Liver Anatomy
Liver
This website is under construction
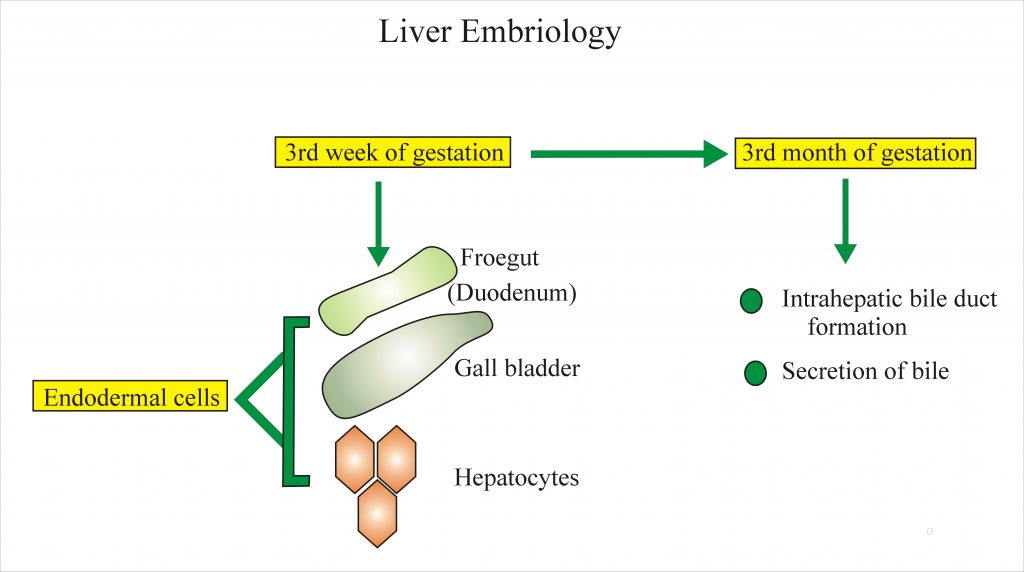
Embryology
The liver develops In the third week of gestation from foregut (primitive duodenum) which develops from endodermal cells. Also, gallbladder and hepatocytes develop from the endodermal cells.
Connective tissue and sinusoids develop from mesenchymal cells.
Intrahepatic bile duct development complete at a 3rd month and bile secretion also start by that time.
The liver is the main organ to store iron and is the site for hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis stops in two months after birth but may be found in occasional foci in the liver. In premature baby these foci are abundant. The weight of the liver in full term baby is 75 to 180g.Umbilical Vein is the main source of blood supply in fetus after delivery it atrophies and gets round ligament. Liver grows slower than other structures in adult liver weighs 1200 to1500 g (1350G)⅕ of the total body weight (2.5% of total body weight)
The weight of the liver in full term baby is 75 to 180 g. Umbilical Vein is the main source of blood supply in fetus after delivery it atrophies and gets round ligament. Liver grows slower than other structures in adult liver weighs 1200 to1500 g (1350G)⅕ of the total body weight (2.5% of total body weight)
Umbilical Vein is the main source of blood supply in fetus after delivery, it atrophies and transforms into round ligament. Liver grows slower than other structures in adult liver weighs 1200 to1500 g (1350G)⅕ of the total body weight (2.5% of total body weight)
The Liver grows slower than other structures. in adult liver weighs 1200 to1500 g (average 1350G) and is 1/5 Th of the total body weight (2.5% of total body weight).
