Stool examination:- Part 4 – Stool for Occult Blood (OB)
Stool for Occult Blood
What sample is needed for Stool Occult Blood?
- This test is done on the stool.
- The random sample can be taken; a 3 mL quantity is enough.
- Avoid the outer portion and take a sample from the central area of the formed stool.
- Three consecutive stool samples are needed.
- Collect the stool in a dry, sterilized, wide-mouth container.
- Instruct the patient to stop taking vitamin C, iron-containing drugs, meat, and vegetables at least three days before the test.
- Fresh stool testing is recommended.
What Precautions are needed for Occult Blood stool?
- The special diet is recommended 48 to 72 hours before the test.
- Also, direct the patient to avoid the following foods:
- No, red meat. The chicken and fish were also stopped.
- Peroxidase-rich vegetables like turnip, spinach, horseradish, mushrooms, broccoli, beans, cauliflower, oranges, bananas, cantaloupe, and grapes.
- No raw fruits.
- Avoid Vitamin C, which causes a false negative reaction by inhibiting the peroxidase reaction.
- Avoid drugs like anticoagulants, aspirin, colchicine, nonsteroidal antiarthritics, iron preparation, and steroids for at least 7 days before the test.
- Drugs that may cause false-positive results are:
- Colchicine, and iron.
- Oxidizing drugs like iodine, bromides, boric acid, and rauwolfia derivatives.
- Drugs that may cause false-negative results are vitamin C, etc.
- Take H/O of bleeding gums.
- Vigorous exercise.
What are the indications of Stool for Occult Blood?
- This is a screening test for colorectal carcinoma.
- This can be used for bleeding ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract.
- This test can be included in the periodic medical checkup.
- This test is advised in older people after 40 who are asymptomatic to rule out GI malignancy.
- This test is essential in hypochromic anemias because of ulcerative or neoplastic diseases.
- Over the age of 50 years, this may be included in the annual check-ups.
What is the definition of Stool for Occult Blood?
- The chemical test reveals the presence of hemoglobin in the stool, which is hidden (occult) and not visible to the naked eye.
- Occult blood is hidden, and a chemical test is required for its detection.
- Normally, only minimal quantities of blood are passed into the gastrointestinal tract. This bleeding quantity is not significant enough to cause the occult blood test to be positive.
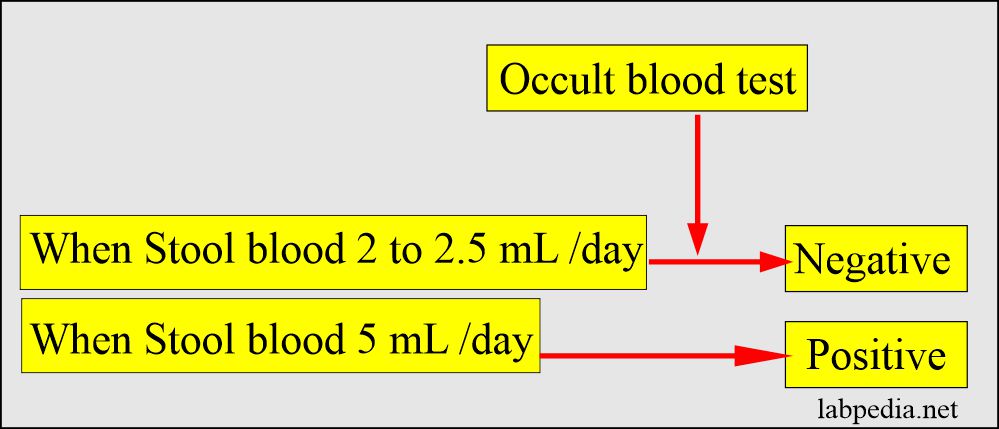
- Normally, 2 to 5 ml of blood passes in the stool daily, but this is not detectable.
- The healthy person passes roughly 2 ml of blood in 150 grams of stool.
- This amount will not show occult blood positive.
- This test will be positive when 5 mL of blood is passed in the stool daily.
What are the facts about Stool Occult Blood?
- Another reference says the occult blood test can detect 2 ml of blood in the stool.
- Another source says >2 mg/g of the stool is positive, and <2 mg/g/day is seen in healthy people, and OB will be negative.
- Occult blood will be positive when the tumors grow in the intestine’s lumen and if they ulcerate and give rise to bleeding.
