Anemia:- Part 3 – Megaloblastic Anemia, Macrocytic, Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid Deficiency
Megaloblastic Anemia
What sample is needed for Megaloblastic Anemias?
- Prepare the peripheral blood smears.
- Can take blood in EDTA.
- Also, a direct fresh blood smear can be made.
- Take blood for the study of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
- A bone marrow examination may be needed.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Megaloblastic Anemia?
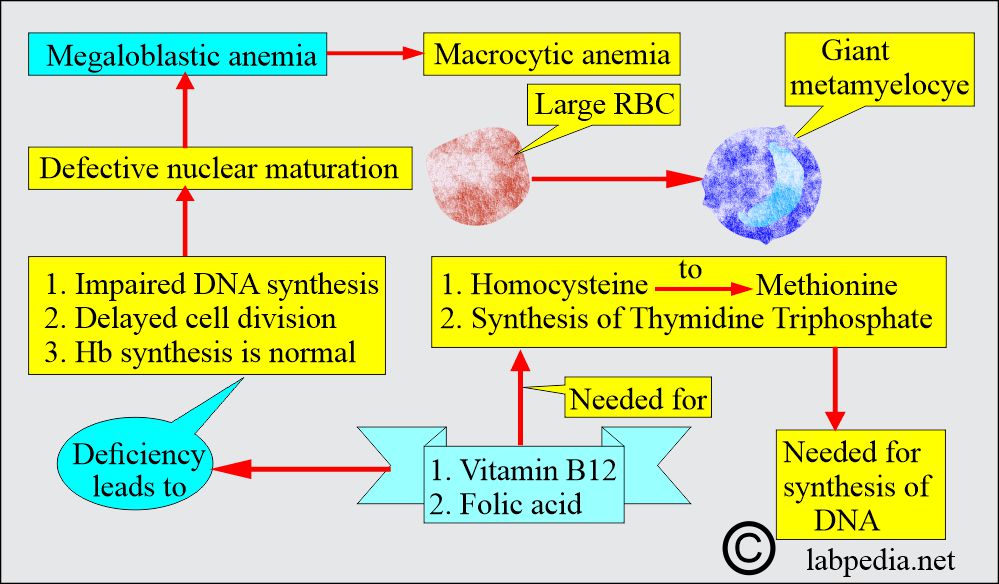
- Megaloblastic anemia is a subgroup of macrocytic anemia characterized by defective nuclear maturation.
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis is defective.
- Vitamin B12 and folic acid are needed to synthesize thymidine triphosphate and convert Homocysteine to Methionine.
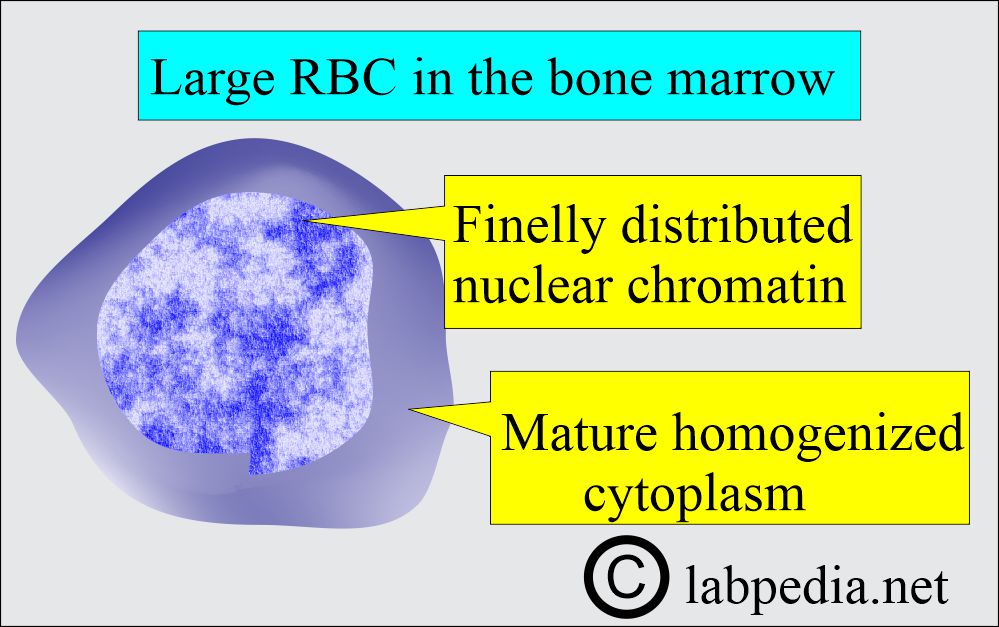
- Megaloblasts, large and abnormal RBC precursors in the bone marrow, and macrocytes in the peripheral blood smear are present.