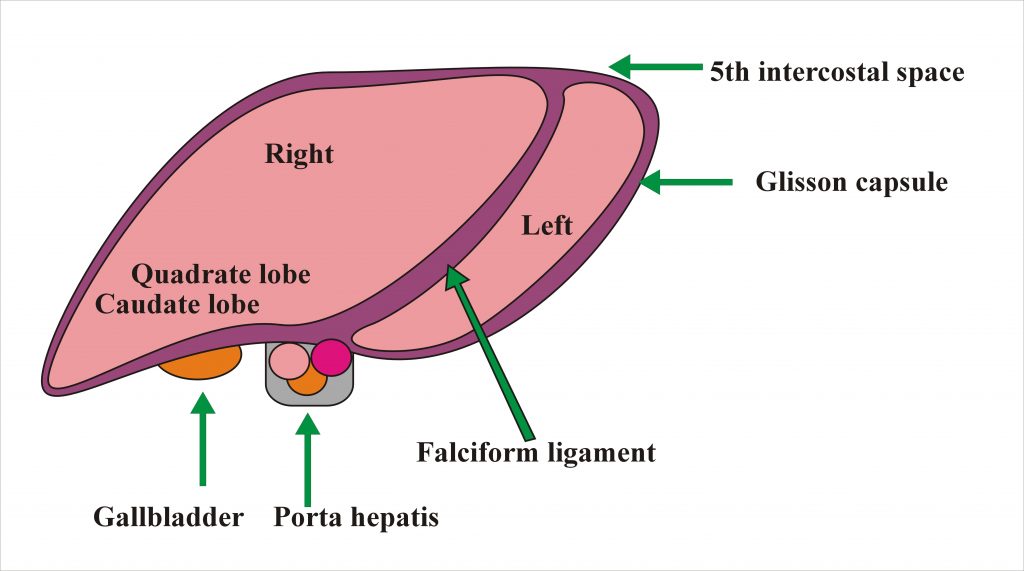
Anatomy
The liver is divided by a falciform ligament into right and left lobes.The right lobe is divided into quadrate lobe (inferior surface) and caudate lobe ( posterior surface).The upper border extends to the 5th intercostal space.
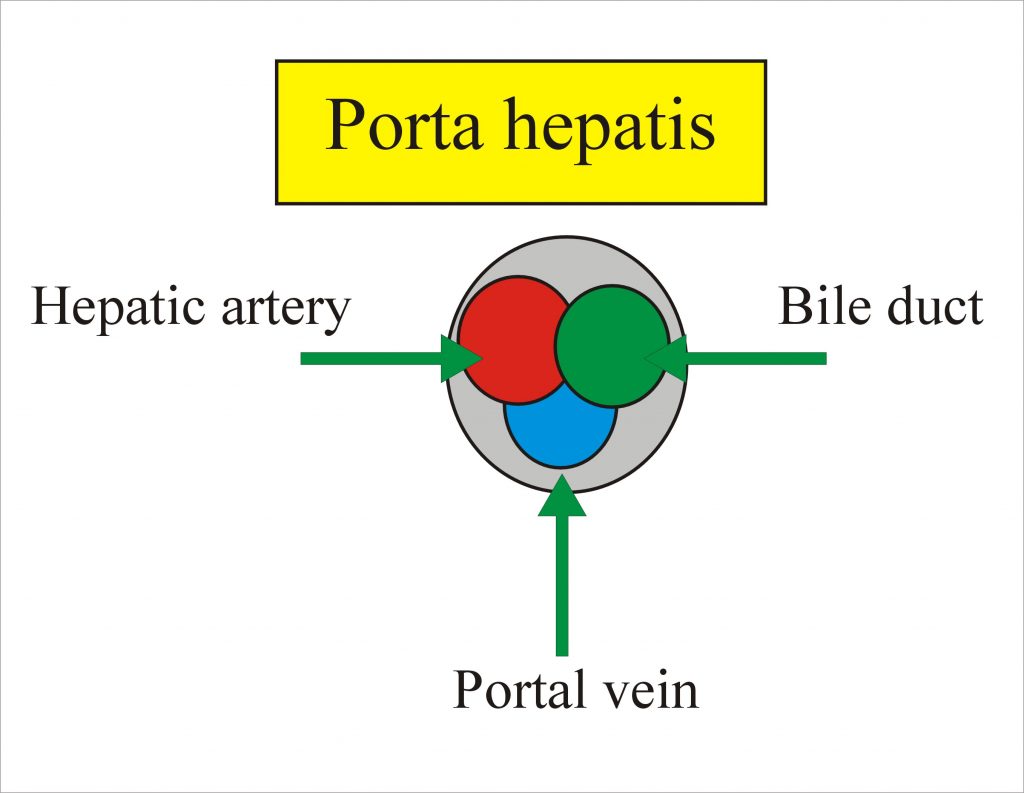
The liver is covered by thin fibrous capsule called Glisson capsule.The gallbladder is under the right lobe. The Porta hepatis is a deep fissure in the inferior surface of the liver through which all the neurovascular structures( except hepatic veins ) and hepatic ducts enter or leave the liver.It contains the right and left hepatic ducts, right and left branches of the hepatic artery and portal vein. The left lobe is six times smaller than the right lobe.