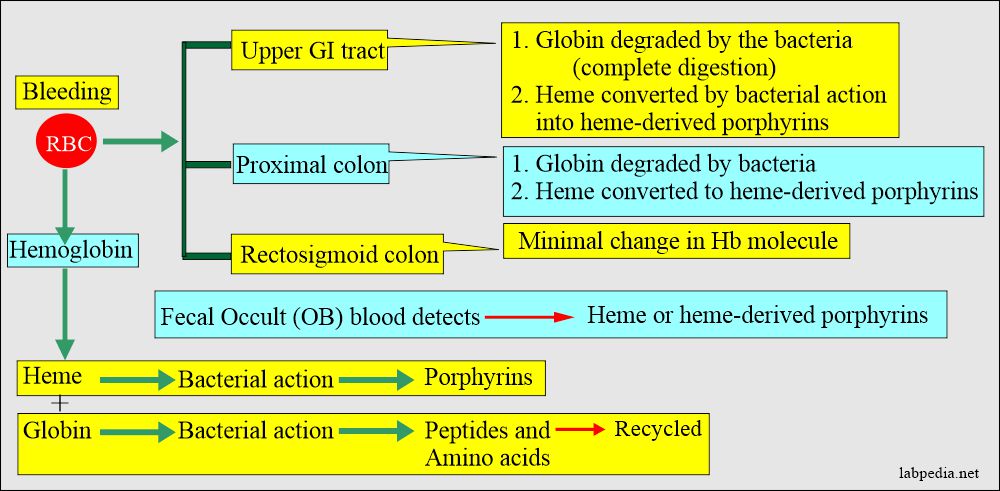
- Bleeding in the upper GI tract produces a black, tarry stool.
- Bleeding from the lower GI tract produces just blood in the stool.
- Fecal occult blood should be tested for either heme or heme-derived porphyrins.
- Heme has a peroxidase-like activity that is detected by the Guaiac dye test.
- A stool that is dark red to tarry black indicates a blood amount of 50 to 75 mL from the upper GI tract.
What is the normal occult blood?
- Occult blood normally is negative.
What are the procedures for Stool Occult Blood?
How would you discuss the chemical method?
- Advises patients to take plenty of vegetables, corn, and non-citrous fruits.
What is the modification of the benzidine stool test?
- Benzidine and 0-toluidine are carcinogenic.
- Reagents:
- Take 95% alcohol 15 mL.
- Dissolve 4- aminophenazone 0.4 grams.
- Add Acetic acid 10% 1 mL.
- H2O2 (Hydrogen peroxide)1 volume and 10 ml of water.
- Procedure:
- Take 10 to 15 mL of distle water and emulsify the stool (10 mm diameter).
- Now centrifuge and take the clear emulsified fluid.
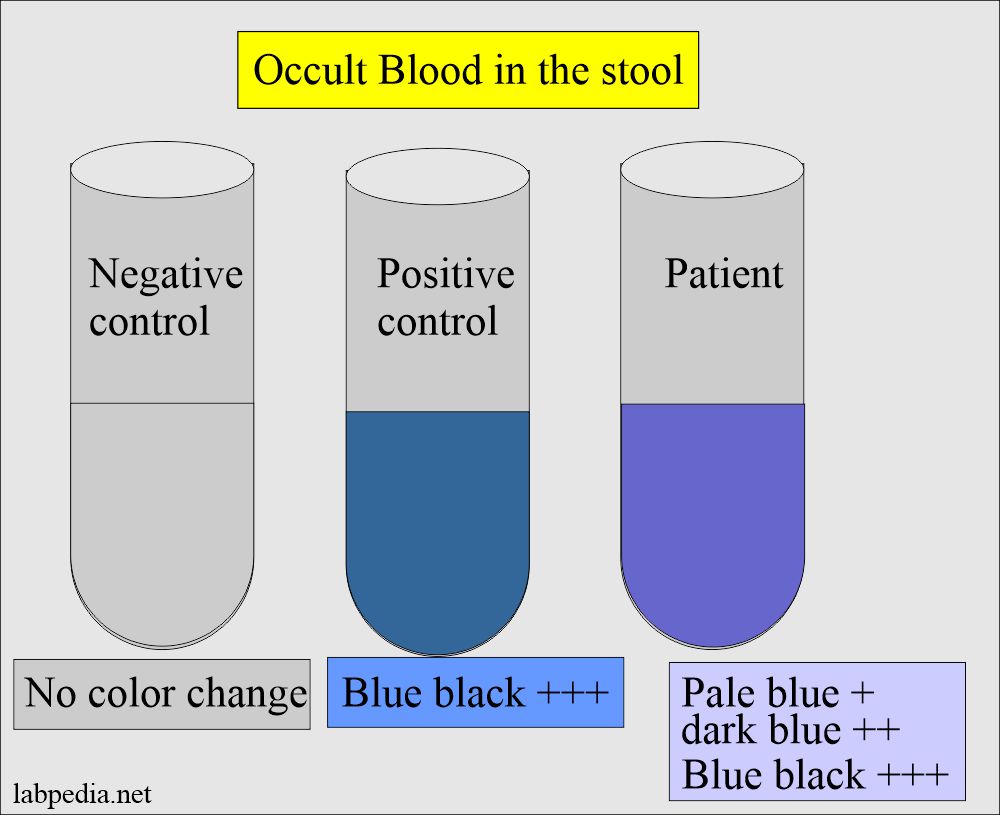
- Take three tubes and label those as a patient, Negative control, and positive control.
