Diabetes mellitus myth and what you should do?
There are so many myths about diabetes mellitus, and we will discuss them one by one.
- In diabetes Mellitus, don’t eat sugar or sweets:
- It doesn’t seem right that once you develop diabetes and can not eat sugar or sweets.
- You can eat sweets but keep in mind your meal plan.
- Eat a minimal amount of sweets.
- Fruits as sweets are an excellent alternative to chocolates, bakery products, and other varieties of sweets.
- According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes can still have sweets, chocolate, or other sugary foods as long they are eaten as part of a healthful meal plan or combined with exercise.
- Healthful meal plan: This will have limited saturated fat. Contain moderate amounts of salt and sugar.
- Some of the recommendations for diabetic (diabetes mellitus) patients are:
- Always read the content of the sweets you are buying and check sugars and added sugars.
- Granola bar (no added sugar) and fresh fruits.
- Trail mix with nuts, seeds, roasted pepitas, and dried cranberries.
- Graham crackers with nut butter.
- Sugar-free cake.
- Pudding made with chia seed.
- Avocado made sweet with low sugar.
- Frozen yogurt (with plain Greek yogurt and berries).
- Research has shown that starches like potatoes and white bread affect blood glucose levels much like sugar, causing sometimes dangerous spikes in blood sugar.
- Oats are the best alternative to white bread or chapati.
- When managing diabetes, experts agree that based on current evidence, sugar-free (candy/biscuits) is a better choice than candy made with regular sugar.
- Eating sugar-free candy will not give glucose spikes and may satisfy your craze for sweets.
- If I eat sugar, any chance to develop diabetes (diabetes mellitus):
- There are two main types of diabetes – type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
- We know that sugar does not cause type 1 diabetes, nor is it caused by anything else in your lifestyle.
- In type 1 diabetes, the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system.
- Sugar also does not cause type 2 diabetes. Some people eat a lot of sugar and sweets, but they don’t develop diabetes.
- How to manage sugar intake in diabetes mellitus:
- Not exceeding the maximum amount of calories per day:
- 2,000 calories per day for women.
- 2,500 calories per day for men.
- Reducing sugar intake to a maximum of 6 teaspoons per day (25g).
- Not exceeding the maximum amount of calories per day:
- I have mild diabetes (diabetes mellitus):
- There is no such terminology; either you are diabetic or not diabetic.
- You may not need insulin injections in type 2 diabetes.
- In literature, people have used the language of mild, moderate, and severe diabetes.
- You may control diabetes by diet and exercise if your blood glucose does not shoot high.
- Is diabetes mellitus is a serious disease:
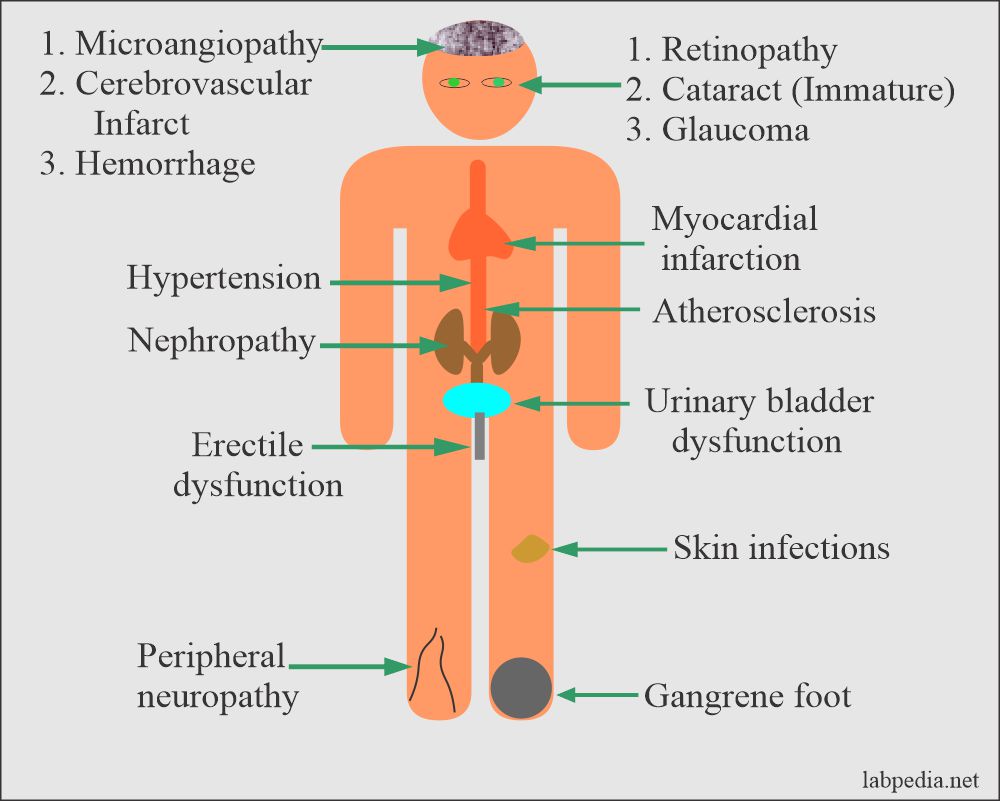
- Diabetes is a serious disease because of its complications.