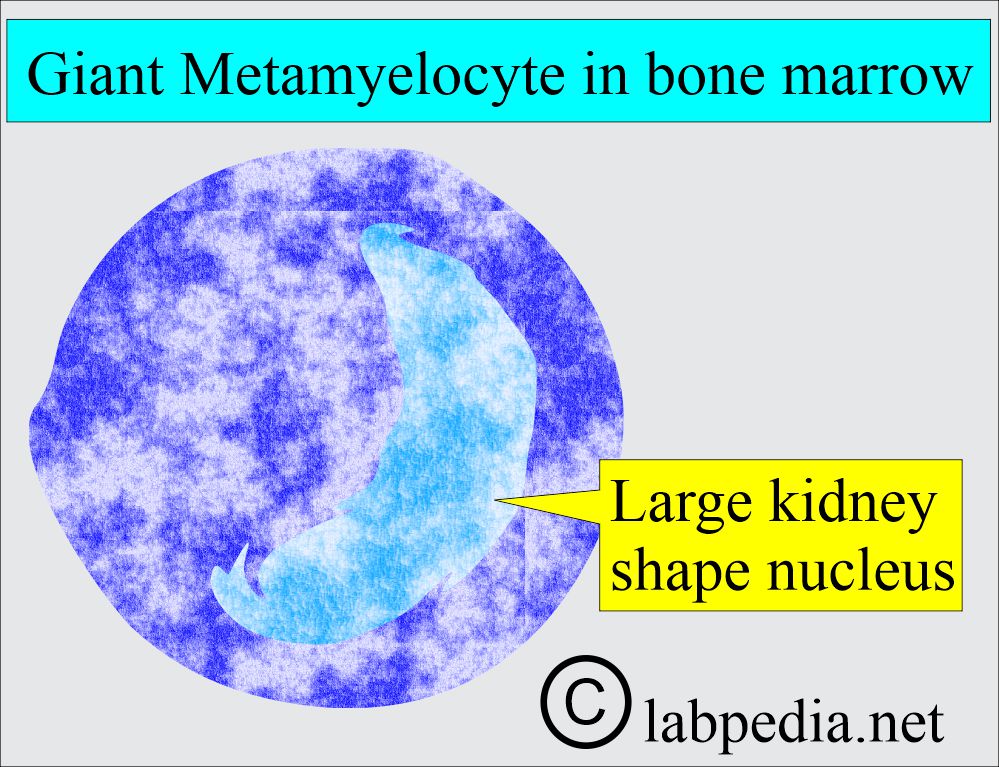
- White blood cells showing giant metamyelocytes in the bone marrow are a characteristic feature.
- Megakaryocytes are also abnormal.
How will you classify megaloblastic anemias?
- Megaloblastic anemia may be of three types:
- Anemia is caused by folate deficiency.
- Anemia is caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Anemia occurs when there is no response to either treatment. This third group does not respond to vitamin B12 or folic acid therapy.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
What is the mechanism of vitamin B12 deficiency?
