Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its Significance
Antinuclear factor (ANF)
What sample is needed for Antinuclear Factor (ANF)?
- This test is performed on the patient’s serum.
- How to obtain a good serum sample: Collect 3 to 5 mL of blood in a disposable syringe or a Vacutainer. Keep the syringe at 37 °C for 15 to 30 minutes and then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes to obtain a clear serum.
- No fasting or preparation is required.
What are the Indications for Antinuclear Factor (ANF)?
- For the diagnosis of Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- Positive in other autoimmune diseases.
What are the precautions for Antinuclear Factor (ANF)?
- Drugs may cause false-positive tests, such as aminosalicylic acid, chlorothiazide, procainamide, hydralazine, acetazolamide, penicillin, phenytoin sodium, and griseofulvin.
- Drugs may cause a false-negative test, like steroids.
- This test may yield a positive result after a viral infection or some chronic infections.
How will you define Antinuclear factor (ANF)?
- Antinuclear factor (ANF) is the same as antinuclear antibody (ANA).
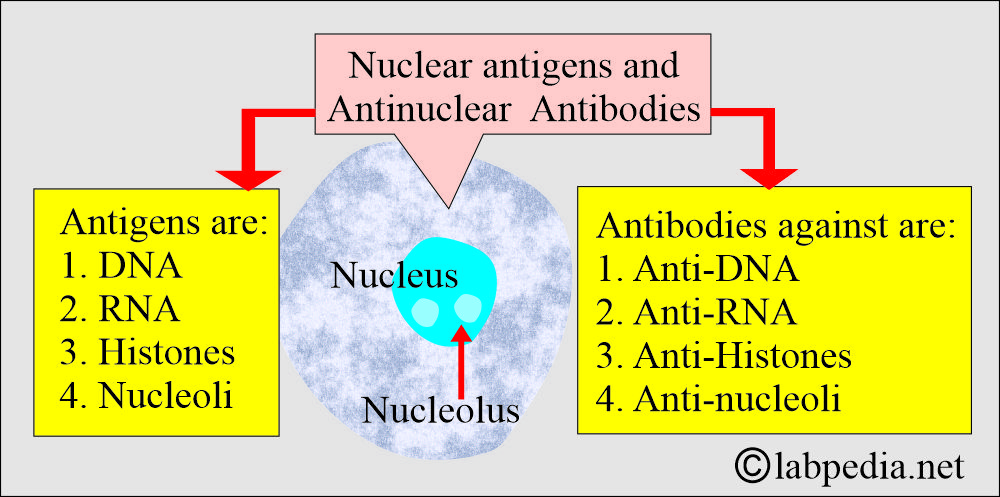
- Antinuclear antibodies are produced in connective tissue diseases (autoimmune diseases) against various antigens in the nucleus, such as RNA, DNA, histones, and ribonucleoproteins.
- Autoantibodies are directed against nuclear material (ANA) or cytoplasmic material, known as anti-cytoplasmic antibodies.
What are the major anti-nuclear antigens?
- DNA (double and single-stranded).
- Histones.
- Nuclear proteins.
- RNA
- 95% of SLE patients show ANA.
What are the commonly used anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) and their significance?
| Types of Anti-nuclear Antigen and Antibody (ANA) | ANA and its diagnostic value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of anti-nuclear factor (anti-nuclear antibody – ANA)?
- This ANA is not a specific SLE test, so it must be supplemented by other tests. However, this is the most sensitive test, detecting SLE with a positivity rate of almost 95%.
