Diabetes Mellitus:- Part 9 – Random Glucose (Diabetes mellitus) and Interpretation
Random Glucose (Diabetes mellitus)
What Sample is needed for a random Glucose?
- This is a random blood sample done on the serum or oxalate blood.
What are the factors on which the Random glucose level depends?
- When and how much did you eat at your last meal?
- This is the rough estimate of the glucose level.
What is the importance of random glucose levels?
- Random blood glucose is without any relation to time or food.
- This is done out of your normal routine testing.
- This is always a nonfasting sample.
How will you interpret the random glucose levels?
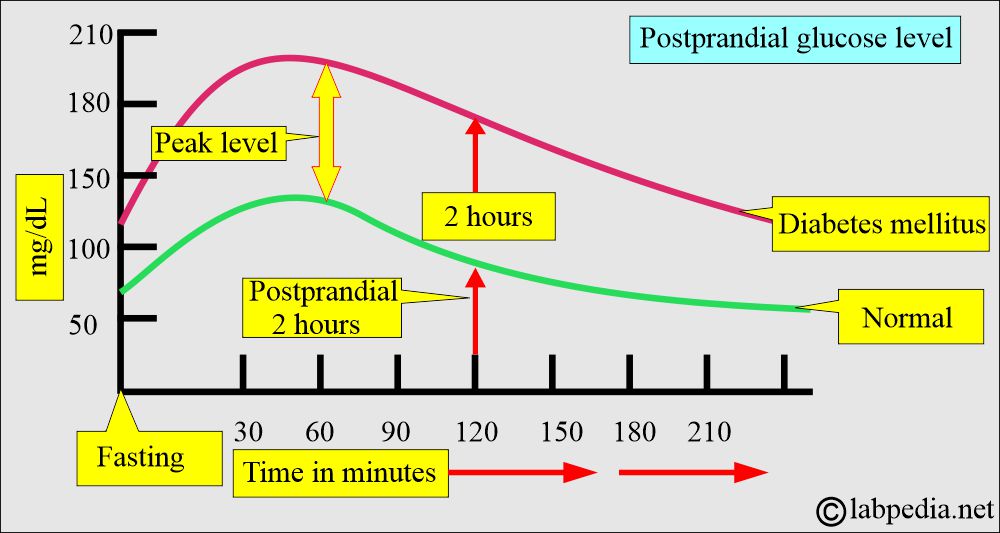
- If the random blood glucose level is above 200 mg/dL and the patient experiences increased thirst, polyuria, and polyphagia, diabetes mellitus is suggested.
- Generally, two-hour glucose samples will reach the fasting level or fall within the normal range.
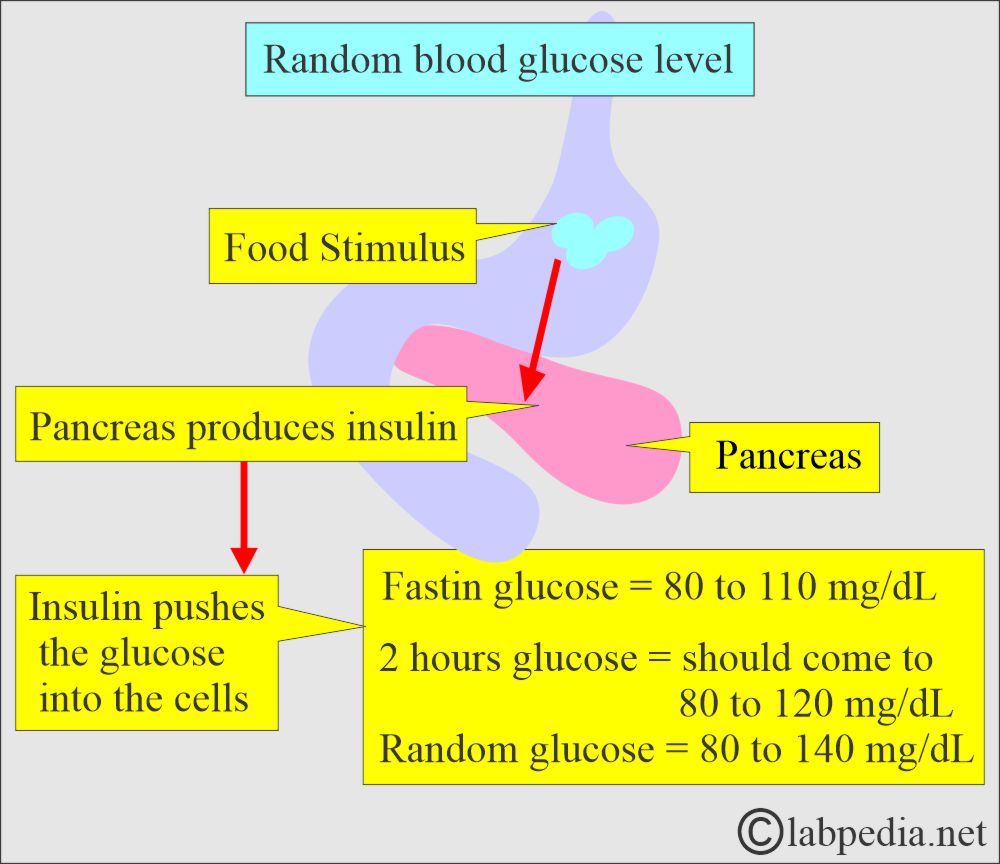
What will be the random blood glucose levels?
- Before the meal = 80 to 120 mg/dl (4.4 to 6.6 mmol/L).
- After the meal and if the person is awake = 100 to 140 mg/dl ( 5.5 to 7.7 mmol/L ).
- At bedtime = 100 to 140 mg/dl ( 5.5 to 7.7 mmol/L).
Normal Random glucose level = 80 to 140 mg/dL (4.4 to 7.8 mmol/L).
What is the reliability of random blood glucose?
- If it is above 200 mg/dL, it indicates diabetes.
What is the Interpretation of the fasting and random glucose levels?
| Fasting glucose level | Normal range and need advice |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Random glucose level | |
|
|
|
|
What is the glucose level in prediabetic and diabetes mellitus?
| Diagnosis | Fasting glucose level | Random glucose level | 2-hour glucose level (in OGTT) | HbA1c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Please see the details in the Fasting glucose level.