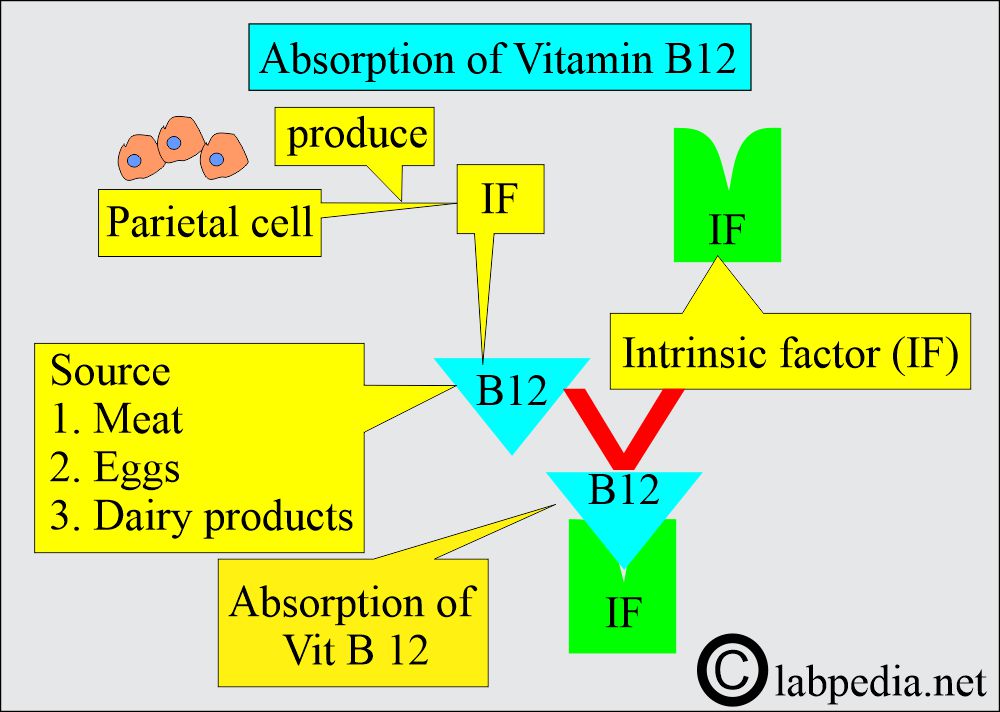
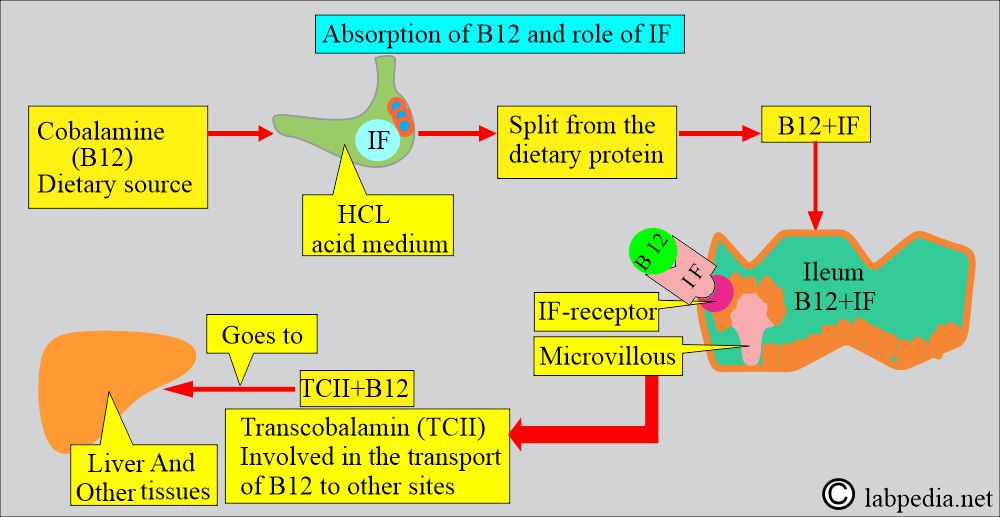
- Vitamin B12 sources are meat, eggs, and dairy products.
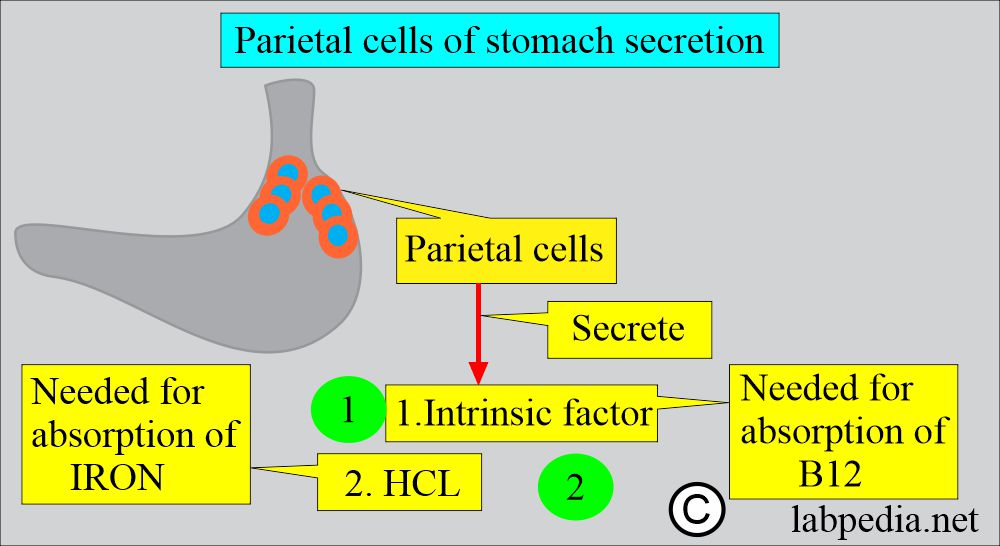
- Gastric parietal cells secrete the Intrinsic factor, which binds to B12 and allows its absorption in the ileum.
