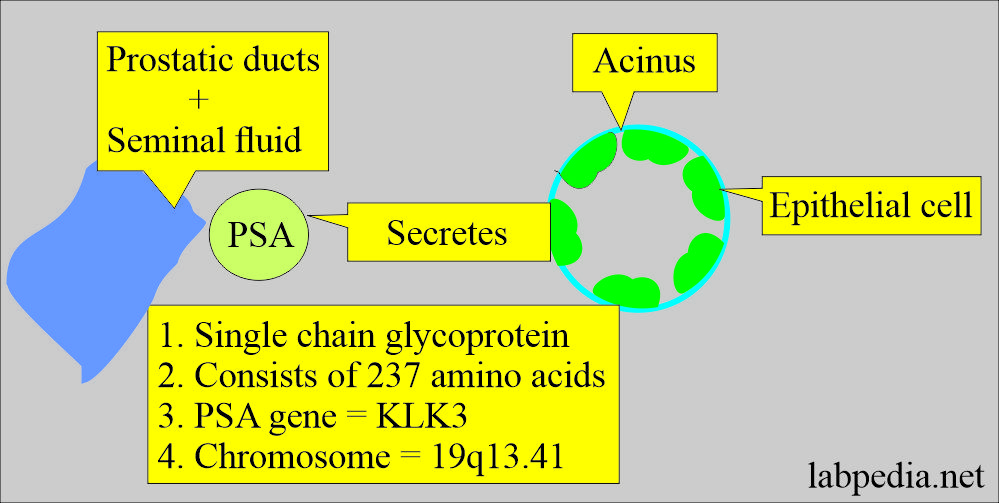
- PSA.
- CA 549.
- PAP.
Markers For Bone tumors:
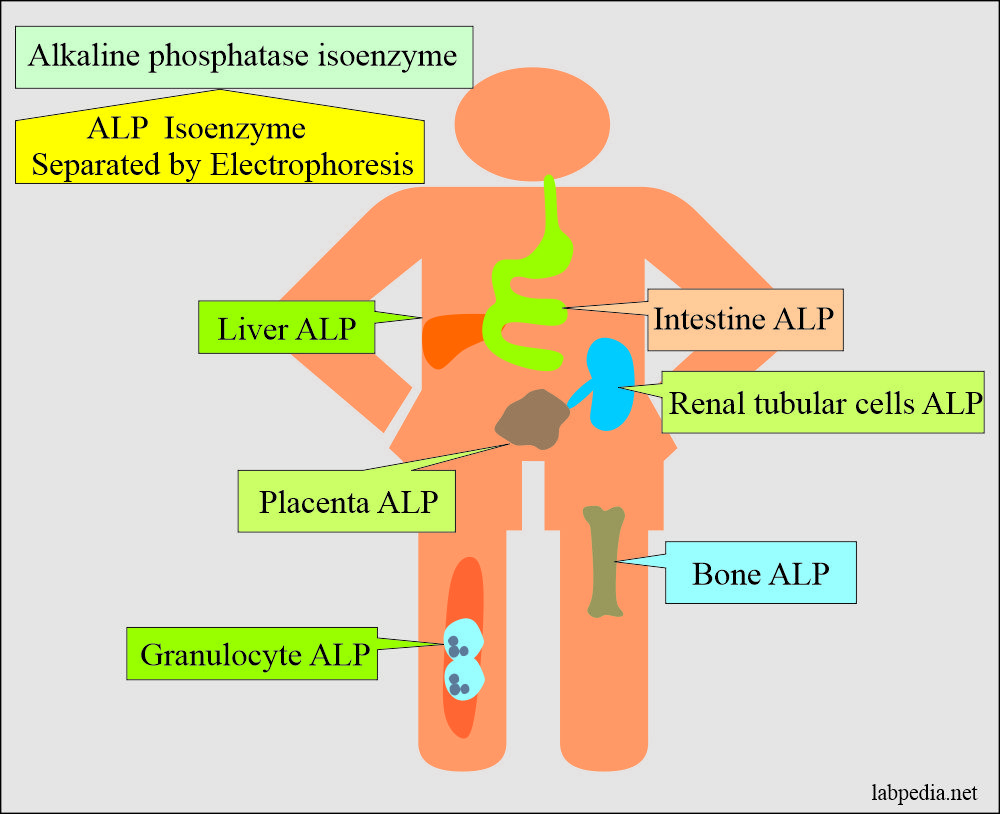
- Alkaline phosphatase.
- LDH.
Markers For Lung tumors:
- CA 15-3.
- CA 549.
- CK-BB.
- Neuron- specific enolase (NSE).
- CEA.
Markers For Liver tumors:
- AFP.
- Alkaline phosphatase.
- CA 19-9.
- LDH.

Markers For Gastrointestinal tumors:
- CEA.
- CA 50.
- CA 19-5.
- CA 19-9
- CA 72-4.