In the porta hepatis, the hepatic artery is anterior, bile duct also anterior and the portal vein is posterior.
Teres ligament developed from an inferior umbilical vein. Ligamentum venosum developed from posterior ductus venosus. The lower edge of the liver is unusual to be 1 to 3 cm below the costal margin.
The connective tissue surrounds all blood vessels and ducts to finest radicals to join inner aspect of Glisson capsule.
Liver Blood supply
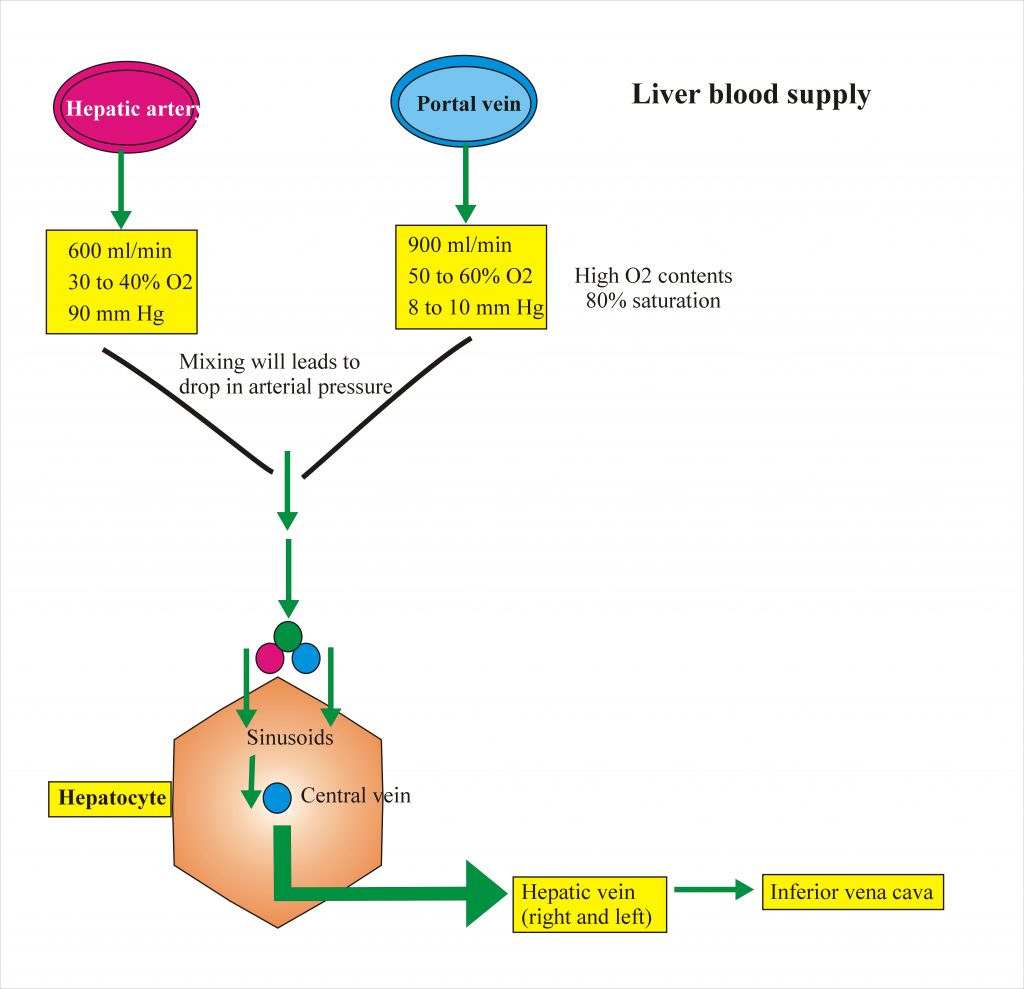
Hepatic artery carries 600 ml of blood per minute while portal vein 900 ml of blood per minutes. Hepatic artery supplies 30 to 40 % of oxygen while portal vein supplies 50 to 60% oxygen. The pressure in the hepatic artery is 90 mm of Hg and in the portal vein is 8 to 10 mm of Hg.
