Anti-Thyroid Antibodies
Anti-Thyroid Antibodies
What sample is needed for Anti-Thyroid Antibody?
- The serum is needed.
- The fasting sample is preferred.
- Stop vitamins before taking the sample.
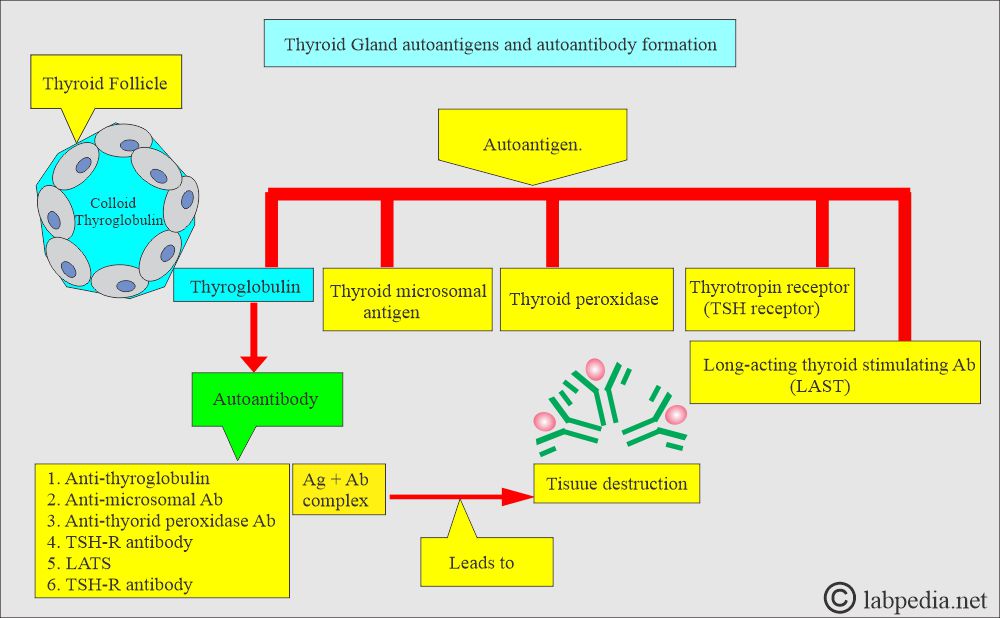
What are the thyroid autoantibodies?
- The auto-antibodies are directed against various self-antigens like cellular components (Antimicrosomal antibodies) or proteins(thyroglobulins).
- These autoantibodies are found in the autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland.
What are the thyroid autoantigens?
- Thyroglobulin.
- Thyroid microsomal antigen (the vesicle-like structure formed from the endoplasmic reticulum when cells are disrupted).
- Thyroperoxidase (a component of thyroid microsomal antigen).
- TSH-Receptor (Thyrotropin receptor).
- Rarely are auto-antigens against:
- TSH.
- T4 and T3
What are the thyroid auto-antibodies?
- Antithyroglobulin antibody.
- Antimicrosomal antibody.
- Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody.
- Long-acting thyroid-stimulating antibody (LATS) includes:
- TSI = thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin.
- TSH-R antibody = thyroid hormone receptor antibody.
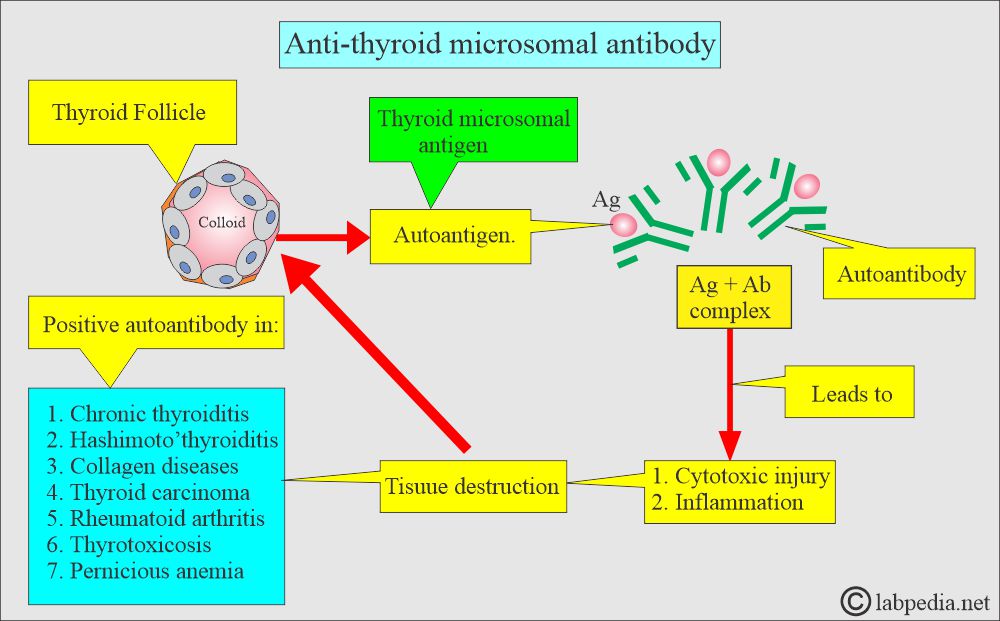
Antithyroid microsomal antibody:
What is the importance of antithyroid microsomal antibody?
- The microsomal antibody is the older name, and now it is correctly called antithyroid peroxidase antibodies.