Markers For Colorectal tumors:
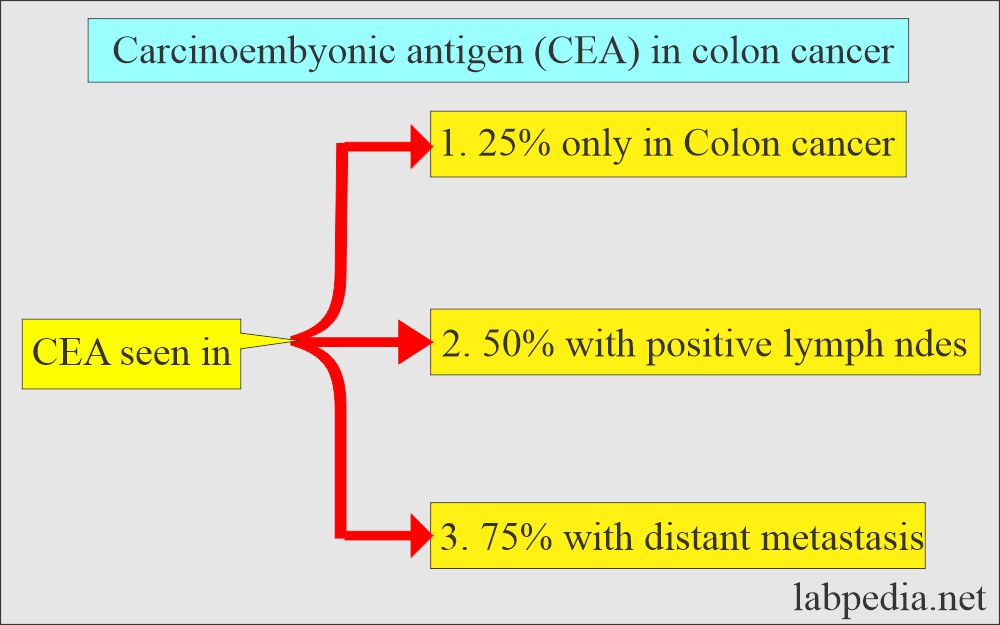
- CEA.
- CA 15-3
- CA 19-9.
- CA 50.
Markers For Ovarian tumors:
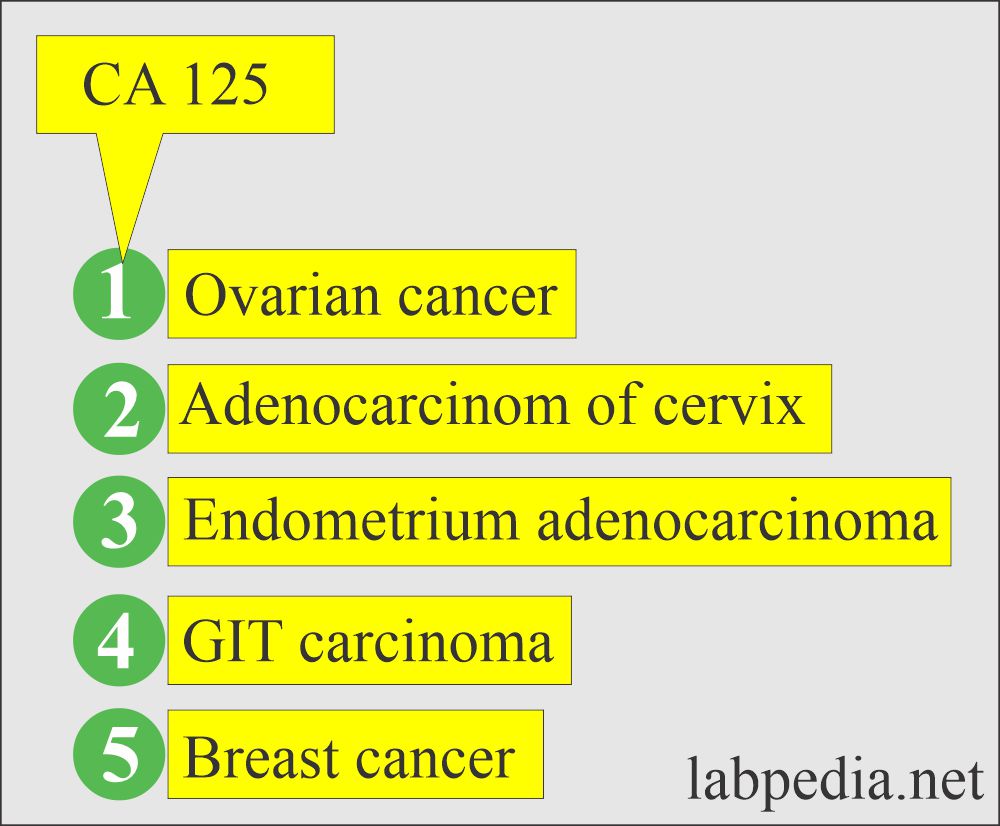
- CA 125.
- CA 15-3
- CA 549.
- CK-BB.
- CA 72-4.
Markers For Pancreatic tumors:
- CEA.
- CA 50.
- CA 19-9.
- CA 15-3.
Monoclonal tumor markers
- How will you define monoclonal antibodies:
- These antibodies are molecules produced in laboratories and bind specifically to a single site like a protein or antigen site.
- These are produced by a single clone of the immune cells and are identical in structure.
- What is the mechanism of monoclonal antibody:
- Each monoclonal antibody reacts with a specific epitope on an antigen.
- These can be used for diagnosis, therapeutic use, and research.
- The first tumor marker was the Bence-Jones protein for multiple myeloma.
- α – fetoprotein was discovered in 1963.
- CEA was discovered in 1965.
- These are defined as antigens on the tumors, which monoclonal antibodies can identify.
- These markers are more specific and sensitive.
| Monoclonal antibodies | Specific for the tumors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|