What are the causes of Vitamin B12 deficiency?
- Decreased intake in the diet.
- Poor diet.
- Vegetarians.
- Malabsorption due to any cause, e.g., gastrectomy (partial or complete), antibodies to intrinsic factor, sprue, celiac disease, malignancies (lymphomas), and parasitic infestation.
- Intestinal causes:
- Jejunal diverticulosis.
- Blind loop stricture.
- Ileal resection.
- Fish tapeworms.
- Increased demand of the body:
- During pregnancy.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Malignant tumors.
- Enzyme deficiency.
Folate deficiency
What are the causes of Folate deficiency?
- Decreased intake:
- Poor diet.
- Inadequate use of vegetables.
- In alcoholism.
- Malabsorption like:
- Steatorrhea.
- Tropical sprue.
- Celiac disease.
- Gluten-induced enteropathy.
- Partial gastrectomy (in some cases).
- Extensive jejunal resection.
- Pathological causes like:
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Myelofibrosis.
- Malignant diseases like:
- Carcinoma.
- Myeloma.
- Lymphoma.
- Increased demand of the body:
- Infancy.
- Pregnancy.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Malignant tumors.
- Drugs:
- Phenytoin.
- Oral contraceptives.
- Folic acid antagonists like triamterene and trimethoprim.
- Anticonvulsant
- Sulfasalazine.
- Inflammatory diseases of the GIT:
- Crohn’s disease.
- Tuberculosis.
- Psoriasis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Exfoliative dermatitis.
- Enzyme deficiency:
What is the clinical presentation of megaloblastic anemia?
- The onset is insidious, and signs and symptoms of anemia gradually appear.
- The patient may have mild jaundice due to an excessive breakdown of RBCs.
- There is glossitis, which is the beefy-red sore tongue.
- There is angular stomatitis.
- The patient may lose weight due to malabsorption.
- There is a purpura due to thrombocytopenia.
- There is pigmentation; the cause is unknown and may be the presenting feature.