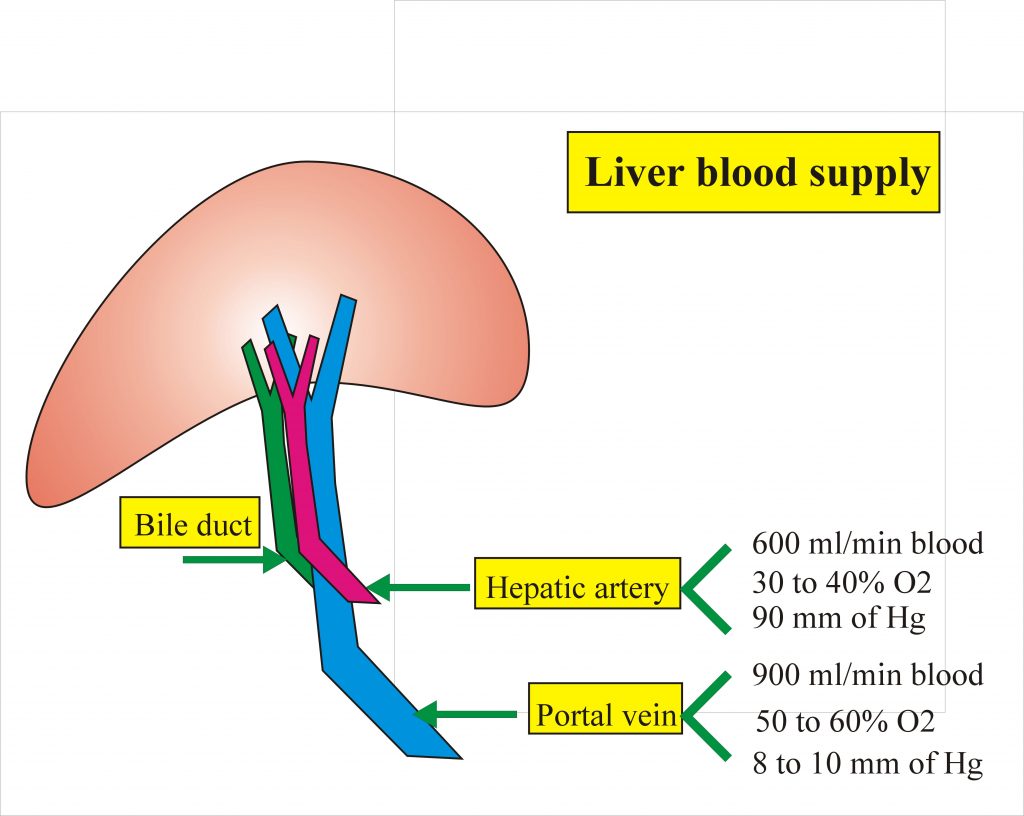
The portal vein has a high level of oxygen content equal to 80% saturation. Mixing of the portal vein and hepatic artery blood leads to drop in the arterial pressure.
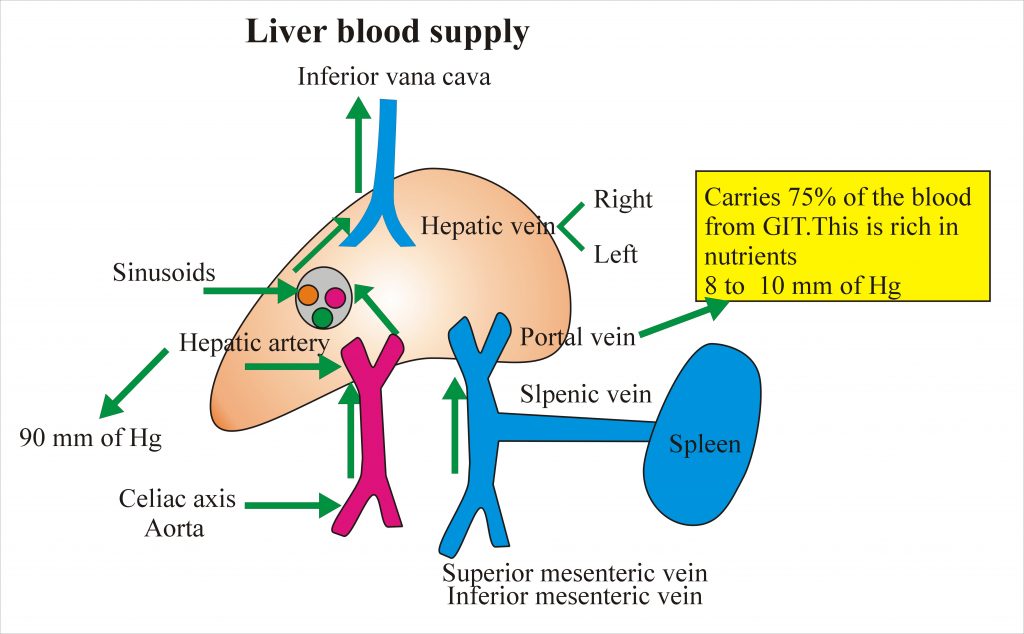
These vessels enter into sinusoids and all sinusoids drain blood to central veins. All central veins give rise to right and left hepatic veins Which continue to inferior vena cava.