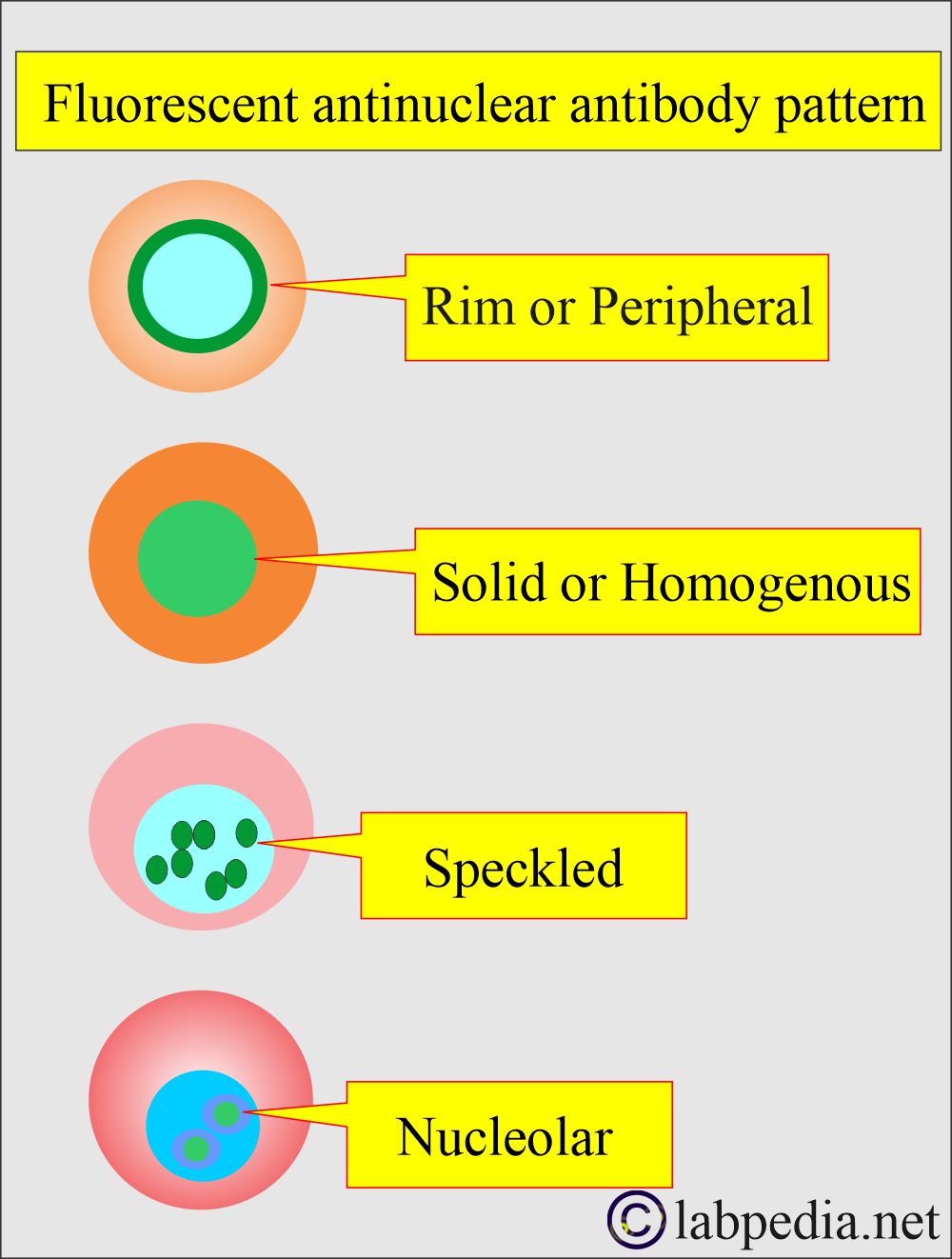
- Fluorescent staining under an ultraviolet microscope shows different patterns and increases the specificity of this test.
- Fluorescent patterns show different staining in the nucleus, e.g.:
- The homogeneous pattern is seen in SLE and mixed connective tissue disease.
- The peripheral outline is only seen in SLE.
- The speckled pattern has been observed in other autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren’s syndrome, Scleroderma, Rheumatoid arthritis, and mixed connective tissue disease.
- The nuclear pattern is seen in Scleroderma and Polymyositis.
What is the pattern of ANA (immunofluorescence staining) in various diseases?
| Diseases | Homogenous pattern | Peripheral Pattern | Speckled pattern | Nucleolar pattern |
|
+ Positive | + Positive | + Positive | + Positive |
|
+ Positive | + Positive | ||
|
+ Positive | + Positive | ||
|
+ Positive | |||
|
+ Positive | |||
|
+ Positive | + Positive |
- ANA is a gamma globulin and belongs to more than one type of immunoglobulin.
- There are ANA-negative cases of SLE.
- Some believe that negative ANA excludes SLE.
What are the diseases with positive (%) antinuclear antibodies?
| Diseases | Positivity of ANA | another source of positivity % | Another source of positivity % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of Antinuclear Factor (ANF) in diagnosis?
- Indirect immunofluorescence is seen when the patient’s serum (antibody) is combined with the cells.
- The EIA technique may replace indirect immunofluorescence.
- ANA has a sensitivity of 99%. A negative ANA test almost excludes active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- This test may be positive for unrelated diseases in patients.
- Around 20% of the normal population has a titer of 1:40.
- Around 5% of the normal population may have a titer of 1:160
- When the cutoff titer is 1:40, then the specificity is around 80%.
- When the cutoff value is 1:160, then the specificity is around 95%.
- ANA is nonspecific; individuals with increasing age show a false-positive result.
- 50% positive by the age of 80 years with a low titer.
What is the procedure for the Antinuclear Factor (ANF)?
- Take 5 to 10 mL of the patient’s blood.
- Traumatize the RBCs with the glass rod or glass beads.
- Incubate for 15 to 30 minutes at 37 °C.
- Centrifuge and make the smear from the buffy coat.
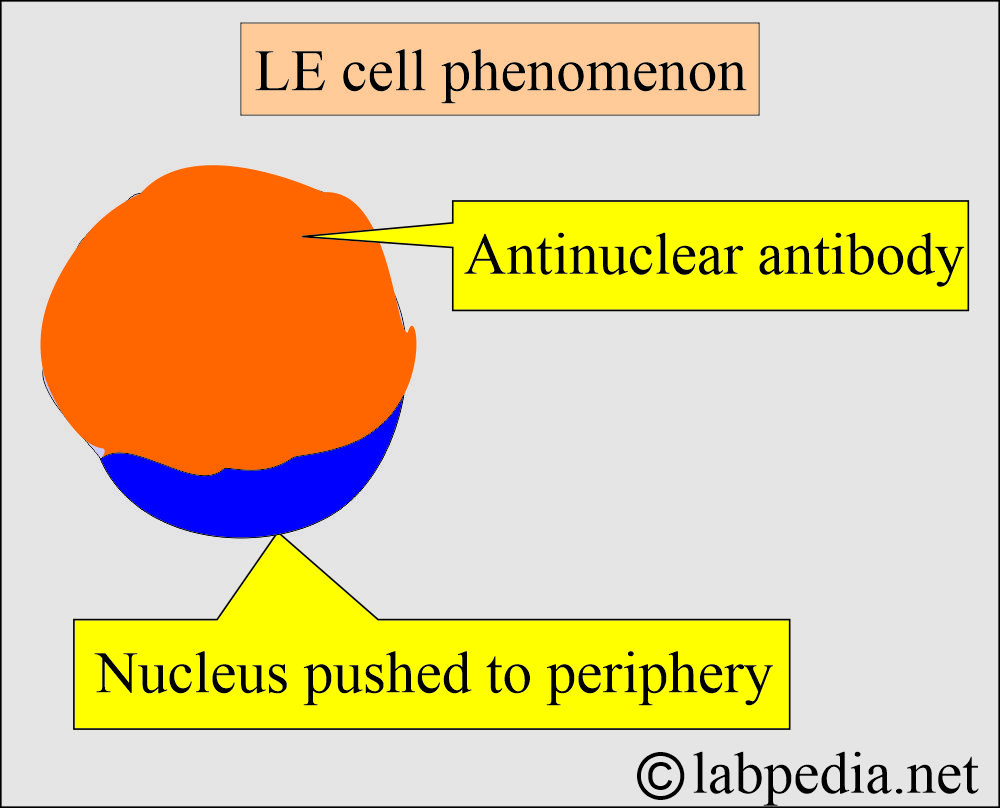
- Screen the slide to find the SLE cell (LE cell phenomenon).
What is the normal Antinuclear Factor (ANF) or ANA?
Source 2
- These are negative.
- Negative at 1:20 dilution.
- When a dilution of the serum is performed, a titer of 1:32 or greater is considered positive.
Source 4
- Negative by ELIZA and IFA method.
- If positive by IFA, the sample is titrated, and the pattern is reported.
- A strong positive result of >3 on ELISA and ≥1:160 by IFA now requires follow-up testing for specific autoantibodies.
How will you interpret Antinuclear Factor (ANF)?
- A positive test does not confirm the disease because its low titers are also seen in older and healthy individuals.
- It helps diagnose Autoimmune diseases, particularly Systemic lupus erythematosus (98%), but with poor specificity.
- This test is positive in 30% to 50% of cases of other autoimmune diseases, such as Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome (70%), Polymyositis, and other related conditions.
- A positive ANA without other symptoms is not diagnostic.
- A high titer is often associated with SLE, and a titer of less than 1:160 is not diagnostic.
- A titer of less than 1:40 is considered negative.
- The titer of 1:40 to 1:80 is considered low positive.
- While a titer of >1:160 is considered positive.
- Approximately 5% of SLE cases exhibit persistently negative results.
- ANA may become negative in the remission of SLE.
- If ANA is negative, then SLE can be excluded.
What are the causes of an increased level of Antinuclear Factor (ANF)?
- SLE.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarteritis Nodosa
- Dermatomyositis.
- Sjögren’s syndrome.
- Other autoimmune diseases.
- Cirrhosis.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Leukemia.
- Scleroderma.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Infections.
- Malignancies.
- Fibromyalgia.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the LE cell phenomenon?
Question 2: What is the significance of ANA for the diagnosis of SLE?

How long do you have to be off a l0 mg dose of prednisone in order to prevent a false negative in ANA test?
Usually, prednisolone will be out of your body in 7 to 10 days.