- In the case of Vitamin B12 or Folate, deficiency leads to:
- Megaloblastic anemia.
- Neuropathy is only due to a deficiency of Vitamin B12.
- Melanin skin pigmentation.
- Infertility.
- There is a decreased osteoblastic activity.
- There may be a neural tube defect in the fetus.
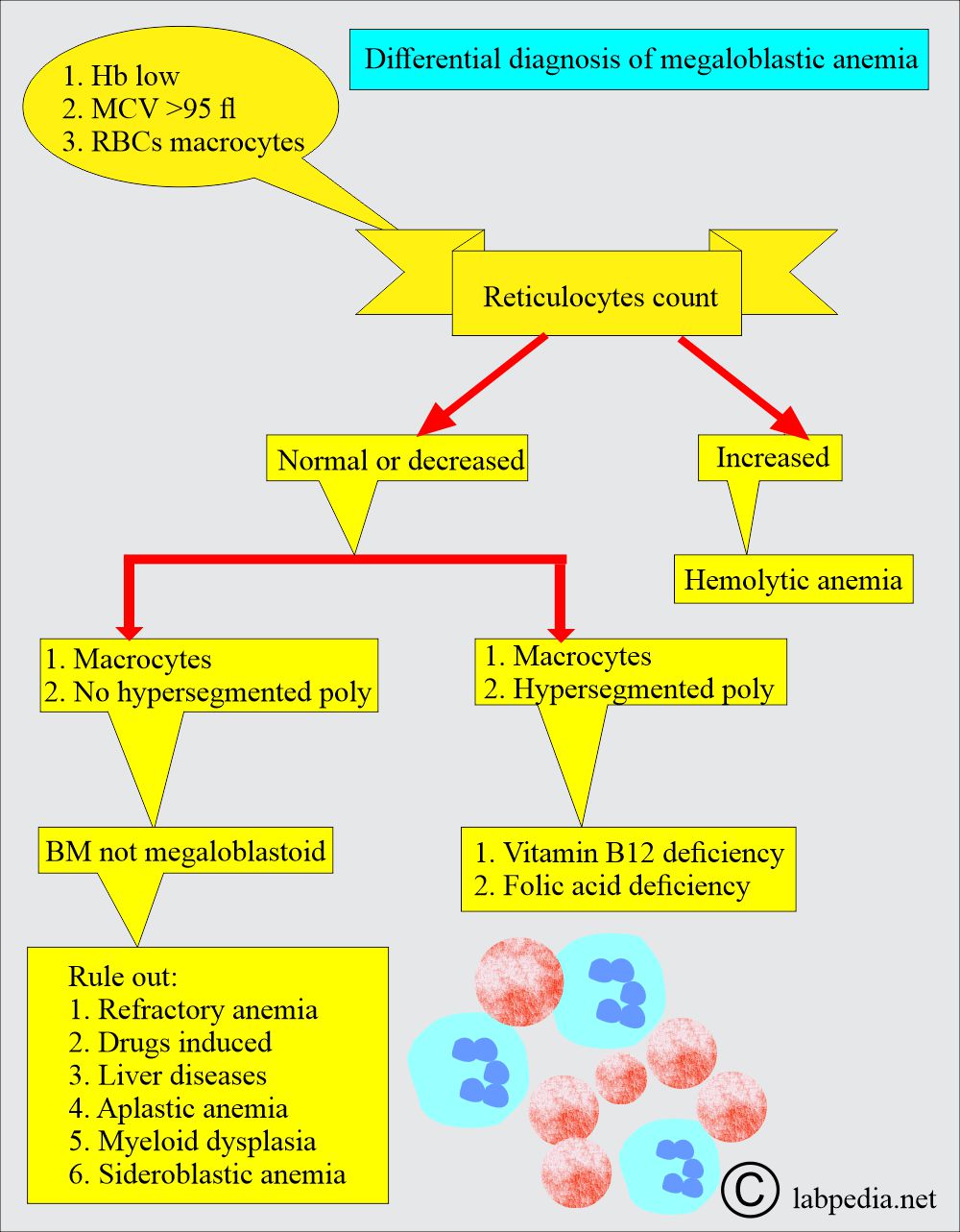
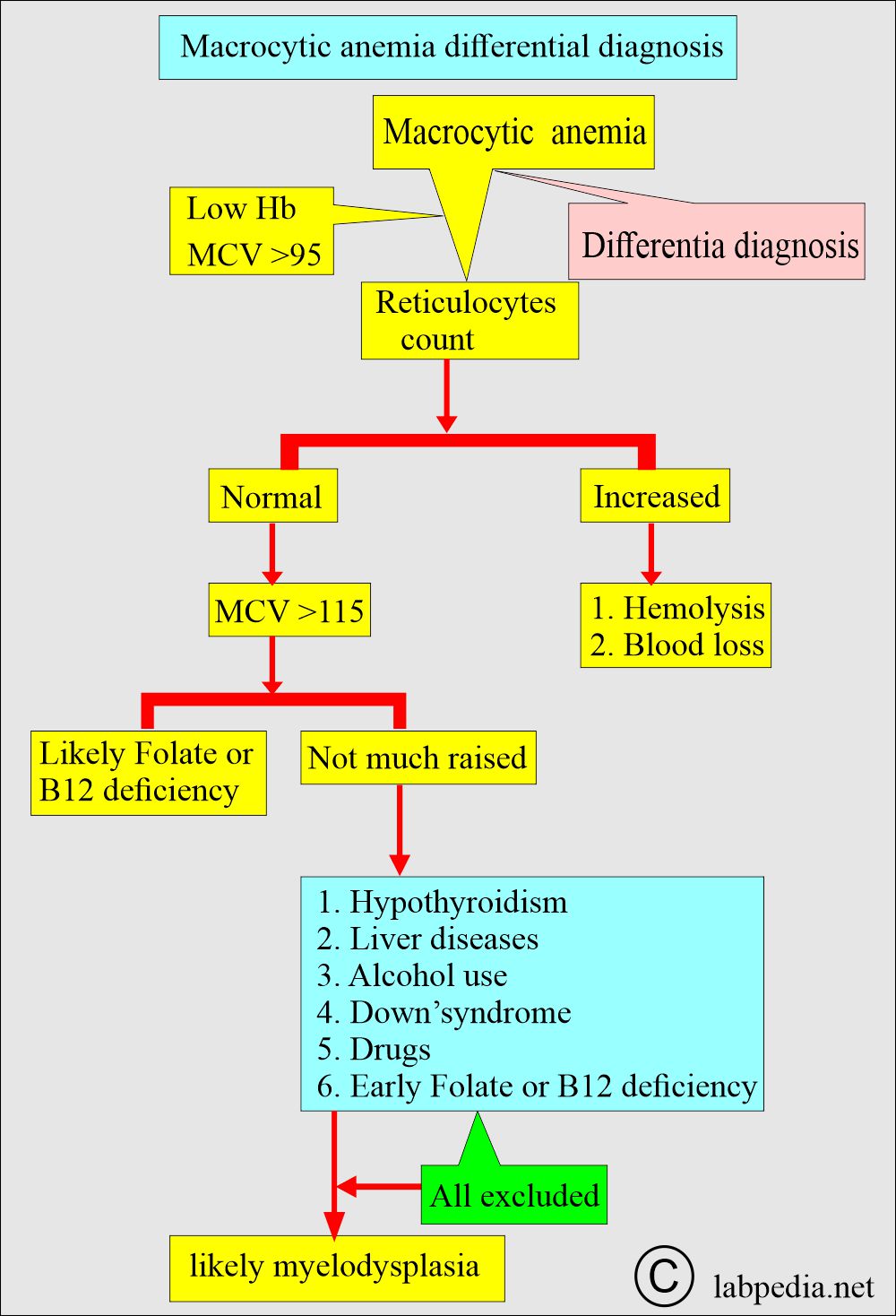
What are the laboratory findings of megaloblastic anemia?
- MCV:
- It is increased to 110 to 115 fl, where the normal value is 77 to 93 fl.
- MCV >99 fL, Increased MCV (>95 ) may reach 100 to 140 µm2.
- MCH:
- It is slightly increased; the normal value is 27 to 32 pg.
- MCHC:
- It is within normal limits, where the normal value is 20 to 25 g/dl.
- It is within normal limits, where the normal value is 20 to 25 g/dl.
- Low hemoglobin.:
- Hemoglobin is typically low (may reach 2 g/dL).
- The peripheral blood:
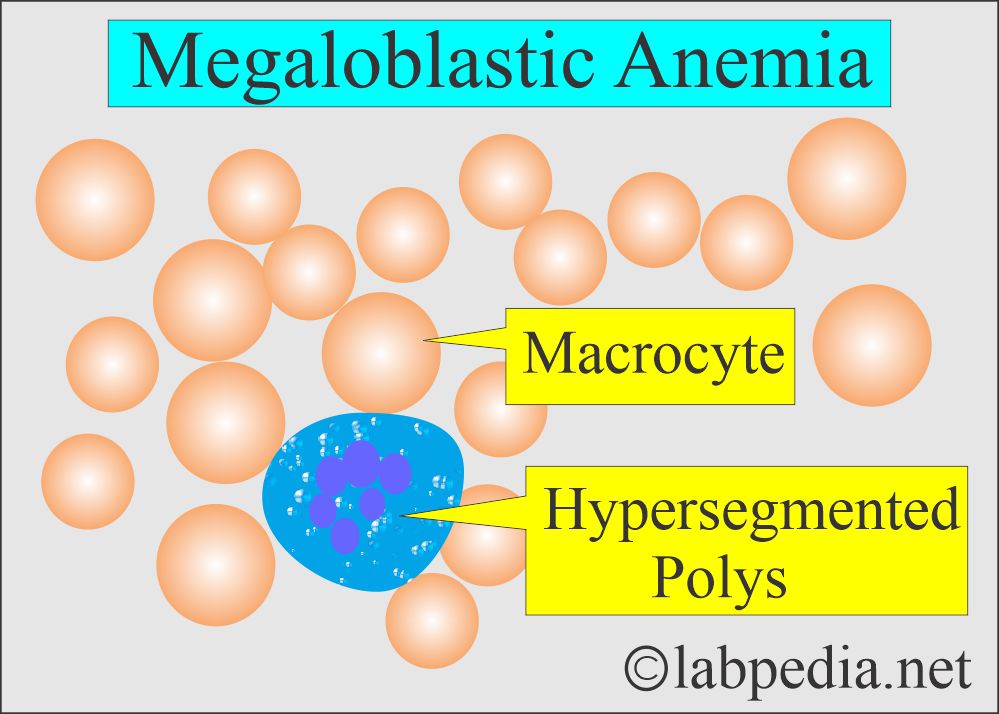
- It shows macrocytosis and many hypersegmented neutrophils.