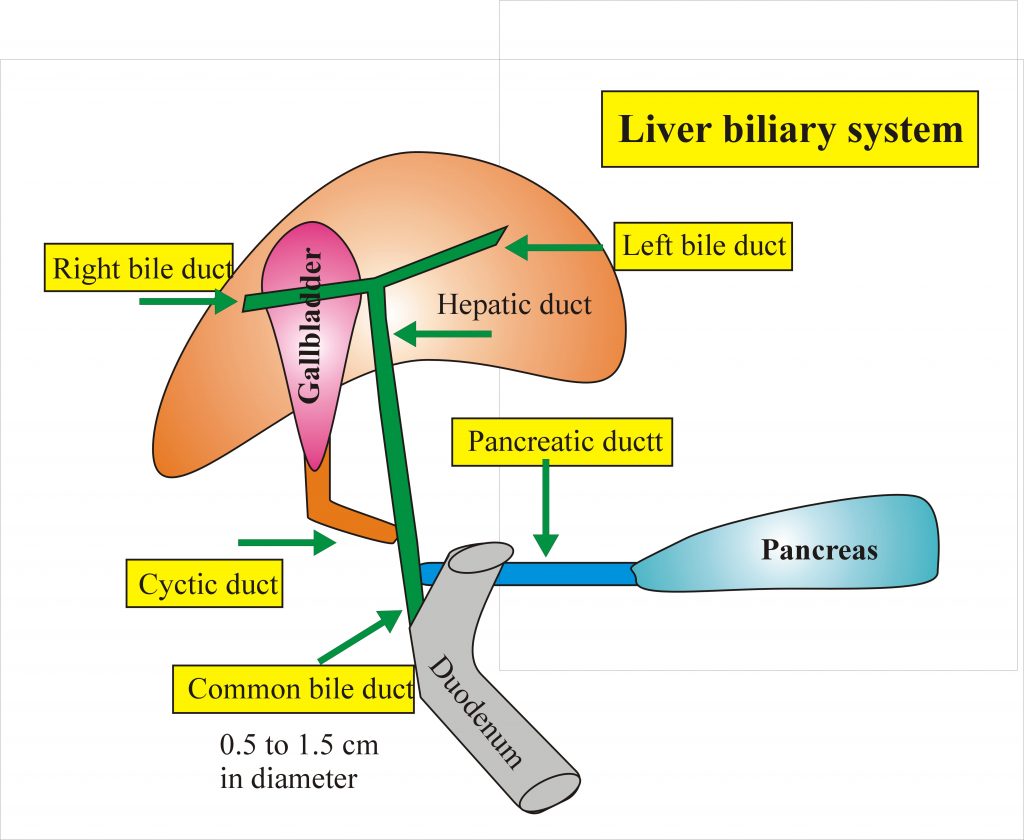
Biliary Tract
From the liver left and right duct joins to form the common hepatic duct.The common hepatic duct is joined by the cystic duct from the gallbladder.They give rise to common bile duct the diameter of the duct is .5 to 1.5cm.The common bile duct is joined by the pancreatic duct and they open to the ampulla of water in the duodenum, the ampulla of water is controlled by sphincter of Oddi which is Spiral valve, is a fold of mucosa.