- These are called microsomal because thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme in the microsomes of thyroid follicular cells.
- This test differentiates between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis in children.
- These are found more in chronic thyroiditis than antithyroglobulin antibodies.
- These are present in 70% to 90% of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- This antibody is against the microsomes of the thyroid cells.
- There is a cytotoxic injury to the thyroid follicles.
What are the methods to detect thyroid microsomal antibody?
Thyroid microsomal antibodies can be detected by:
- Complement fixation test.
- Immunofluorescence of tissue biopsy.
- Passive hemagglutination.
- ELISA method.
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA).
What are the normal Antimicrosomal antibodies?
- Negative = < 1:100
- 5% to 10% are present in healthy people without thyroid disease.
Antithyroid peroxidase antibody:
What is the significance of antithyroid peroxidase antibody?
- Anti-thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies are replacing atimicrosomal antibodies and anti-thyroglobulins.
- This is recognized as the thyroid microsomes’ principal and possibly only autoantigen component.
- This is suggested as a routine in the case of thyroid autoimmune disease.
- The thyroid microsomal antibodies are difficult to detect.
- There are irrelevant thyroid antigens, autoantibodies, and contamination of microsomes with thyroglobulin.
- The thyroperoxidase antibody eliminates these complications.
- The RIA and chemiluminescence can detect these antibodies.
- The above two methods are more accurate than passive hemagglutination.
- Antiperoxidase antibodies are seen in the following:
- These are seen in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, idiopathic myxedema, and most cases.
- These are positive in 90% of the cases of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- The high titer of these antibodies suggests Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, but its negative value does not rule out Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody is seen in the following:
- A titer of >1:1,000 is seen in Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Grave’s disease.
- Diabetes mellitus type 1.
- It may be seen in nonimmune thyroid disease.
- What is the normal anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody?
- Titer = <1:100
Thyrotropin receptor antibody (TSH-R antibody):
What is the significance of thyrotropin receptor antibody (TSH-R antibody)?
- Some immunoglobulins bind to the thyroid cell membrane near or to the TSH-receptor site.
- These are often seen in the blood of Graves’ disease patients.
- These are also found in other thyroid autoimmune diseases.
- What are the functions of the TSH-R antibody?
- In some cases, they may have a stimulatory effect.
- In some cases, they block the TSH-receptor site and decrease thyroid function.
- In some, there may be no effect.
- Their functional role may be in the pathogenesis of Graves’ disease.
- It is found as a long-acting thyroid stimulator in these patients’ serum.
What are the causes of an Antithyroid antibody-positive test?
- Chronic thyroiditis (40% to 70 %).
- Thyrotoxicosis (Graves’ disease).
- Hypothyroidism.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Other autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
What are the various auto-antibodies and thyroid diseases?
| Disease | Anti-thyroglobulin antibody | Anti-microsomal antibody |
Antithyroperoxidase antibody |
Long-acting thyroid stimulating antibody (LATS) |
| Grave’s disease | positive 30% | positive 60 to 80% | positive >85% | positive 100% |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | positive 70 to 90% | positive 80% | positive 100% | negative |
| Lymphocytic thyroiditis | positive 30 to 50% | positive 50% | positive | negative |
| Thyroid carcinoma | positive 20 to 50% | positive 15% | negative | |
| Normal person | positive low titer | positive low titer, 5 to 10% | positive 5 to 10% |
- LATS antibodies are of two types:
- TSI = Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin.
- TSH-R antibody = Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibody.
- Please see more details on the Antithyroglobulin antibody.+
What are the causes of Antimicrosomal autoantibodies?
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Thyroid cancer.
- Myxedema.
- Sjögren’s syndrome.
- Goiter.
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
- Lupus erythematosus.
What are the conditions for antimicrosomal antibody/antithyroglobulin Ab positivity?
| Clinical disease | Antimicrosomal antibody | Antithyroglobulin antibody |
| Grave’s disease | 75% (71% to 86%) | 55% (29% to 65%) |
| Hashimoto’s disease | 97% (92% to 100%) | 70% (50% to 86%) |
| Nontoxic nodular goiter | 27% | 5% to 50% |
| Primary myxedema | 75% (67% to 86%) | 55% (50% to 64%) |
| Thyroid carcinoma | 20% | 20% |
| Female, normal | 15% | 2% to 20% |
| Male, normal | 0% to 3% | 0% to 2% |
- Either hemagglutination or immunofluorescent methodology can do the above tests.
How will you summarize thyroid autoantibodies?
1. Anti-thyroglobulin antibody:
- These antibodies are a sign of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- There is a high level of these antibodies.
- These are positive in Graves’ disease.
- Positive in follicular and papillary carcinoma.
- Other autoimmune disorders:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
2. Thyroid peroxidase antibody:
- These antibodies are a sign of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- 90% of the patients are positive for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- These are autoimmune antibodies that lead to hypothyroidism.
- Graves’ disease is hyperthyroidism.
- It is positive in 70% to 80% of Graves’ disease.
3. Thyroid microsomal antibodies:
- These antibodies are present in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- It differentiates Hashimoto’s thyroiditis from chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis.
4. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor:
- These antibodies are signs of Graves’ disease.
- 90% of the Graves’ disease patients have positive results for this antibody.
- It can be done to follow up on Graves’ disease.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Can you find an anti-microsomal antibody in people without thyroid disease?
Question 2: Which test is specific for the diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis?