Tumor Marker:- Part 5 – M-band, NMP 22, BTA, Oncogenes (Genetic Markers)
Tumor Markers
- Tumor markers in the diagnosis and monitoring of tumors are some more examples.
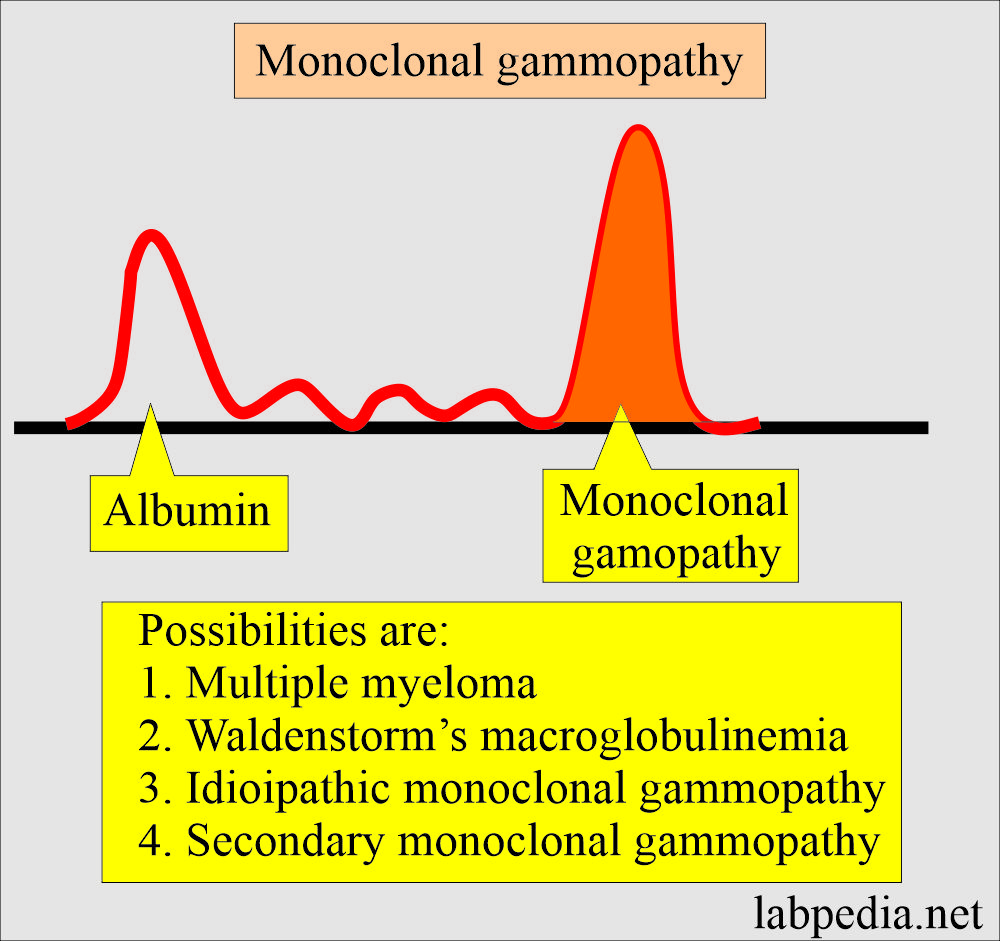
M-Band of Multiple Myeloma
- The monoclonal band of immunoglobulin is used as a tumor marker.
Myeloma components:
- M-band or monoclonal paraprotein is used to diagnose multiple myeloma.
- Myeloma protein is an abnormal immunoglobulin fragment, such as an immunoglobulin light chain, that is produced in excess by an abnormal monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells, typically in multiple myeloma.
- Other terms used are M-protein, M-component, M-spike, or paraprotein.
- This M-protein is found in serum and urine electrophoresis.
- > 90 % of patients will Multiple myelomas shows M-band in electrophoresis.
- The M band (protein) is paraprotein visible on electrophoresis. Giving a tall peak on a densitometer, also called M-spike.
Bence-Jones proteinuria:
- It is protein is a light chain excreted in the urine of Multiple myeloma cases.
- Decreasing the level of Bence-Jones protein in the treatment shows a good response to treatment.
- M-band in the myeloma patients on electrophoresis, when total protein is 8.8 g/dL:
| Protein fractions | Result in % | The result of myeloma patient g/dL | Normal range g/dL |
| Albumin | 35.2 | 3.1 | 3.5 to 5.2 |
| α1 – globulin | 3.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 to 0.4 |
| α2 – globulin | 6.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 to 0.8 |
| β – globulin | 8.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 to 1.1 |
| γ – globulin (M-band) | 46.6 | 4.1 | 0.6 to 1.3 |
NMP 22 (Nuclear matrix apparatus protein 22)
- Other names are Bladder cancer marker or bladder tumor antigen.
- Definition of NMP 22:
- NMP 22 detects a nuclear protein, called NuMA (Nuclear mitotic apparatus), that is released from the nuclei of the tumor cells when they die.
- Mechanism of NMP 22:
- Nuclear matrix proteins make the internal structure of the nucleus.
- This bladder tumor antigen is a factor H-related protein that is produced by the bladder tumor.
- NMP 22 is a nuclear matrix protein that is deposited in the urine during the apoptosis of bladder cancer cells.
- Their role is the regulation of DNA replication and synthesis of RNA.
- This protein is excreted in the urine.
- Normally none or very little amount of this protein is found in the urine.
- This is recommended for the follow-up of Transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary tract.
- This is a cheaper marker for the recurrence of bladder cancer.
- This is elevated in bladder cancer.
- NMP22 is a good screening test for a patient who is at greater risk of developing bladder cancer.
- NMP22 may be raised in the tumor involving the ureter and renal pelvis.
- NMP 22 interpretations:
- NMP 22 is advised in patients who have urinary blaader cancer.
- It is quite sensitive but nonspecific.
- When NMP 22 performed after 1 to 6 weeks of the urinary bladder tumor surgery, is raised indicates recurrence of the tumor.
- NMP 22 results are normal in 80% of the patients with no disease.
- Infection may give false positive results due to the inflammatory cells (WBCs). Basically WBCs are the source of the false positive result.
Urine sample:
- This protein is unstable in the urine. If urine is not stabilized immediately, they can get a false result.
Normal NMP22:
-
- <10 units/mL.
Bladder tumor-associated Antigen (BTA)
- BTA are high molecular weight polypeptides.
- BTA presence in the urine may be due to the following:
- Involvement of the basement membrane in the tumor. OR
- Produced by the tumor. OR
- Combination of both.
- BTA represents 70% sensitivity and 70% specificity.
- BTA test was positive in 40% of the cases on cystoscopy, proving bladder tumor.
- While cytology gives only 17% positivity.
- BTA is a marker of a bladder tumor.
- But BTA is not a good screening test because this may be raised in other conditions like:
- Recent urologic surgery.
- Calculi.
- Urinary tract infection.
Normal source 2:
-
- <14 units/mL
Genetic markers
- This is considered that multiple genetic alterations may lead to uncontrolled proliferation of the cells and result in cancers.
- This gene abnormality also gives rise to metastases.
- Evaluation of chromosomal changes may help to diagnose cancers.
- c-erb B-2 is also called an HER-2/neu gene.
Indications for genetic testing:
- It is advised for the diagnosis of carrier identification like sickle cell trait, and Tay-Sach disease.
- It advised for prenatal diagnosis of abnormal;it like Down’s syndroem.
- It is advised for screening of newborns for comgenital hypothyroidism, and PKU.
There are two types of genes:
Oncogene :
- These are the cell activation genes. Promote tumor formation.
Suppressor gene:
- These genes are involved in recognizing and repairing damaged DNA.
Table of Oncogenes
| Oncogene | Type of cancer |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suppressor gene
- This is studied that normal cell contains a gene that suppresses the expression of malignancy.
- The loss of the chromosome 5 gene leads to increased cell growth.
- Metastasis occurs with the loss of genes.
- The significance of the detection of mutation in the tumor suppressor gene help in the diagnosis and prognosis of the tumor.
- This mutation of the suppressor gene also helps to predict susceptibility when the mutation is carried in the germline e.g., breast cancer genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Table of Suppressor gene:
| Suppressor gene | Tumor |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of tumor markers
| Test | Marker of tumor |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The various enzyme in different tumors:
| Enzymes | Organs involved in tumor |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Liver, bone, and sarcoma |
| Amylase | Pancreas |
| Aldolase | Liver |
| Creatine kinase-BB | Breast, colon, ovary, prostate, and lung |
| Gamma-glutamyltransferase | Liver |
| Lactate dehydrogenase | Lymphomas, leukemias, liver, and other organs |
| 5 nucleotidase | Liver |
| Prostatic acid phosphatase | Prostate |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is BTA?
Question 2: What are the oncogene?
- Please see in Tumor marker parts 1, 2, and 3.