- Occasionally, you may see leucopenia and thrombocytopenia.
- Reticulocytes:
- These are not in comparison to the degree of anemia.
What is the picture of megaloblastic anemia on a Peripheral blood smear?
- Hemoglobin is reduced to 9 to 10 G /dl.
- The total RBC count is reduced.
- WBCs are normal or decreased. Around 5% of Polyps have more than 5 lobes; normally, these have 3 to 4 lobes.
- DLC shows marked neutropenia and relative lymphocytosis. There are macrocytes (macroovalocytes) or hypersegmented neutrophils; these are characteristics of megaloblastic anemia.
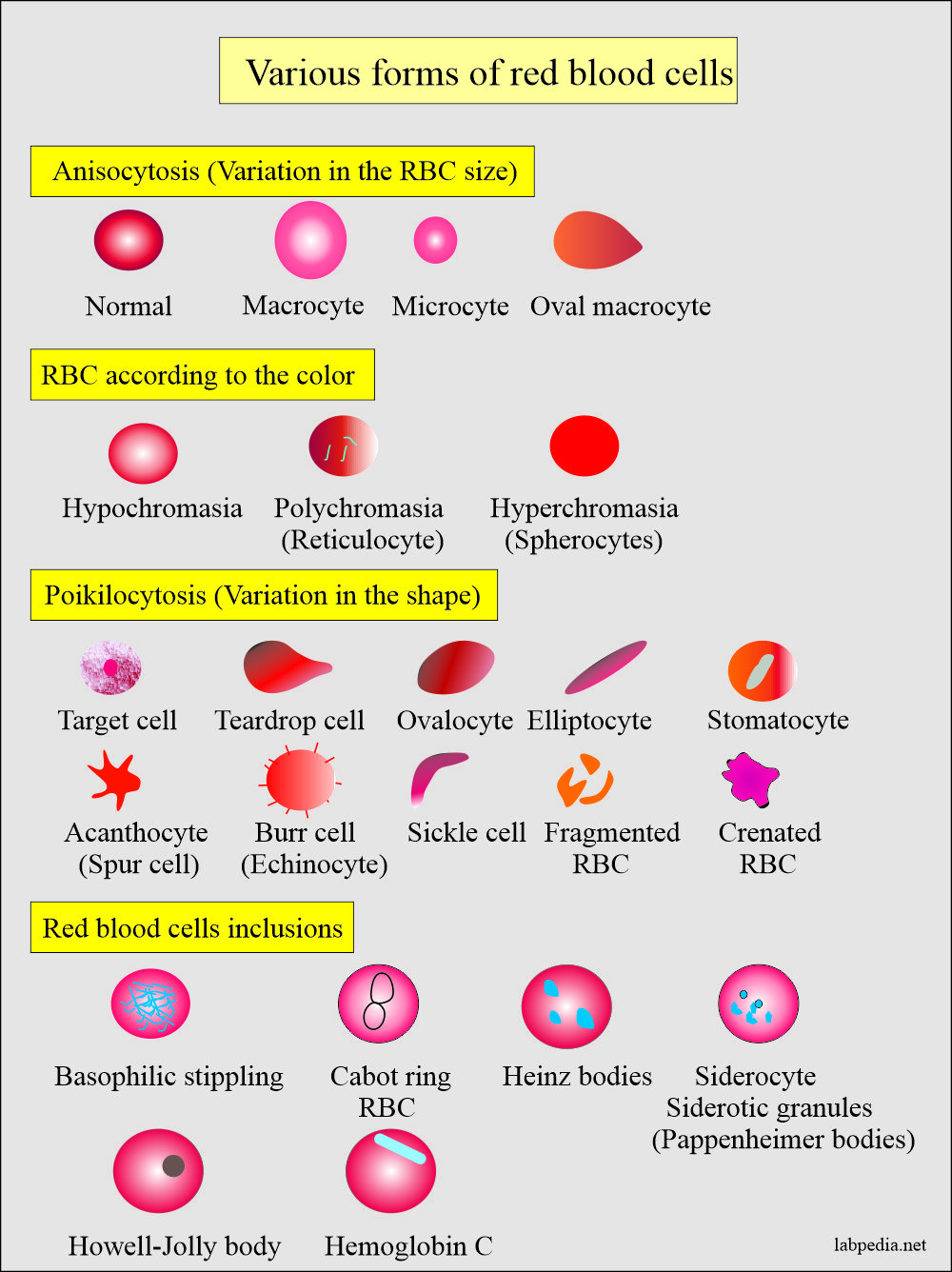
- Peripheral blood smears show anisocytosis and poikilocytosis with Macrocytes with MCV = 100 to 140 µm2.