- Add 5 mL of emulsified stool material to the patient tube.
- Add distle water to the negative control.
- Add one drop of blood to the positive control.
- Now layer 5 mL of the mixed aminophenazone-prepared reagent above the suspension, and don’t mix. Just layer it over the suspension.
- Now add 10 drops of Hydrogen peroxide (10 volumes) and don’t mix (dilute 1 mL of H2O2 with 10 mL of D.water.).
- Check the result as follows:
- It would help if you made a fresh sample to run this test every time.
- The false-positive test is seen if the patient’s stool has a peroxidase-like substance.
- A false-negative reaction is seen in the case of excess ascorbic acid in the stool.
- In the case of suspected cases, repeat the test two more times.
How would you discuss the Guaiac test principle and interpretations?
- Drawbacks:
- The disadvantage of the Guaiac test is that it may react with non-Hb peroxidase present in the stool, such as vegetables and meat.
- Vitamin C inhibits the Guaiac reaction.
- Guaiac reaction test sensitivity is 40%, so many times, it can not detect tumors in the early stages.
- Procedure:
- A more sensitive reaction developed, with sensitivity and specificity of about 80% and 94%, respectively.
- A drop of water (rehydration) is added to the slide before testing in the Guaiac test.
- This step increases the sensitivity but decreases the specificity.
- More cancers are detected after the rehydration, but a higher number of false positives leads to further investigation, such as a barium meal study or sigmoidoscopy.
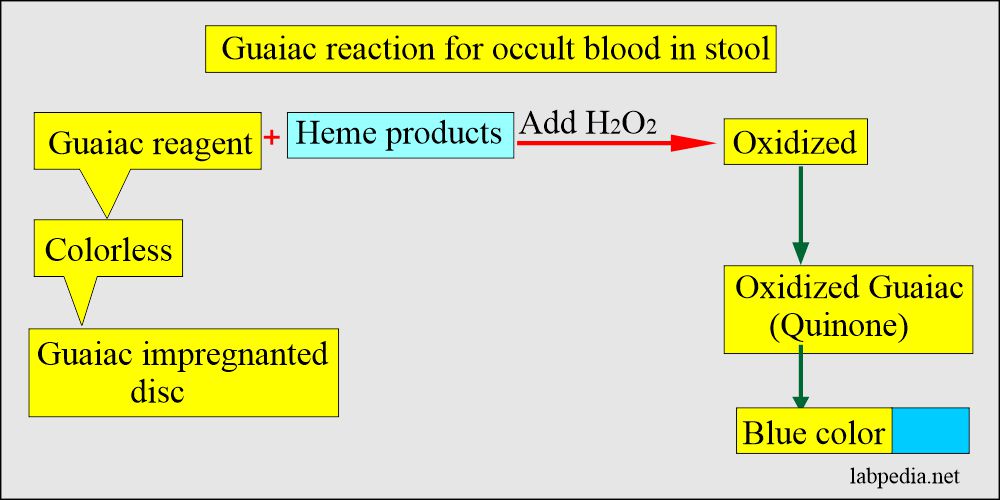
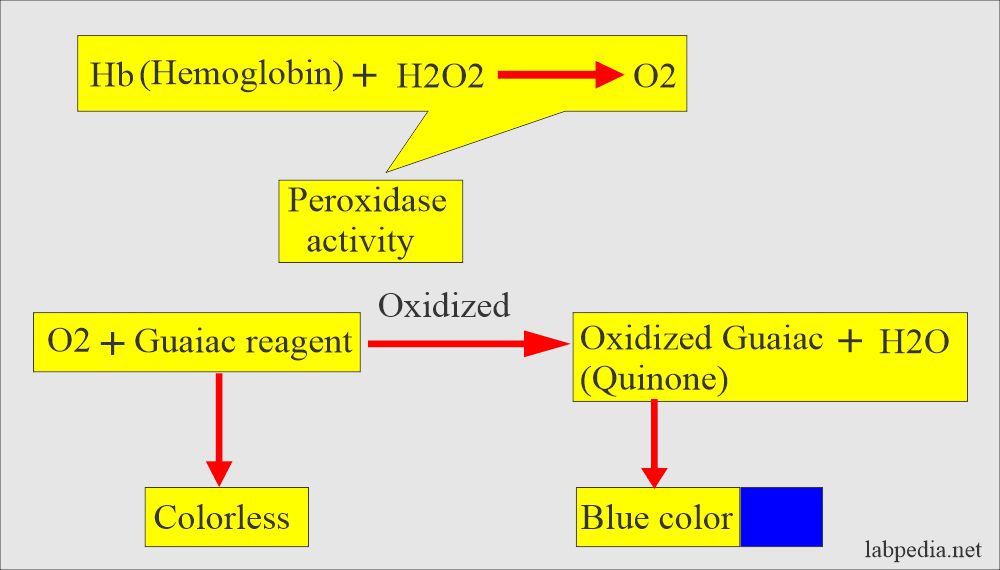
- What is the principle of the Guaiac test?
- The stool sample is applied to the guaiac-impregnated paper.
- Then, the developer solution, which consists of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) and denatured alcohol, is added.
- Interpretation of the Guaiac test:
- Any appearance of the blue color is a positive test.
- The intensity of color development does not matter, whether it is a week or strong.
- If the paper before the test turned blue or blue-green, it should be discarded.
- American Cancer Society recommends three consecutive samples for colorectal cancer screening.
- False-positive OB test is seen in:
- Ingested meat.
- Peroxidase-rich vegetables like turnip, horseradish, mushroom, broccoli, beans, sprouts, cauliflower, oranges, bananas, cantaloupe, and grapes.
- Drugs like anticoagulants, aspirin, iron preparation, antiarthritic nonsteroidal medicines, and steroids may lead to bleeding.