- Diabetes is like a rat in your house, who will destroy your wires, make the fridge nonfunctioning, and may eat clothes.
You can see this diagram where no organ is spared:
- Any effect of blood glucose level:
- Most of the time, high or low blood glucose levels don’t produce any symptoms.
- One hour after the meal will be the maximum level of blood glucose.
- Ideally, check blood glucose after 2 hours of the meal.
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose is the key to the better control of diabetes.
- It is ideal for checking the blood glucose level before going to sleep.
- Checking the fasting glucose level is also helpful to monitor the breakfast.
What you should do once you develop diabetes:
- Regular checking:
- Regular checking of the blood glucose will keep your blood glucose level in the range.
- Regular checking will delay the complications.
- Should check blood glucose at least once daily.
- Advised every 3 to 6 months HbA1c.
- HbA1c
HbA1c value Interpretation 4% to 5.6% Normal 5.7% to 6.4% Prediabetic >6.5% Diabetes - Fasting glucose level = <100 mg/dl (5.6 nmol/L) is normal.
- Fasting glucose level = 105 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 nmol/L) is considered prediabetic.
- Fasting glucose level = >126 mg/dL (>5.6 nmol/L), at two occasion is considered diabetes.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20371451
- A random blood sugar level of less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) is normal.
- A reading of more than 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) after two hours indicates diabetes.
- Fasting glucose level = <100 mg/dl (5.6 nmol/L) is normal.
- A reading between 140 and 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L and 11.0 mmol/L) indicates prediabetes.
Expected glucose level:
| Time for glucose checking | Glucose level |
| Before meal | 80 to 120 mg/dL |
| After meal | <180 mg/dL |
| At bedtime | 100 to 140 mg/dL |
| American Diabetes Association recommendations: | |
| Needs to take action in the following values | |
| Before meal | >140 mg/dL |
| At bedtime | >160 mg/dL |
- Eat smarter:
- The right diet is the tool to control your blood glucose level and weight.
- You need not quit your favorite diet.
- Please see these links, and you will get a guide on how to regulate your diet.
- https://labpedia.net/diabetes-mellitus-and-calculation-of-the-calories/
- Diet for Diabetics and Counting of The Carbohydrates (Carbs) – Labpedia.net
- Try to lose weight if you are overweight:
- Obesity predisposes to diabetes.
- Losing weight is the essential action you can take.
- If you lose excess pounds of weight will help to control diabetes.
- At all ages, the risk of type 2 diabetes rises with increasing body weight.
- The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is three to seven times higher in those affected by obesity than in normal-weight adults.
- 20 times more likely in those with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 35 kg/m.
- Although there’s no cure for type 2 diabetes, studies show that some people can reverse diabetes.
- Diet changes and weight loss may keep your blood glucose level under control.
- After losing weight and the exercise, you may not need the drugs.
- In case you are not taking any medicine, it does not mean that your diabetes is cured.
- Regular exercise is very important for diabetics (diabetes mellitus):
- Regular exercise help to control the spike of blood glucose.
- The exercise may be variable in intensity but need to be done regularly every day or 5 times a week.
- Exercise improves blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes.
- Exercise reduces cardiovascular risk factors.
- Exercise helps to reduce weight.
- Excercise gives a sense of well-being due to the release of endorphins.
- Regular exercise may delay the development of diabetes type 2 or even may prevent it.
- Role of treatment:
- Once someone develops diabetes, then he/she should take medications regularly.
- Medications will be accompanied by diet and exercise.