- Myelocytes may be seen.
- RBCs show Macrocytosis, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, polychromasia, punctate basophilia, and occasionally nucleated RBCs.
- Platelets show thrombocytopenia and the presence of giant platelets.
- Reticulocytes are normal or decreased.
- The reticulocyte index is used to evaluate effective RBC production.
- Normally, it increases after blood loss or hemolysis.
- Decrease in:
- Nutritional deficiency.
- Marrow aplasia or replacement.
- Exposure to toxic agents.
- Biochemical findings are:
- High serum iron.
- Indirect bilirubin is high.
- Serum LDH is raised.
- A high gastrin level indicates pernicious anemia.
- Vitamin B12 level is low in B12 deficiency in serum and RBCs.
- The folic acid level is low in folic acid deficiency in serum and RBCs.
- Antibodies to gastric cells and intrinsic factors are seen in pernicious anemia.
- An abnormal Schilling test is seen in pernicious anemia.
What will the bone marrow picture be in megaloblastic anemia?
- It is usually not needed to make the diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency.
- It is hyperplastic with megaloblastic erythropoiesis.
- Megaloblasts and normoblasts are seen.
- Megaloblastic changes are associated with the degree of severity of the anemia.
- Leucopoiesis is abnormal. Macropolycytes are seen. There are hypersegmented nuclei.
- The myeloid and erythroid ratio is reduced.
- Megakaryocytes are usually normal or slightly increased.
- Hemosiderin storage is normal.
- Vitamins and biochemical tests:
- Vitamin B12 serum level is reduced; the normal values are 160 to 925 ng/dl.
- Vitamin B12 in the RBCs also decreased; the normal value was 72 to 512 ng/dl.
- Serum Folate level is also decreased in folic acid deficiency, where the normal value is 10 to 15 µg /L.
- RBC folate is also reduced and may be very low. The normal value is 300 to 350 µg /L.
- Iron in plasma is raised or normal.
- Serum bilirubin is moderately raised and is predominantly unconjugated bilirubin.
- Serum LDH is also raised due to ineffective erythropoiesis. In severe cases, there is a markedly increased level.
What are the Diagnostic tests for megaloblastic anemia?
- The diagnostic test is an assay of Vit B12, which is <90 pg/mL.
- The associated normal level of Folate indicates a B12 deficiency.
- The diagnostic test for Folate is the estimation of the folate level.
- If Folate is <3 ng/mL with a normal B12 level suggests Folate deficiency.
- Serum homocysteine levels increase with B12 or Folate deficiency.
- Antibodies against intrinsic factors strongly suggest B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia).
- Urine methylmalonic acid levels are increased in B12 deficiency.
- The Schilling test is also diagnostic.
What is the differential diagnosis of Megaloblastic anemia?
| Clinical characteristics | Serum vitamin B12 deficiency | Serum folate deficiency | RBC folate level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>150 ng/mL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you summarize Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency and lab findings?
| Parameters | Results (Lab findings) |
| Peripheral blood smear and complete blood count |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the clinical and laboratory findings in Vitamin B12 and Folate deficiencies?
| Lab/clinical parameters | Pernicious anemia (Vit B12 Deficiency) | Folate deficiency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the level of vitamin B12 to diagnose megaloblastic anemia?
Question 2: What are the sources of vitamin B12?

Thanks for your team ?
Thanks for appreciation
Excellent and very informative.
Thanks.
very detailed and very good
Thanks.
Really informative and beautiful diagrams.
Can I use the diagrams for academic presentation at national level?
ou are welcome to use these diagram. I will appreciate if you can mention us (labpedia.net), where ever is possible.