- White cells and bacteria also cause a false positive test.
- Other drugs causing false-positive tests are boric acid, colchicine, bromides, and iodine.
- False-negative OB test is seen in:
- Vit C may cause a false negative when taken more than 250 mg/day.
- Foods and juices are rich in vitamin C.
- Oxidants also cause a false-negative result.
- An iron supplement containing vitamin C >250 mg.
What are the other tests for the detection of colorectal carcinomas?
The fluorometric method:
- This method is specific for heme and porphyrins.
- Value < 2 mg/g of the stool is negative.
- A value> 2 mg/g of the stool is positive for colorectal carcinoma.
Immunological kits methods:
- These are sensitive for detecting the human hemoglobin component of globin.
- A monoclonal antibody against the hemoglobin is used. These antibodies are specific for hemoglobin.
- Mostly, agglutination is reported to be positive by coated antibodies or latex particles.
- These tests are called the fecal immunochemical tests for fecal occult blood.
- The disadvantage is that it may not detect bleeding from the upper GI tract because the globin is digested or degraded when it gets into feces.
DNA stool method:
- This is a new technique to detect precancerous and malignant tumors.
- The benign lesion does not bleed, which may be missed by Guaiac or other tests in occult blood screening.
- All precancerous lesions shed cells with abnormal DNA, so precancerous lesions can be removed before they transform into malignant conditions.
What would you advise For the detection of colorectal cancer?
- Occult blood in the stool.
- Sigmoidoscopy.
- Colonoscopy.
What are the advantages of the early detection of colorectal cancer?
- When screening starts at the age of 50 years, it will reduce death by colorectal malignancies.
- In one reference, this may be a 60% reduction.
What are the causes of positive OB tests?
- Gastrointestinal tumors.
- Rectal carcinoma.
- Gastric carcinoma.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Diverticulosis.
- Varices.
- Ischemic bowel disease.
- Arteriovenous malformations of the GI tract.
- Hemorrhoids.
- Blood is swallowed from the oral cavity or nasopharynx.
- Adenoma.
- Peptic ulcer.
- Gastritis.
- Amyloidosis.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma.
- NOTE. Please see more details in other stool parts 1 and 2.
Questions and answers:
- Question 1: What is the advantage of screening of the population at the age of 50.
- Question 2: What is the result of the Guaiac test.