Coagulation:- part 3 – Critical Coagulation Tests
Critical Coagulation Tests
What tests are advised for screening of coagulation abnormalities?
- Platelet count (140,000 to 340,000 /cmm).
- Bleeding time (Ivy method <4 min and Duke method 1 to 4 min).
- Clot retraction is a qualitative process that begins within 30 to 60 minutes and is typically completed within 24 hours, but usually within 6 hours.
- Coagulation time or clotting time (5 to 15 minutes in glass tubes and 19 to 60 minutes in the siliconized tube).
- Fibrinolysins are negative.
- Prothrombin time, one stage (same as control, and it should be 11 to 16 seconds).
- Thromboplastin generation time (compared to normal control).
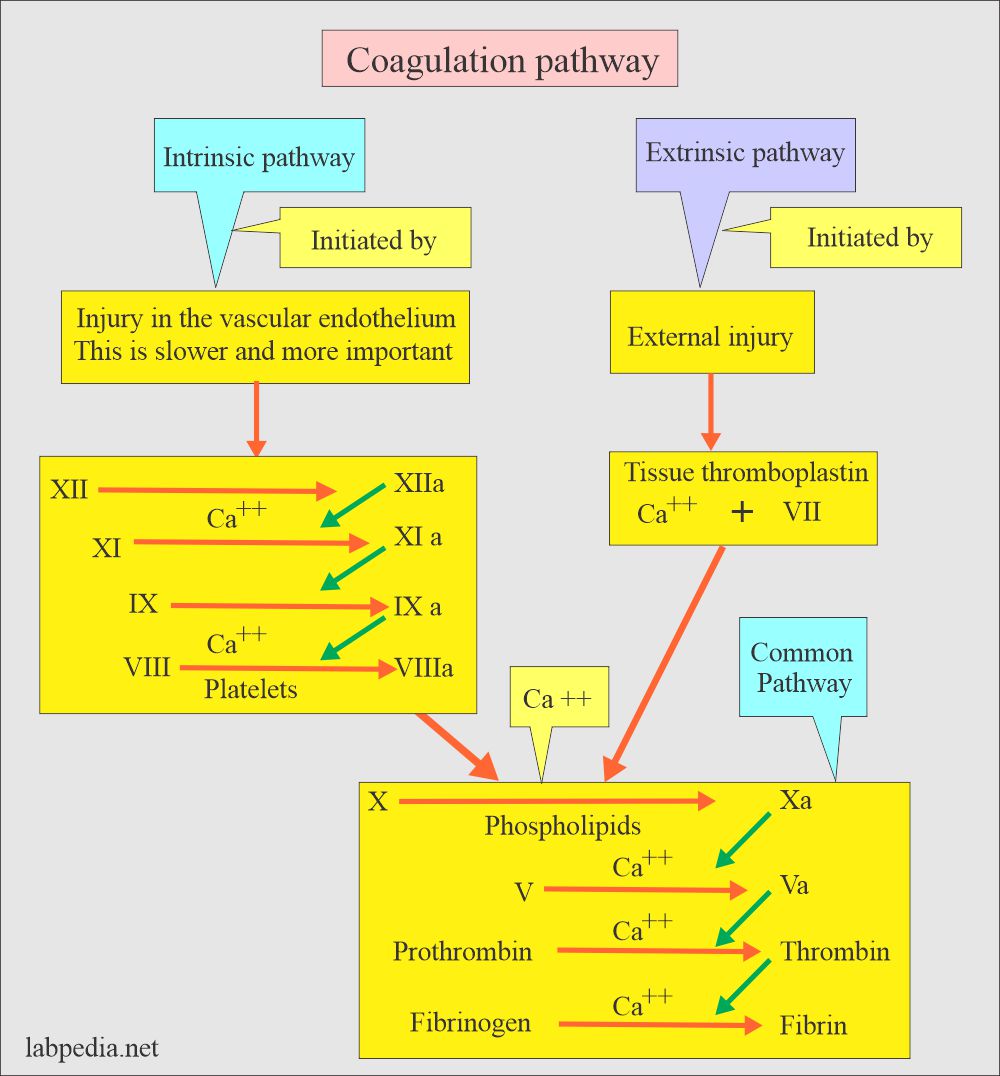
- To measure the intrinsic system, advise:
- Activated partial thromboplastin APTT.
- To measure the extrinsic system, advise:
- One stage prothrombin time PT.
What is the critical coagulation screening test workup?
| Test | Normal values | Normal values source (4) | Critical values (source 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
What are the critical values of the blood coagulation screening tests?
- Platelets = <50,000/cmm or > 1 million/cmm.
- APTT = >70 seconds.
- PTT = >100 seconds.
- Fibrinogen = <100 mg/dL.
What are the differential diagnoses of bleeding disorders?
| APTT | PT | Platelets count | Causes of bleeding disorders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the critical value of fibrinogen?
Question 2: What is the critical value of APTT?