Risk factors for Diabetes Mellitus and Recommendations
Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus and Recommendations
- The risk for diabetes increases with age. So, it is recommended that blood glucose and HbA1c be checked every three years after 45 years.
- American Diabetes Association recommends frequent testing for young people who have a high-risk family.
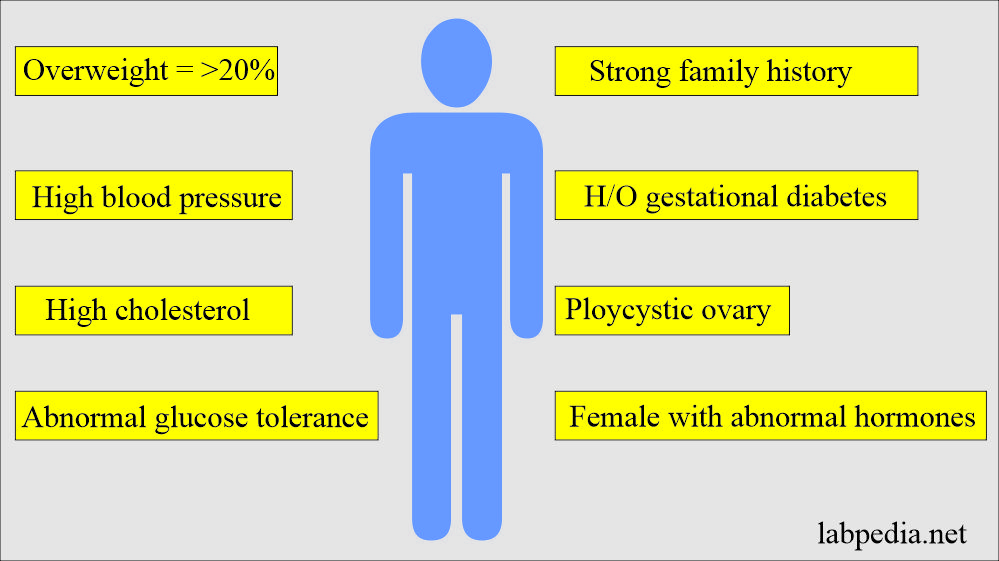
What are the risk factors for diabetes mellitus?
- The people who are >20% overweight.
- With a strong family history of diabetes.
- With the presence of high blood pressure.
- With a history of high cholesterol.
- In the case of a history of gestational diabetes mellitus.
- If a lady gives birth to a baby with >9 pounds weight.
- In the case of abnormal glucose tolerance.
- On two or more occasions, the fasting glucose level was between 110 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL.
- The oral glucose tolerance test shows that the 2 hours of glucose ranged between 140 mg/dL and 199 mg/dL.
- If one has abnormal glucose tolerance, one is at risk of developing diabetes mellitus each year, which is 1% to 10%.
- The more inactive you are and the more overweight you are, the more chances you have to develop diabetes mellitus in abnormal glucose tolerance.
- Abnormal glucose tolerance is the warning sign, and you can prevent developing diabetes by:
- Modification of the lifestyle.
- Diet control.
- Do routine exercise.
- Can start metformin
- In females with polycystic ovary syndrome.
- In females with abnormal hormone disorders marked by insulin resistance.
- There is increased risk among African Americans, Asian Americans, Native Americans, Pacific Islanders, and Hispanic Americans.
What are the recommendations for diabetes for the increased risk group?
- The American Diabetes Association recommends checking blood glucose every 2 years after the age of 10 years.
- Frequent checking in overweight children, particularly if they have other additional issues.